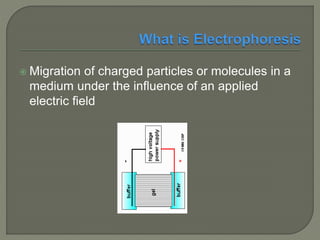
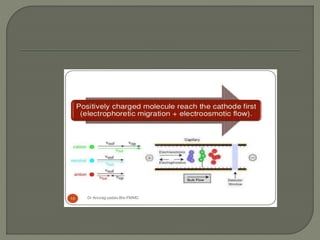
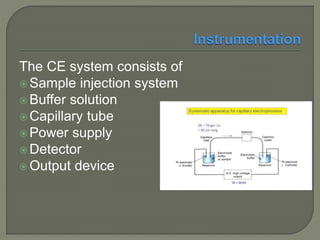
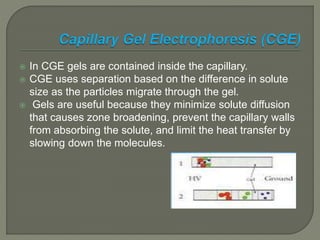
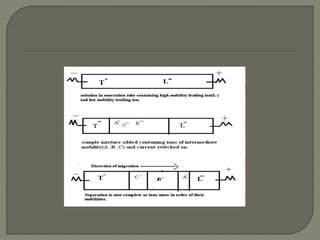
The document discusses various electrophoresis techniques used in pharmaceutical analysis, including capillary electrophoresis (CE) and its advantages such as high separation efficiency and short analysis times. It highlights the differences in analyte migration based on charge and size, as well as the applications of various methods in determining molecular weights and separating components. Additionally, it outlines the equipment components, operational methods, and the advantages and disadvantages associated with these techniques.