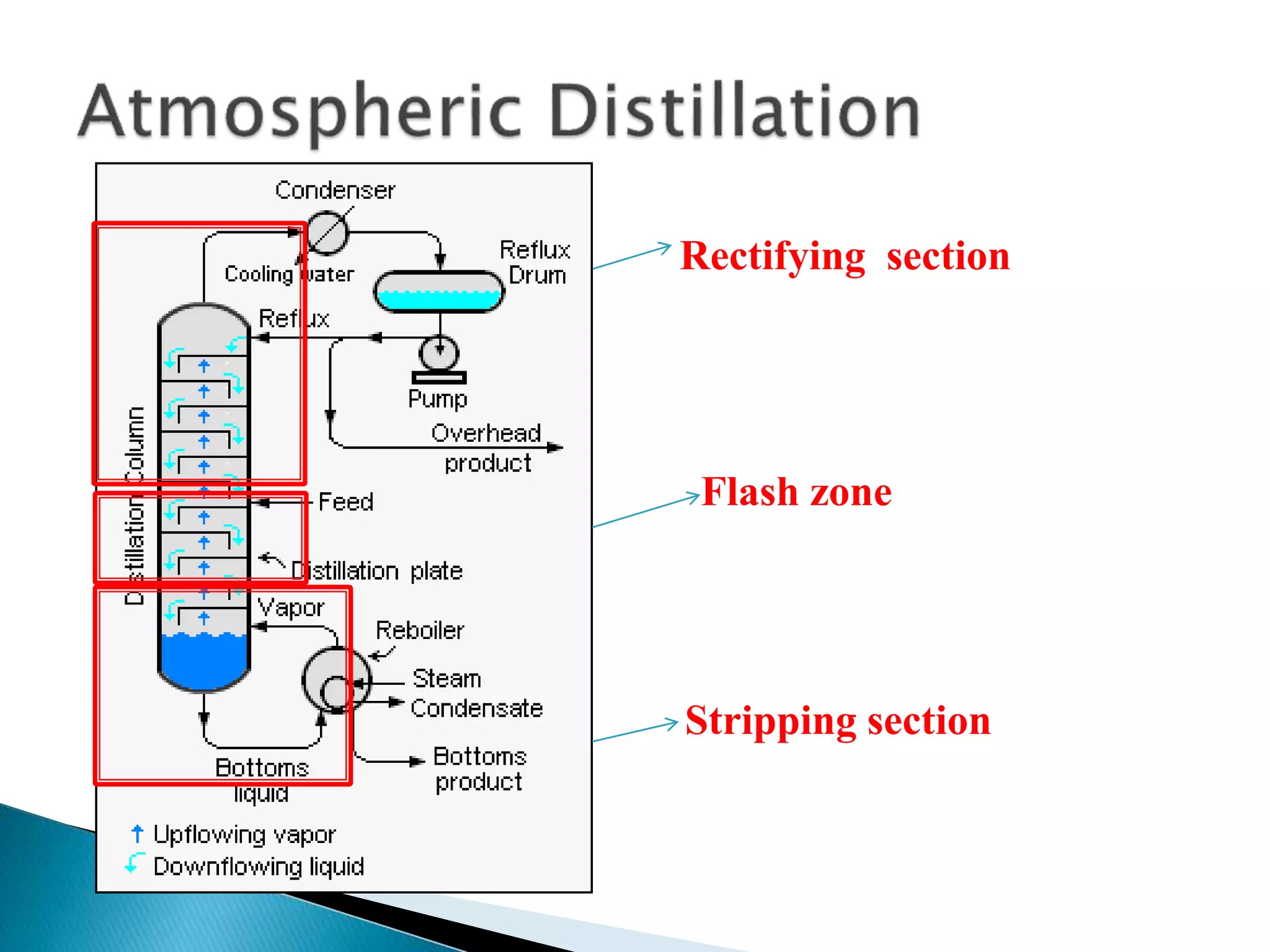
The document summarizes the process of crude oil distillation. Crude oil is heated through heat exchangers to 550°F and then further heated to 750°F in a furnace before entering the flash zone of an atmospheric fractionator. Reboilers provide heat to the bottom of distillation columns by boiling the liquid to generate vapors that drive the separation process. Temperature above 370-380°F can cause cracking and coking in atmospheric columns, so residue is sent to vacuum distillation where pressure is reduced below vapor pressure to distill the most volatile liquids.