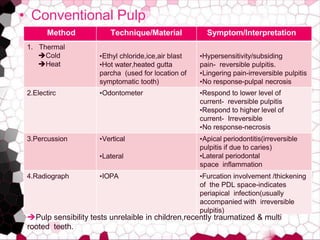
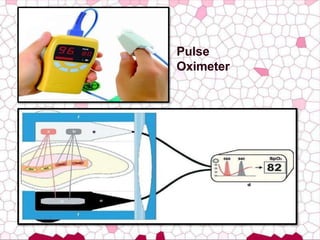
This document discusses diagnosis of pulp pathology. It begins by defining the dental pulp and its relationship to dentin. It then discusses diagnostic procedures, noting that diagnosis involves evaluating signs and symptoms along with results from diagnostic tests like medical/dental history reviews, radiographs, and clinical examinations. The document outlines specific examination steps including evaluating the coronal and pulpal areas, along with history and radiograph findings, to make a diagnosis. It also discusses various pulp testing methods like thermal, electric, percussion, and introduces newer methods like laser Doppler flowmetry, pulse oximetry, and duel wavelength spectrometry to objectively assess pulp vitality.