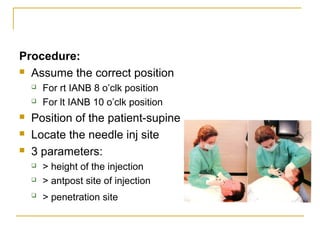
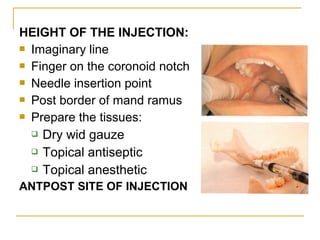
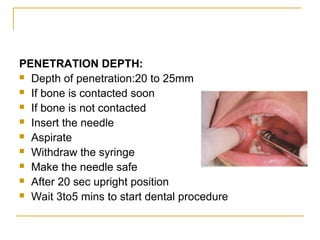
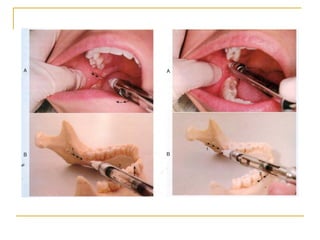
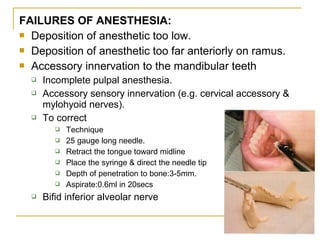
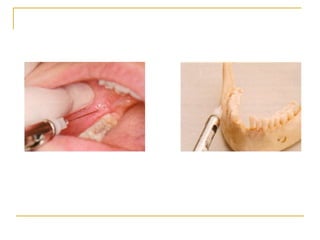
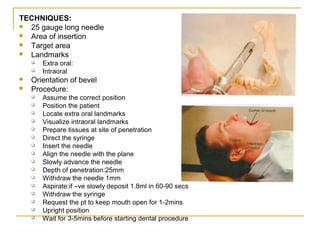
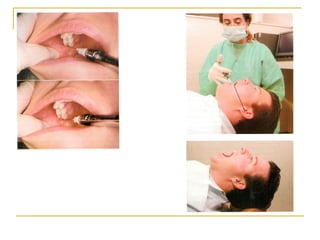
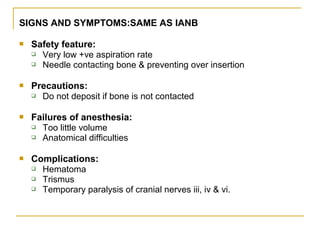
The document outlines various mandibular injection techniques for dental anesthesia, primarily focusing on the inferior alveolar nerve block and its applications, indications, and contraindications. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of different methods, potential complications, and techniques for effective administration. Detailed procedural steps, safety features, and managing failures are also included to enhance the understanding of these techniques.