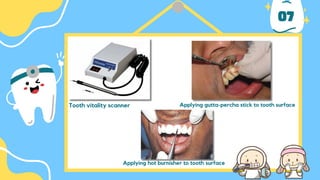
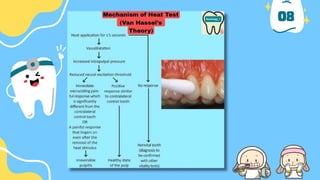
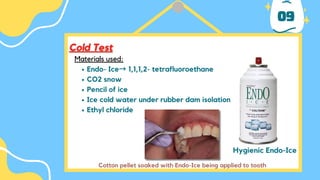
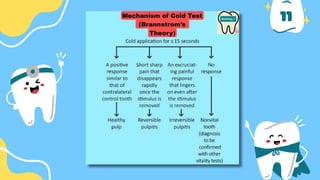
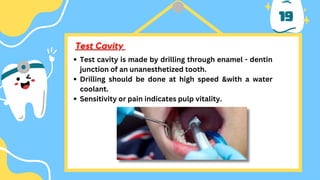
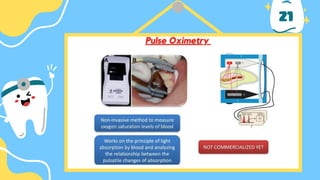
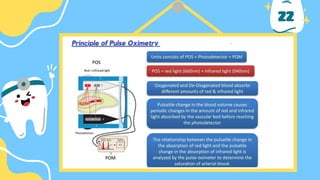
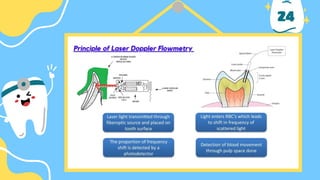
The document outlines the importance of accurate diagnosis and treatment planning in dental procedures, detailing various diagnostic techniques for assessing pulp vitality, including visual inspections, thermal testing, and electric pulp tests. It emphasizes the use of multiple tests to ensure accurate results, as well as the limitations of certain methods like EPT and reliance on new technologies. Key recommendations include isolating tooth areas during testing and understanding when to use specific diagnostic procedures.