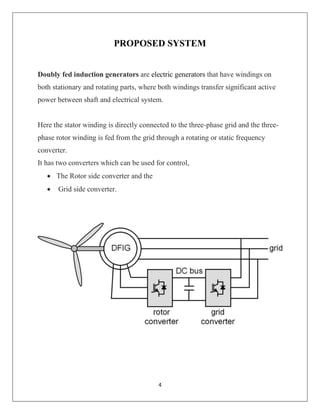
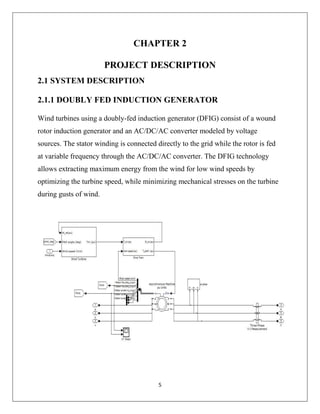
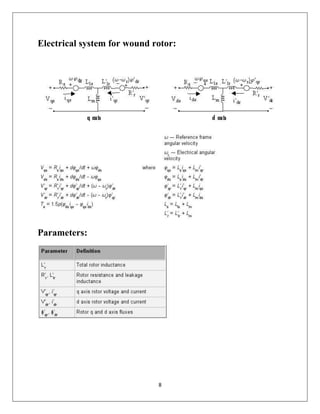
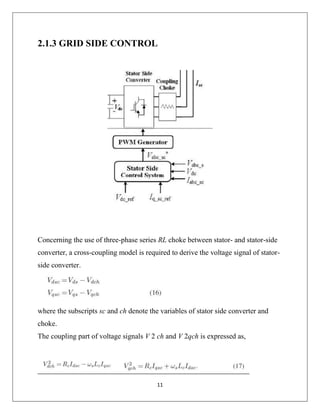
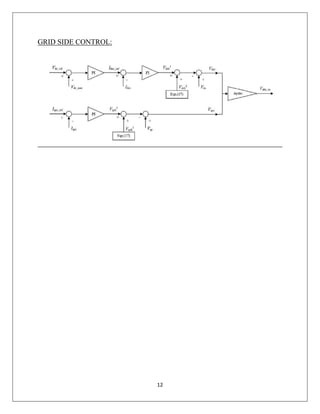
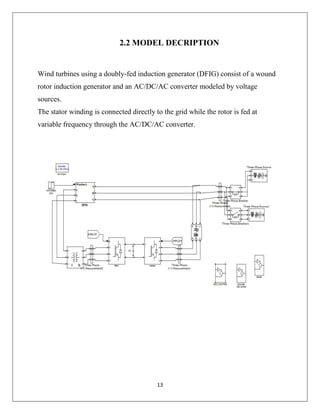
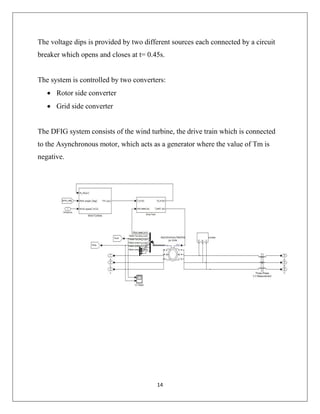
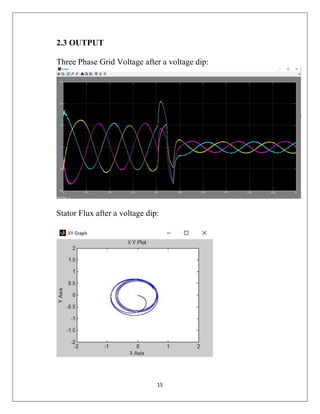
The document reports on a study of the dynamic behavior of doubly fed induction generators (DFIGs) during three-phase voltage dips. DFIGs are commonly used in large wind turbines. While they provide benefits, they are very sensitive to grid disturbances like voltage dips. The paper develops a theoretical analysis of the machine's behavior during voltage dips to better understand the problem. Experimental results agree with the theoretical analysis, validating the proposed model. The analysis provides insight that can help improve protections and solutions for DFIGs during grid faults.