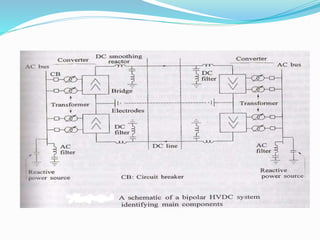
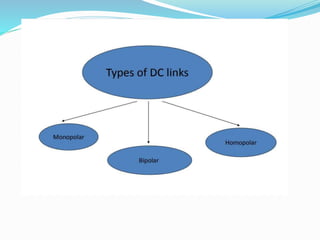
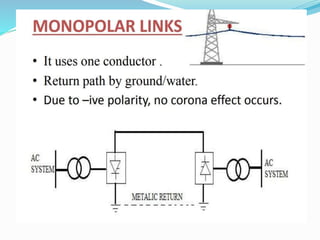
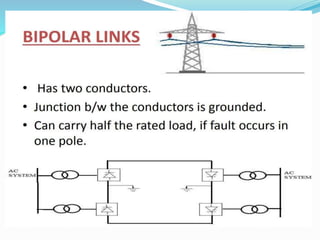
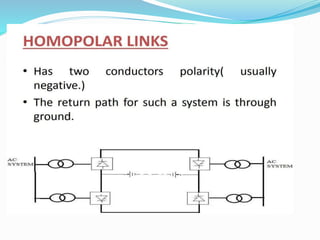
HVDC LIGHT TRANSMISSION
The document discusses HVDC (high voltage direct current) light transmission. Key points:
1. HVDC uses direct current for efficient long distance power transmission, including underwater.
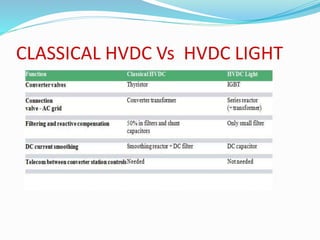
2. Modern HVDC uses IGBT semiconductor technology in converters to transform AC to DC and vice versa.
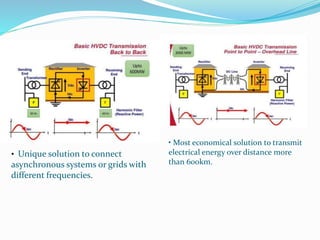
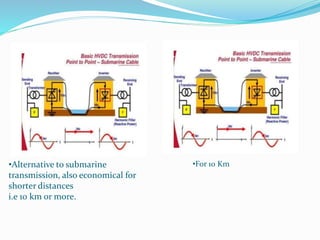
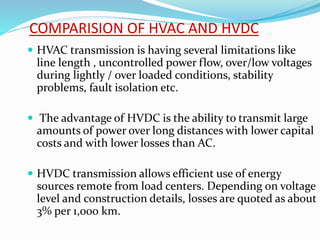
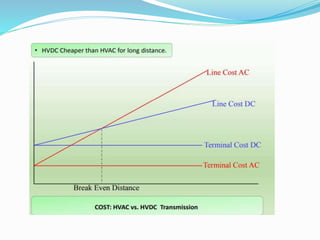
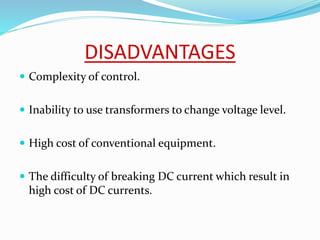
3. HVDC has advantages over HVAC like transmitting power over long distances with lower losses, and allowing connection of asynchronous grids. It is most economical for distances over 600km.