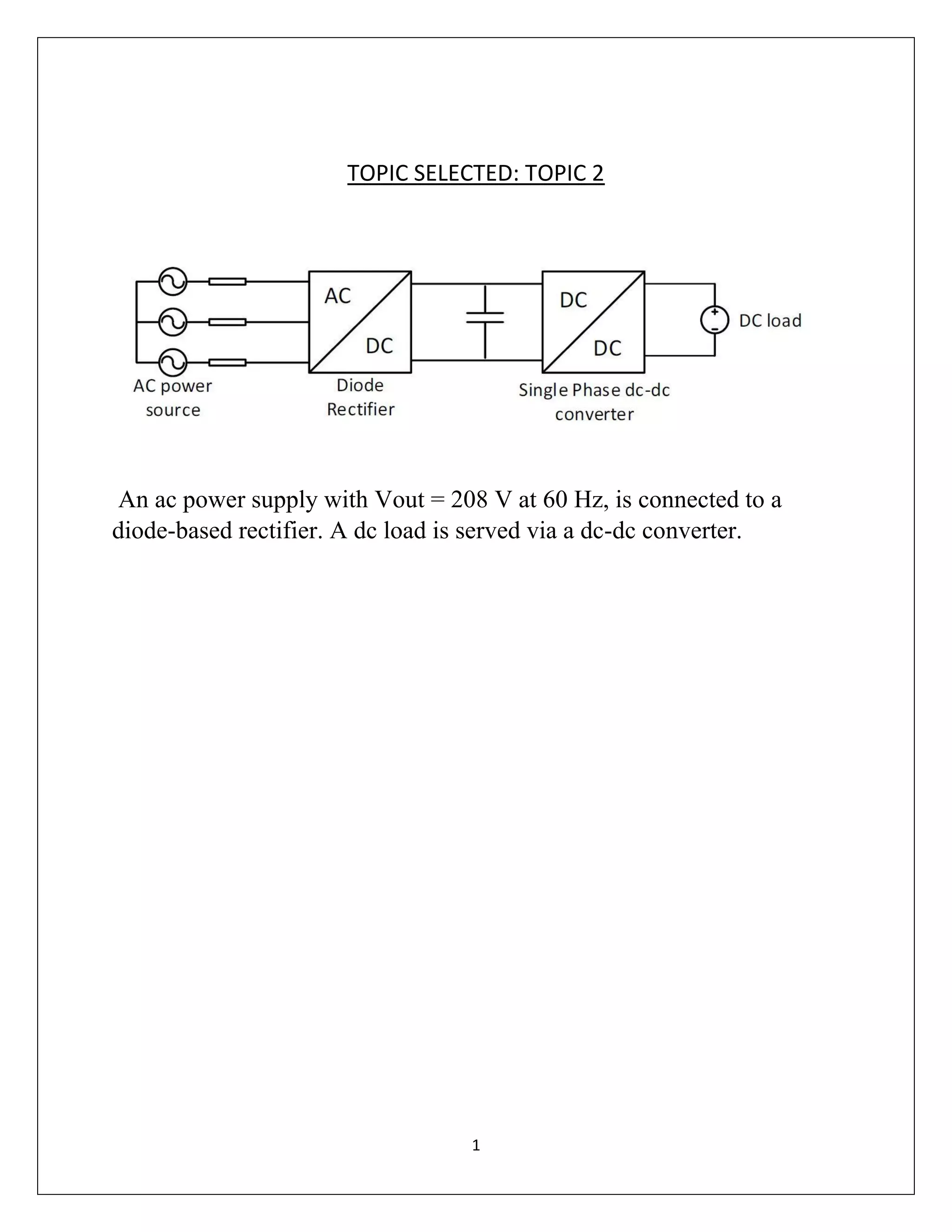
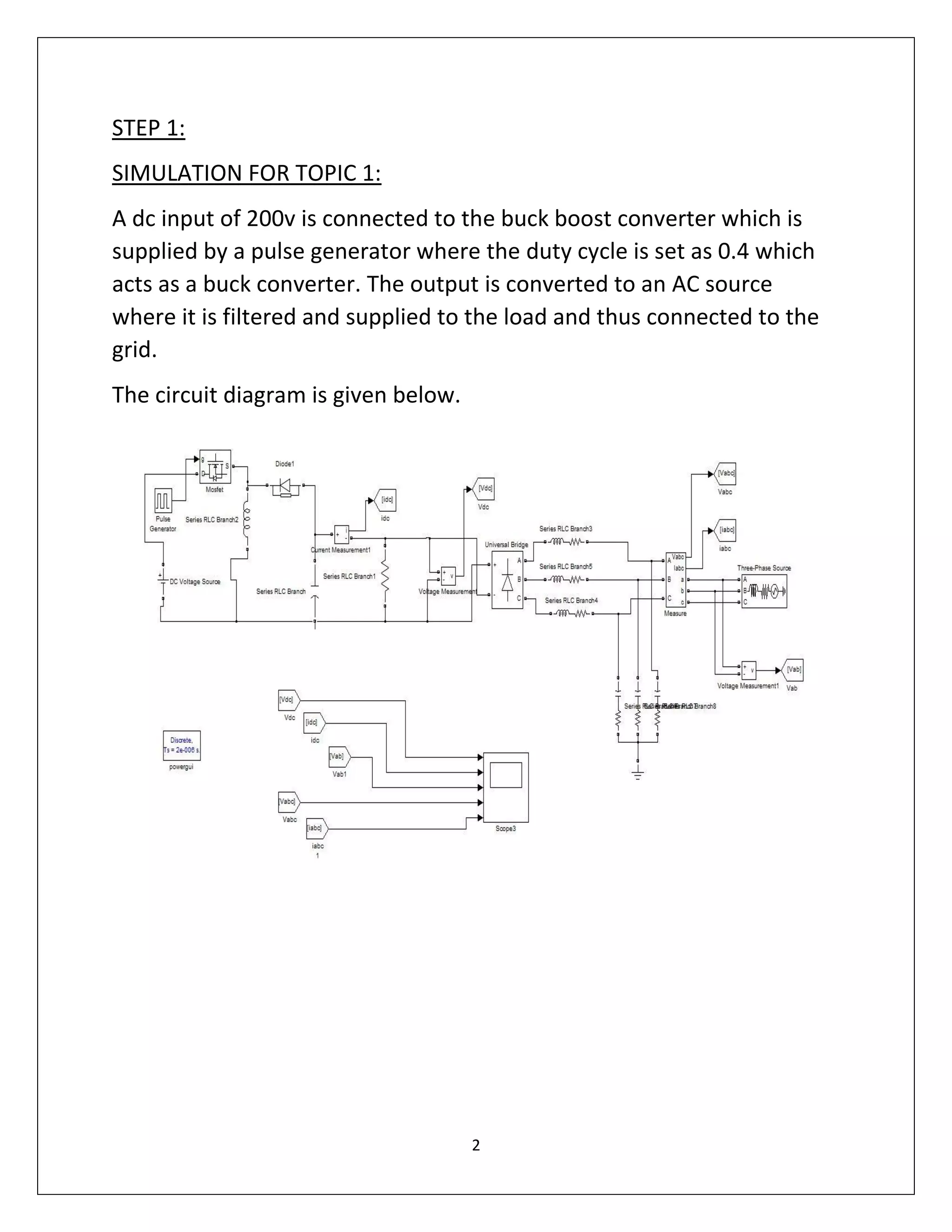
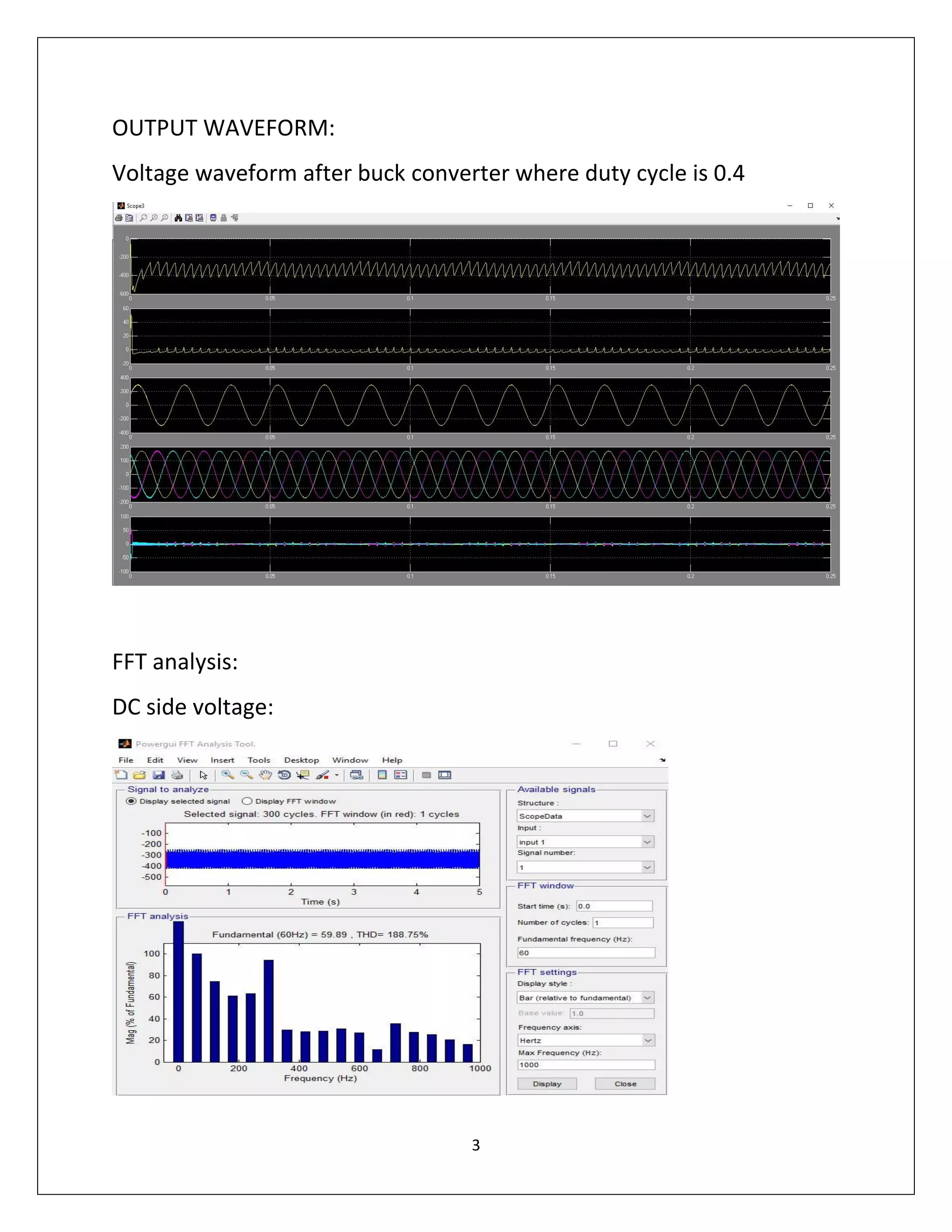
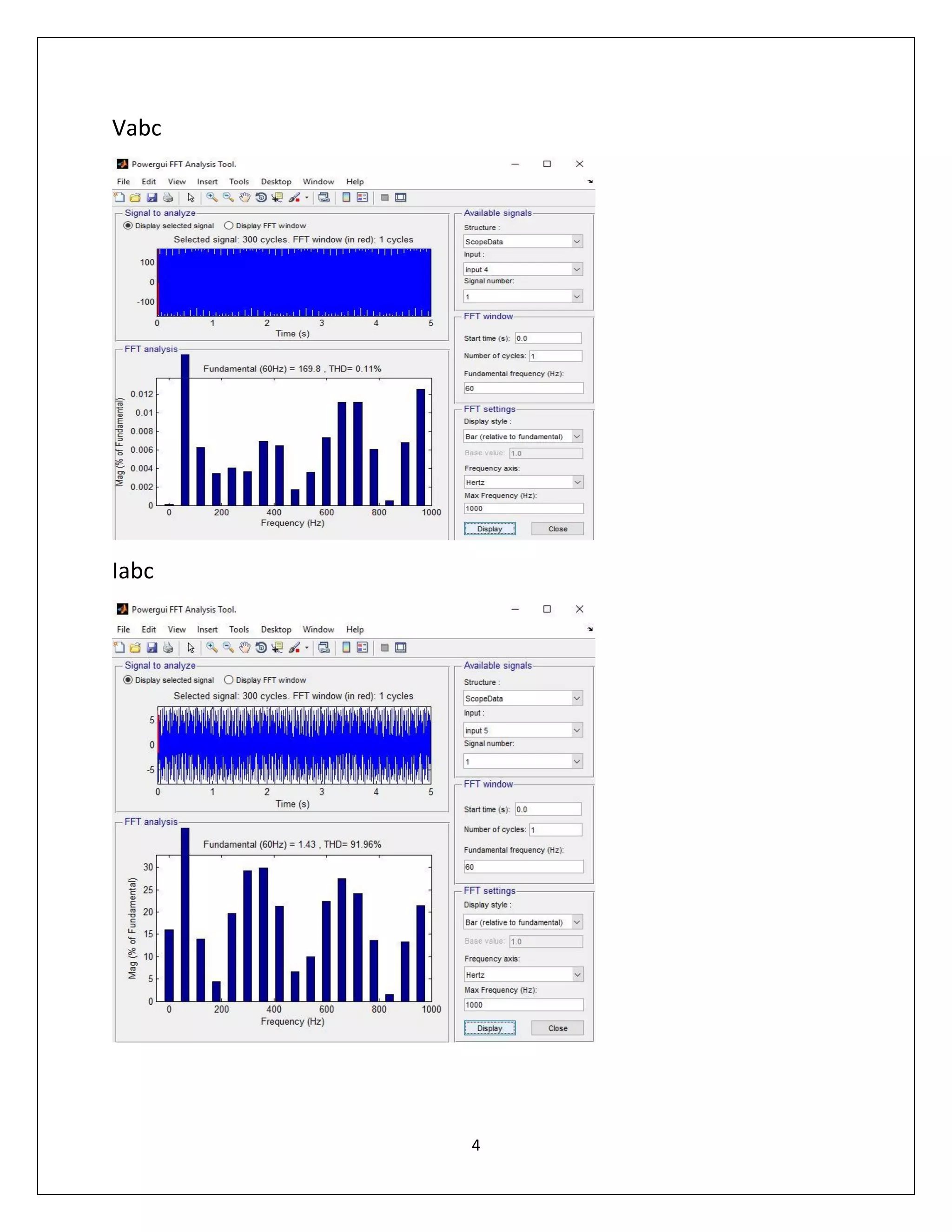
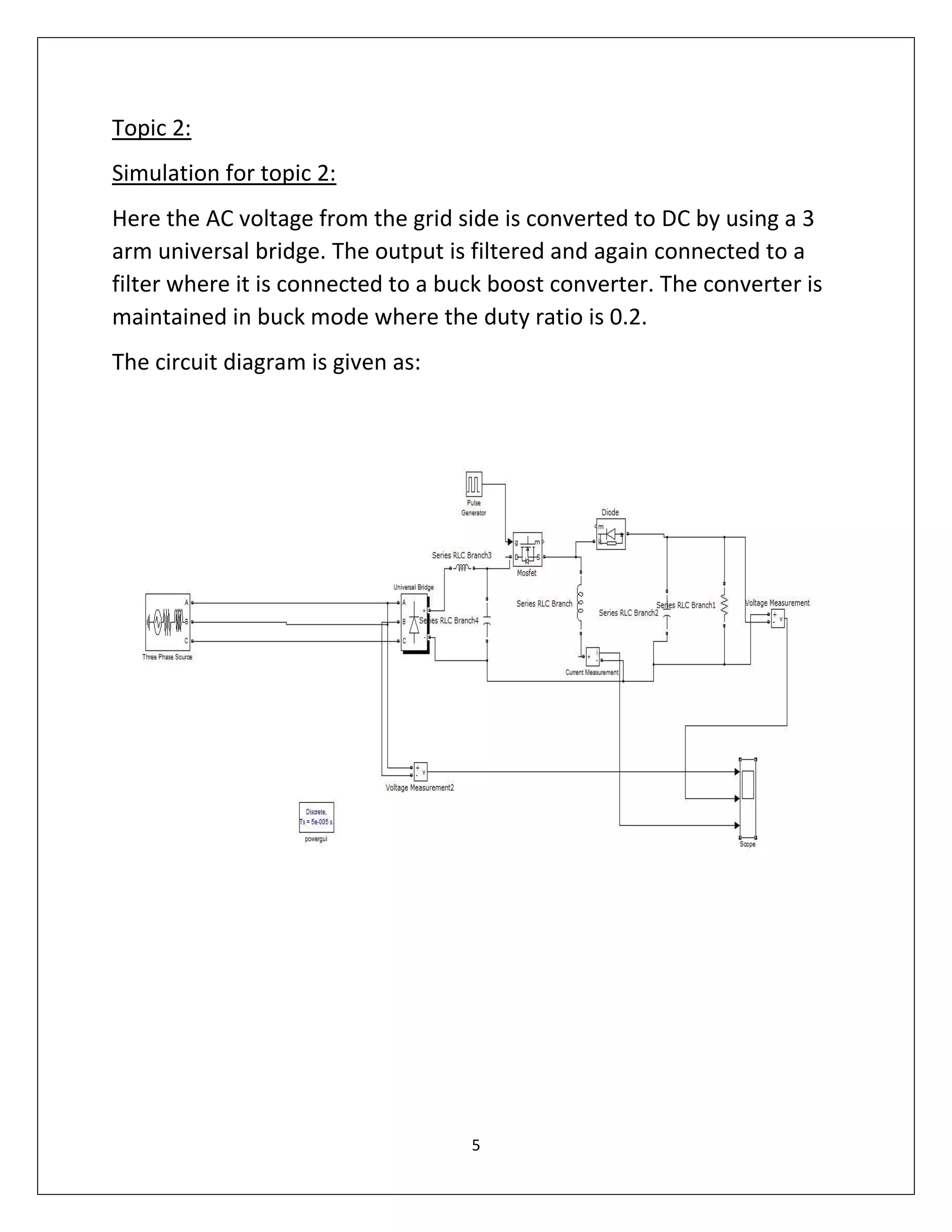
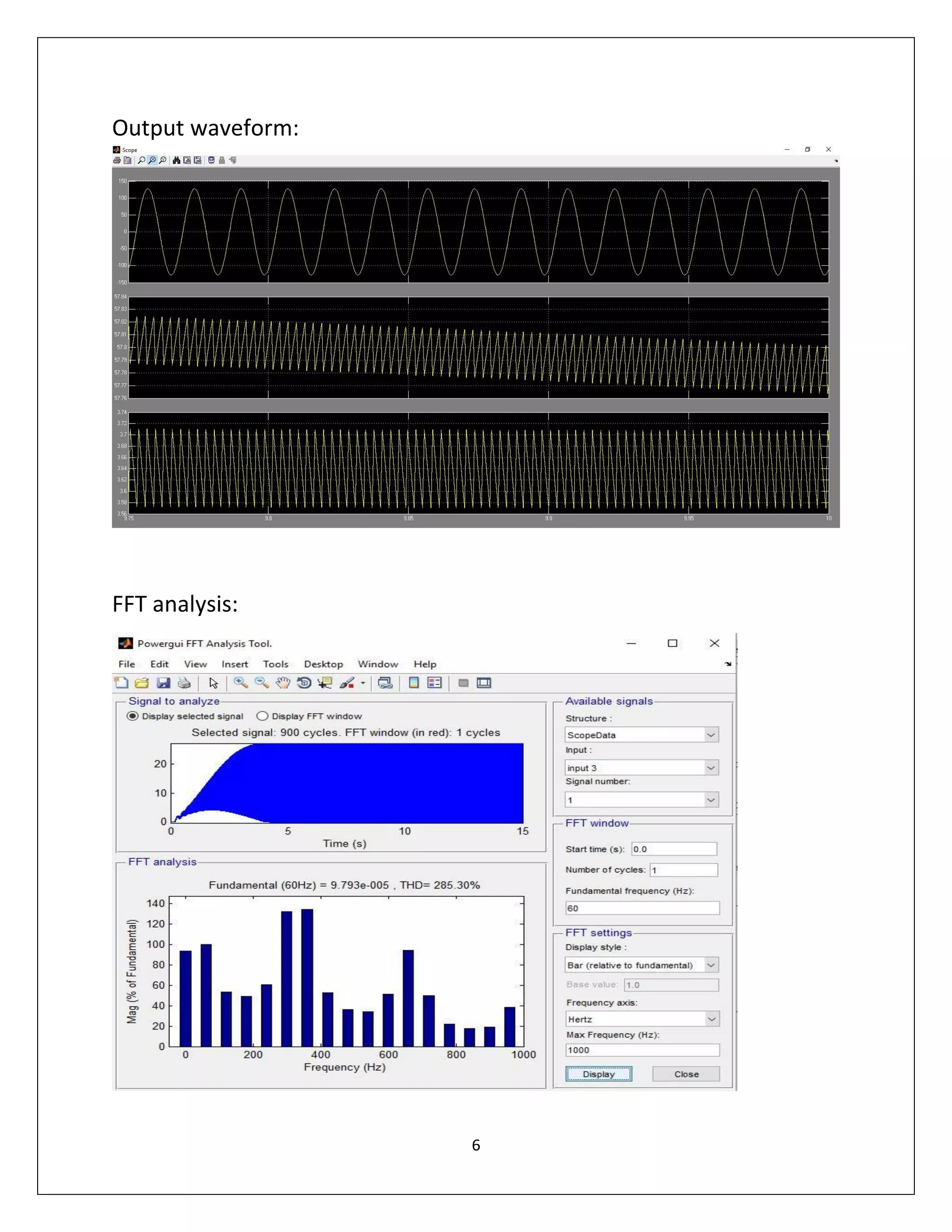
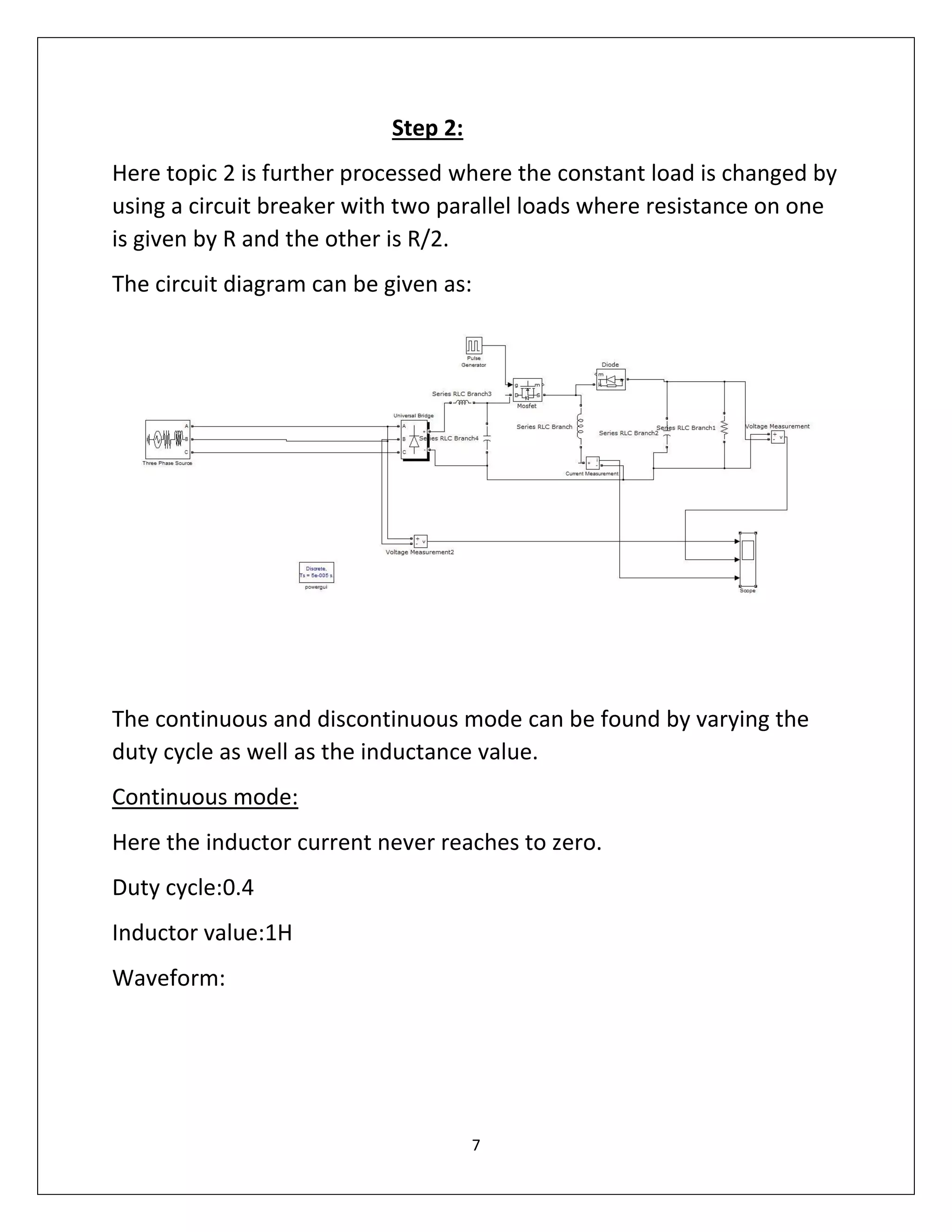
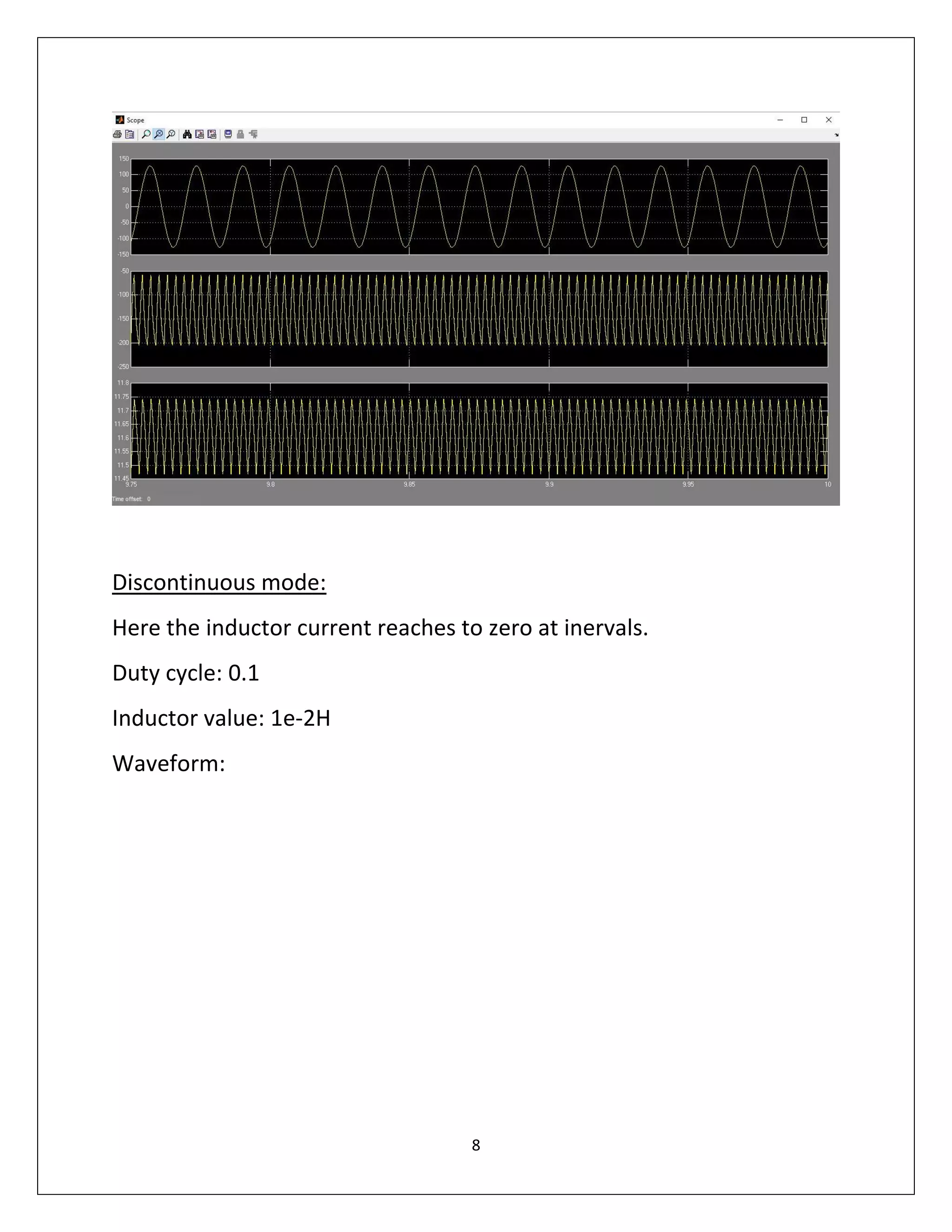
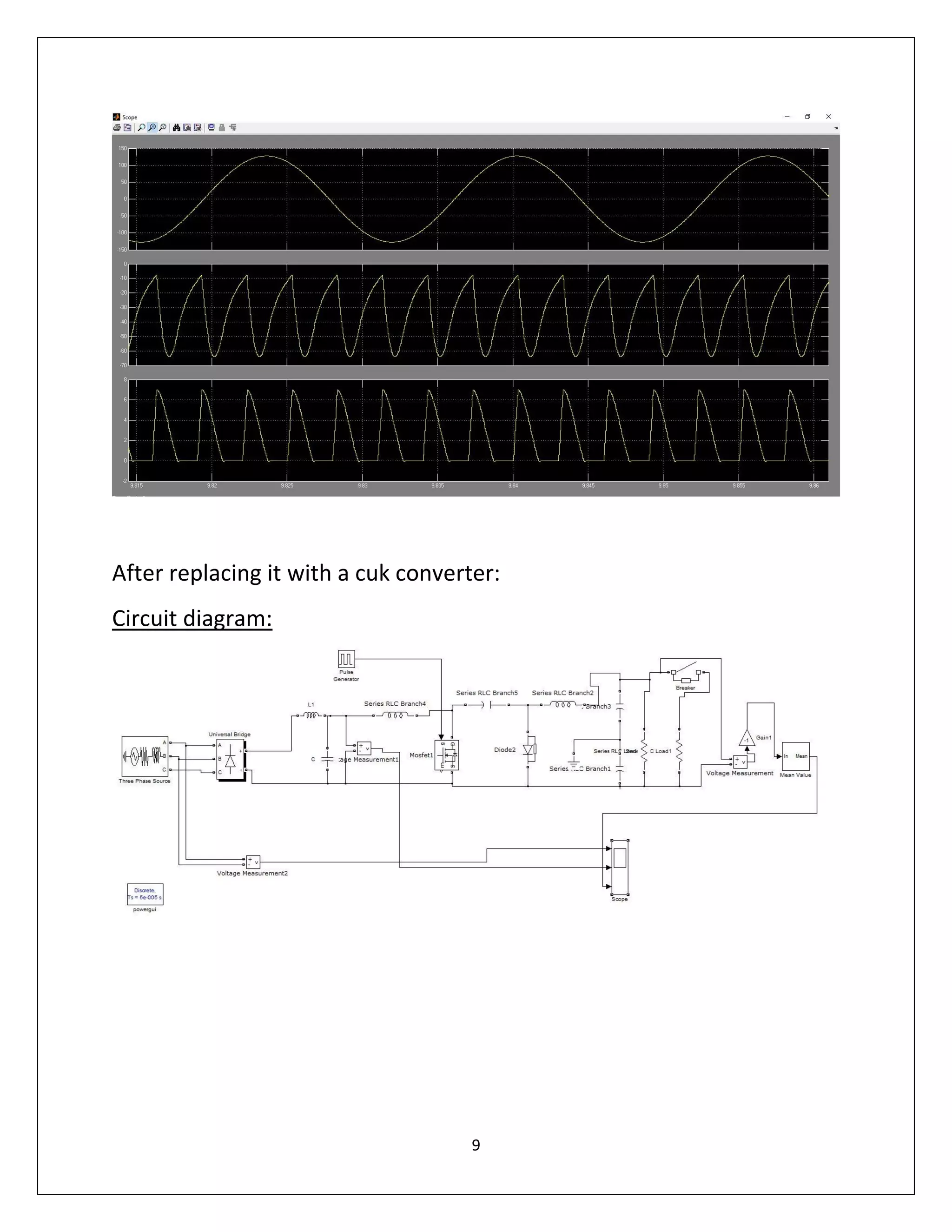
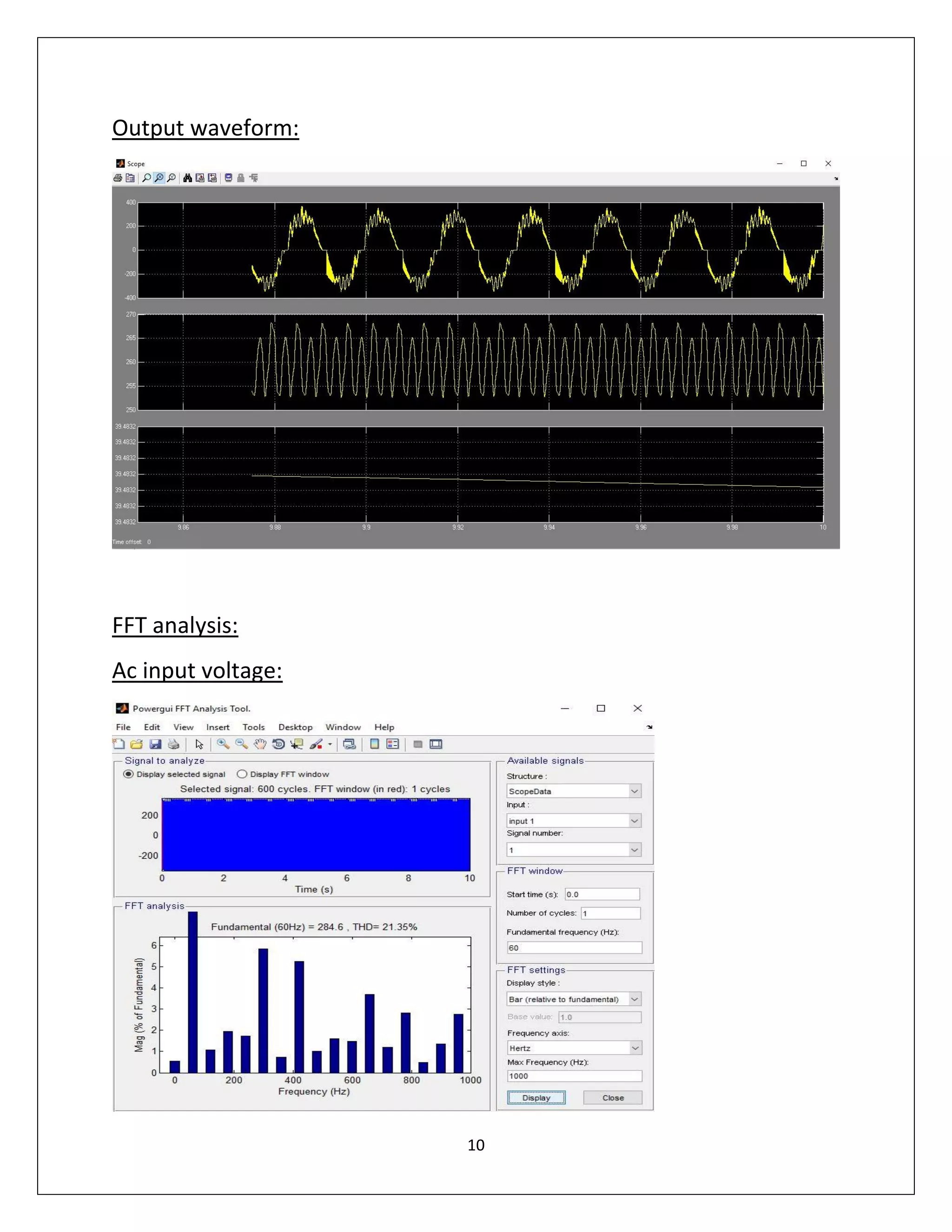
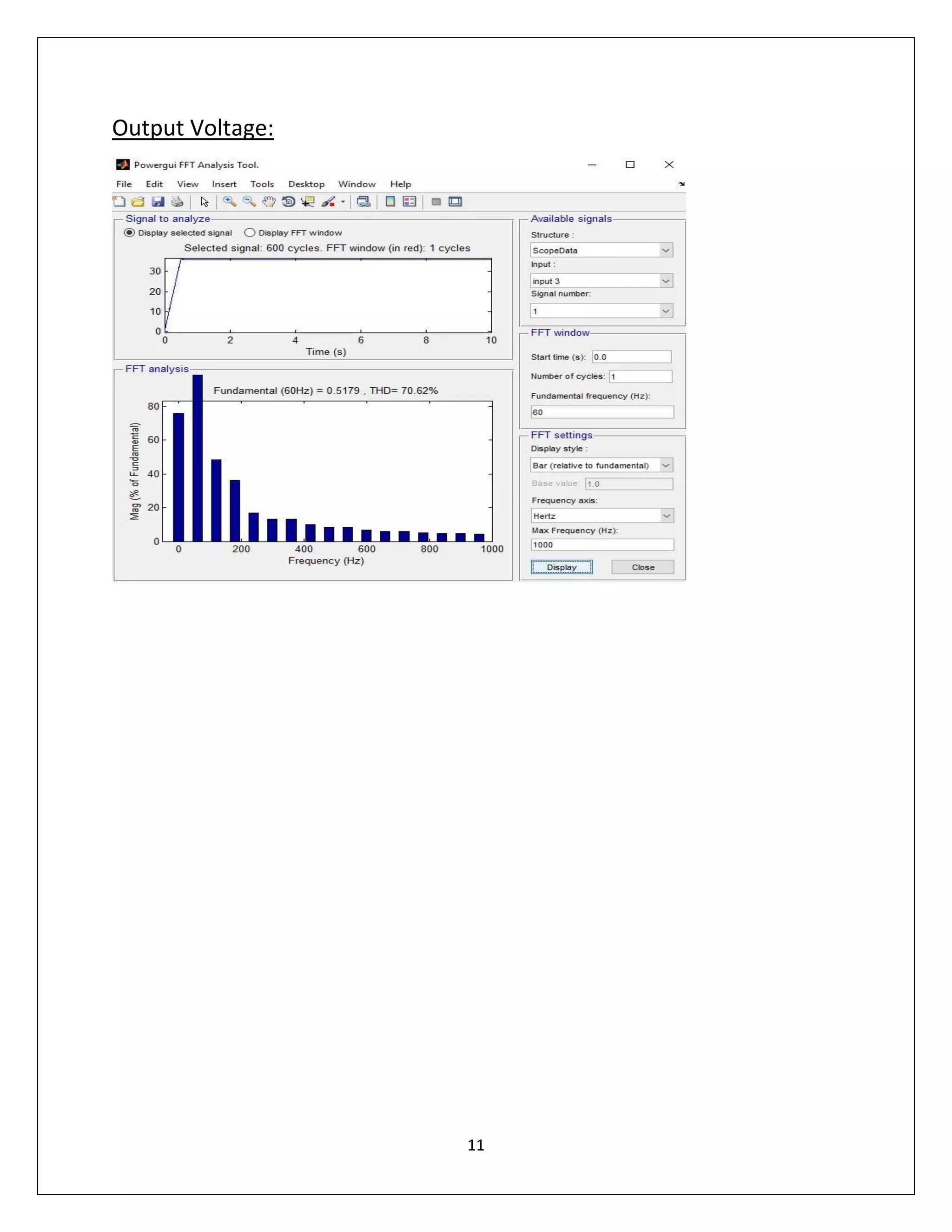
This document summarizes a course project on power electronics. It simulates an AC power supply connected to a rectifier to serve a DC load via a DC-DC converter. The simulation shows the output waveform and FFT analysis. It then simulates an AC to DC conversion using a 3-arm bridge and buck-boost converter. Different loads are tested by changing resistance and operating modes are explored by varying duty cycle and inductance.