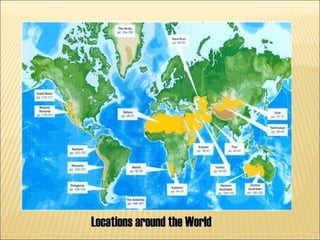
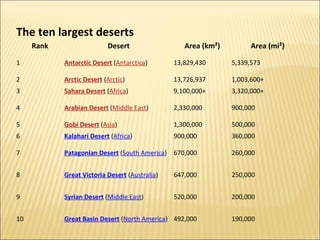
i. A biome is a geographic area characterized by specific kinds of plants and animals, with deserts being one type of biome.
ii. Deserts have hot climates with less than 25 cm of annual precipitation and daily temperature extremes.
iii. Many desert plants and animals have adapted to their environment through mechanisms like storing water and nocturnal behavior.