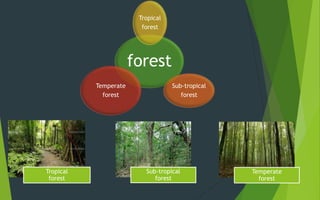
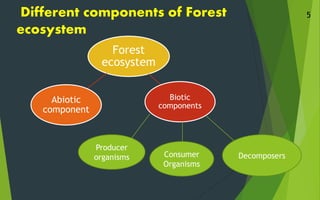
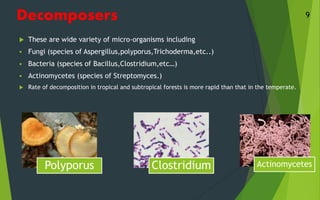
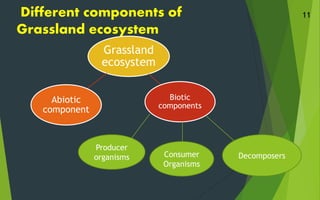
This document summarizes and compares the structure and function of forest and grassland ecosystems. It outlines the key abiotic and biotic components of each system. Forest ecosystems contain a diversity of tree species that serve as primary producers, along with various herbivores, omnivores, and decomposers like fungi and bacteria. Grassland ecosystems are found in regions with moderate rainfall and are dominated by grasses and forbs as producers, and grazing herbivores as primary consumers. Decomposers like fungi and bacteria break down dead organic matter in both forest and grassland systems.