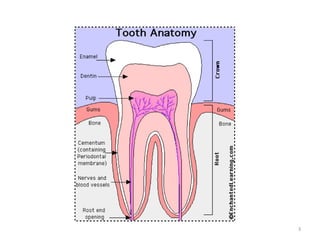
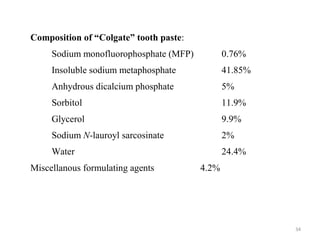
The document discusses various dental products used for oral health including antiplaque agents like chlorhexidine and povidone-iodine, anticaries agents like fluorides, and dentifrices. It provides details on the composition, mechanisms of action, uses, and side effects of these agents. The goal of these products is to inhibit plaque formation, prevent dental caries, and promote oral hygiene.