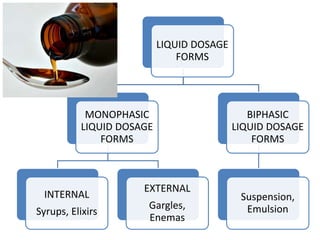
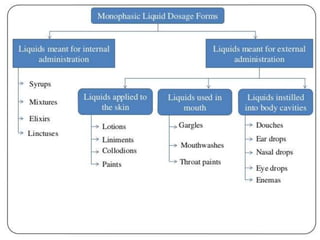
This document discusses monophasic liquid dosage forms, which contain components dissolved in a single phase. It provides examples of internal monophasic liquids like syrups and elixirs, and external liquids like gargles and enemas. The advantages of liquids include ease of administration, rapid drug absorption, and uniform dosing. Disadvantages include bulkiness, potential for microbial growth, and reduced drug stability compared to solids. A variety of oral, ocular, nasal and rectal liquids are also described.