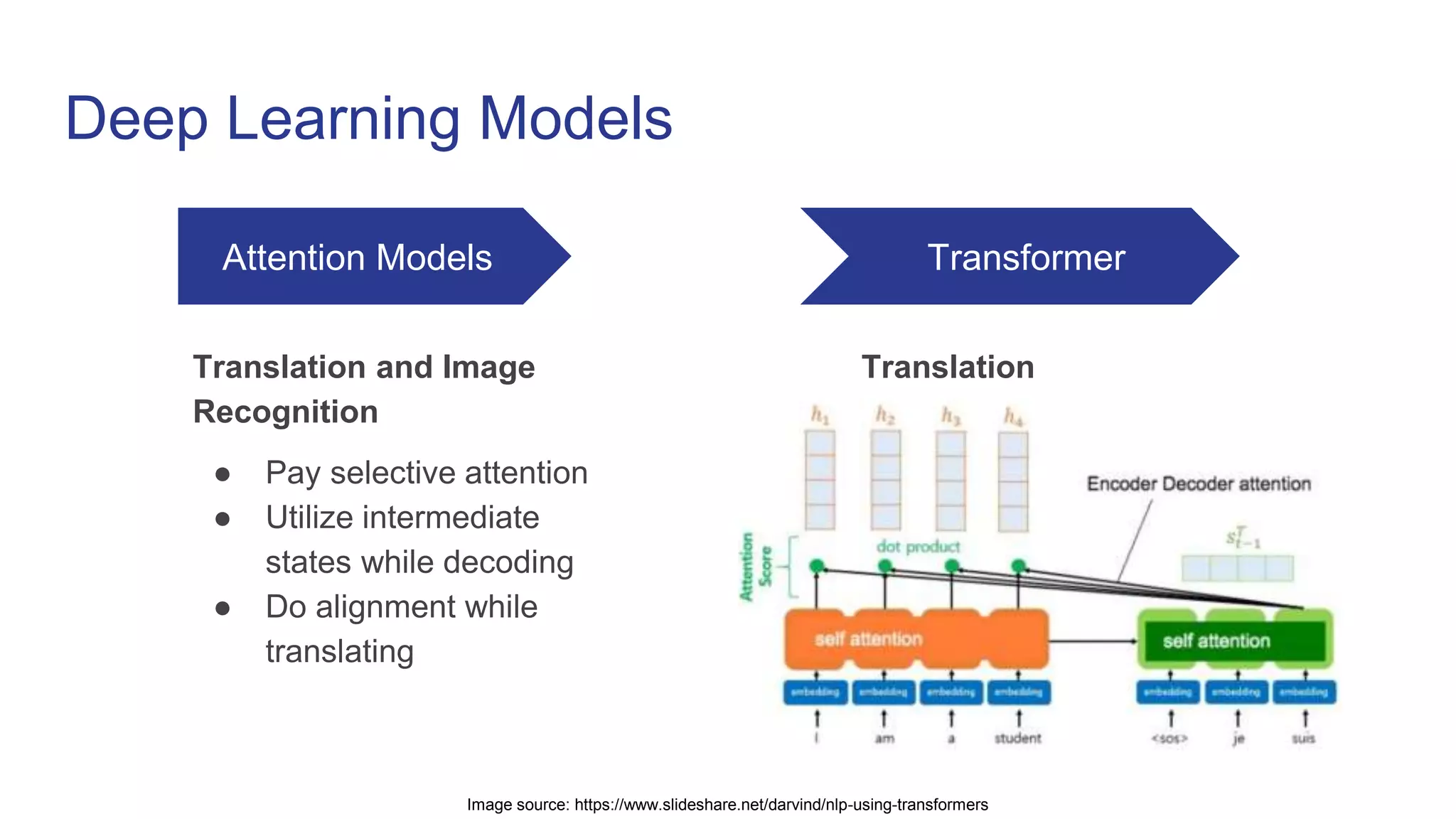
This document provides an overview of natural language processing (NLP) and the evolution of its techniques from symbolic and statistical methods to neural networks and deep learning. It explains the transformer architecture, focusing on its use of self-attention for sequence-to-sequence tasks and its advantages in handling long-range dependencies. The document also highlights challenges such as context fragmentation due to fixed-length input segments and discusses future directions, including transformer XL and BERT.