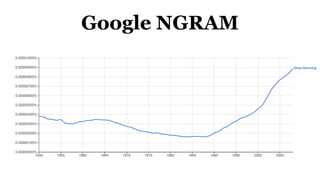
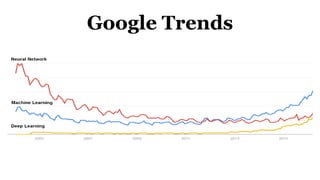
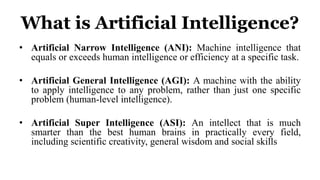
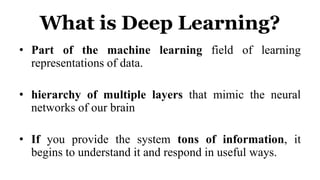
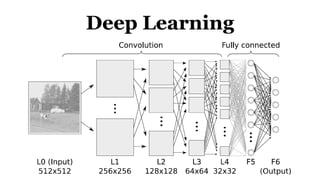
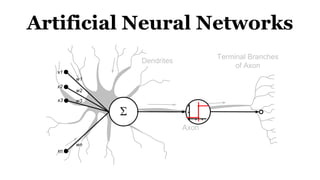
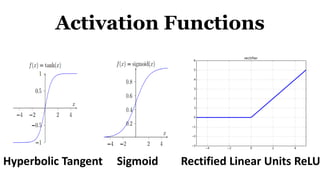
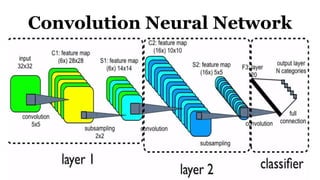
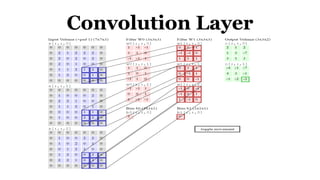
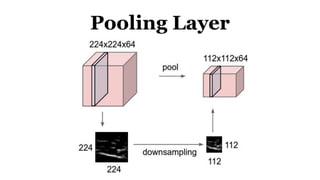
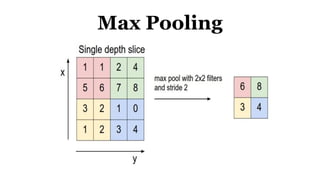
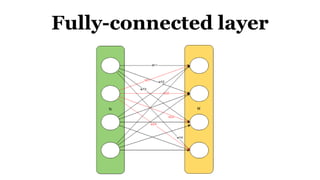
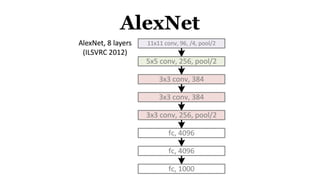
Deep learning is a type of machine learning that uses neural networks inspired by the human brain. It has been successfully applied to problems like image recognition, speech recognition, and natural language processing. Deep learning requires large datasets, clear goals, computing power, and neural network architectures. Popular deep learning models include convolutional neural networks and recurrent neural networks. Researchers like Geoffry Hinton and companies like Google have advanced the field through innovations that have won image recognition challenges. Deep learning will continue solving harder artificial intelligence problems by learning from massive amounts of data.