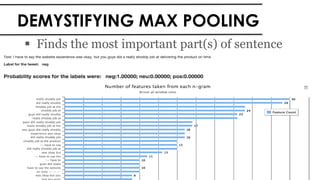
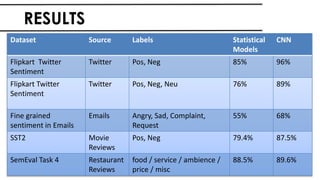
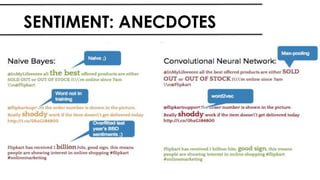
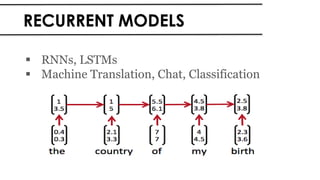
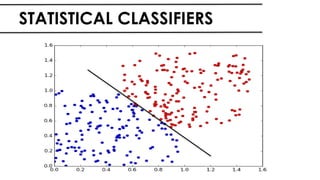
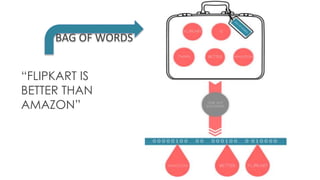
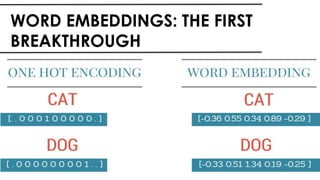
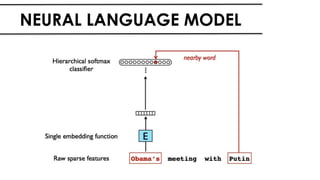
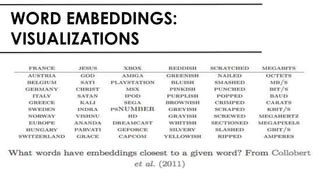
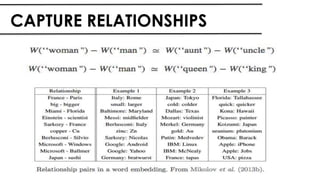
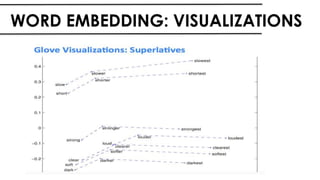
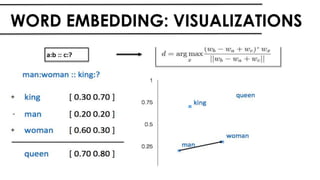
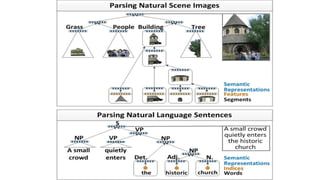
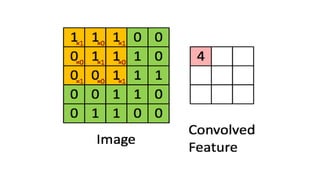
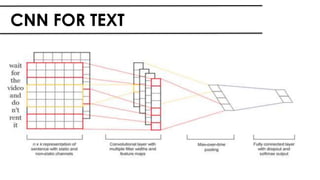
The document discusses the vital role of Natural Language Processing (NLP) in handling the growing data generated online, highlighting various applications like sentiment analysis and customer support. It details the evolution of NLP techniques from rule-based systems to deep learning approaches, emphasizing the effectiveness of deep neural networks in improving accuracy and feature extraction. Additionally, it addresses challenges faced in NLP, such as data sparsity and the complexities of word meaning, while showcasing how advanced models like CNNs and RNNs enhance text classification and understanding.





















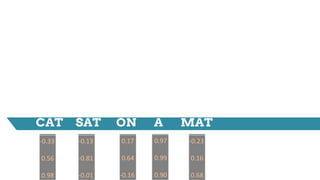
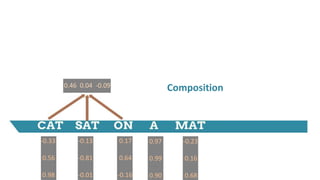
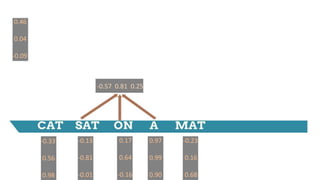
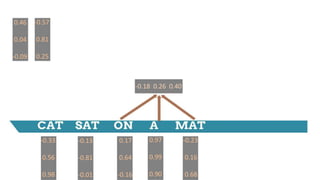
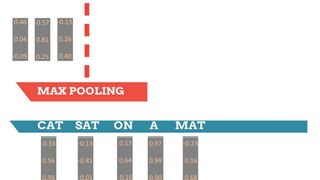
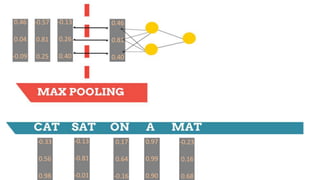
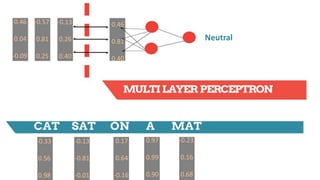
![-0.33
0.56
0.98
-0.13
-0.81
-0.01
0.17
0.64
-0.16
0.97
0.99
0.90
-0.23
0.16
0.68
Weight Matrix
(3 x 9)
[-0.33 0.56 0.98 -0.13 -0.81 -0.01 0.17 0.64 -0.16]
[-0.33 0.56 0.98 -0.13 -0.81
-0.01 0.17 0.64 -0.16]
[0.46 0.04 -0.09]
0.46 0.04 -0.09](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlnlpv1refined-150721095026-lva1-app6891/85/Deep-Learning-for-Natural-Language-Processing-42-320.jpg)