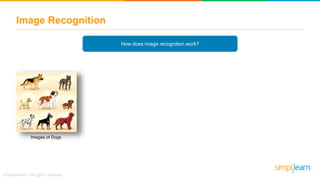
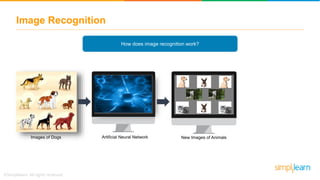
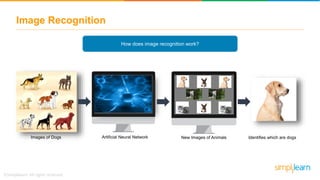
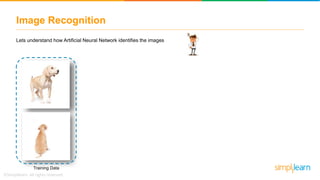
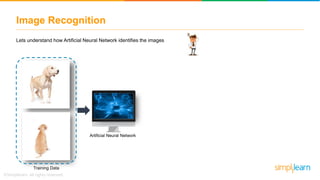
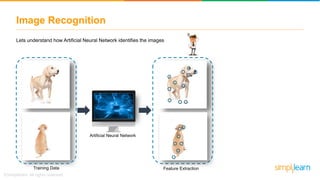
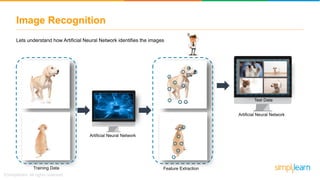
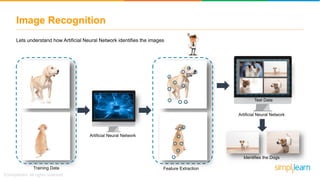
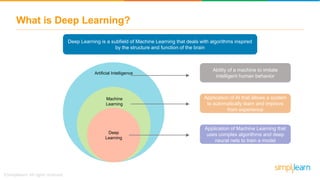
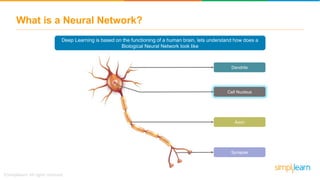
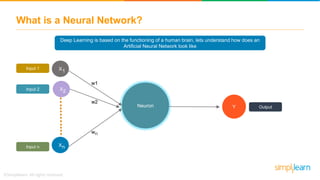
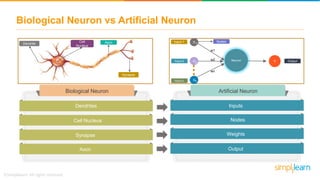
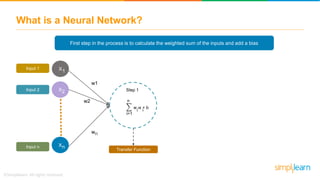
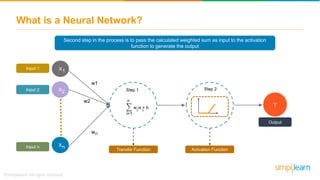
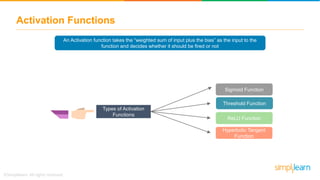
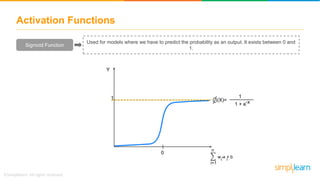
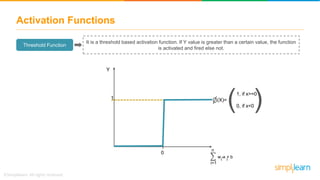
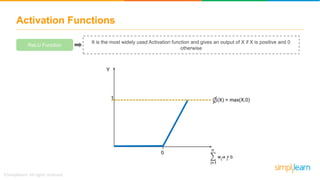
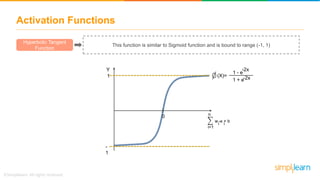
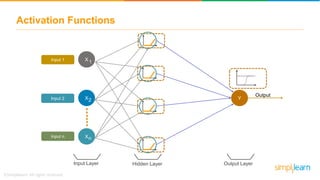
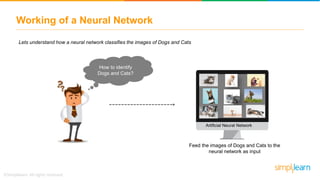
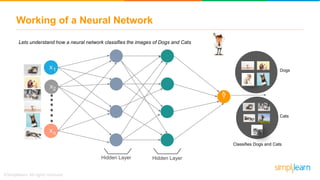
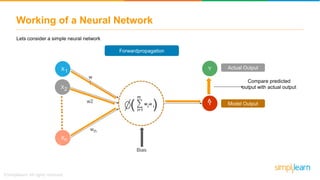
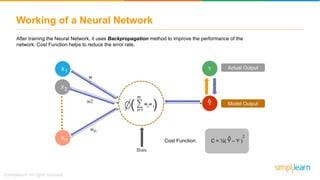
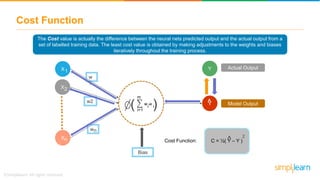
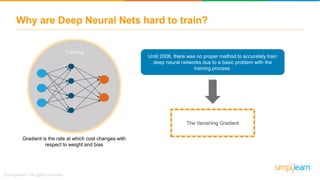
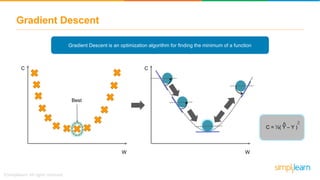
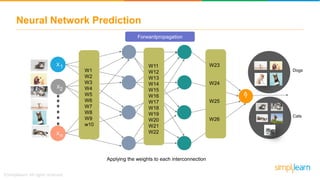
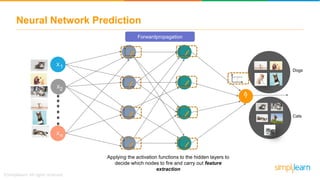
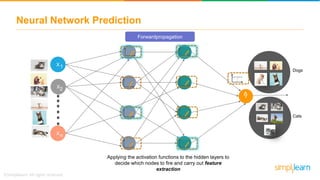
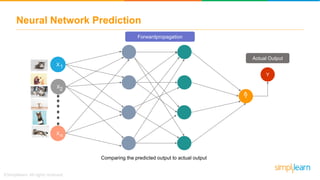
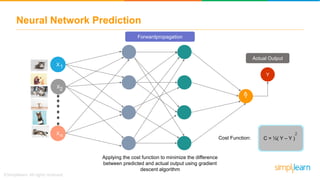
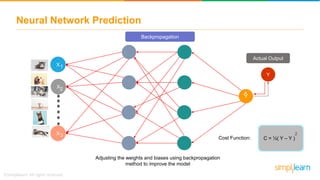
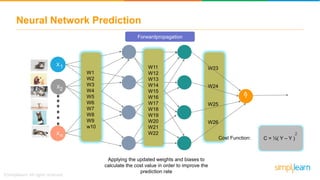
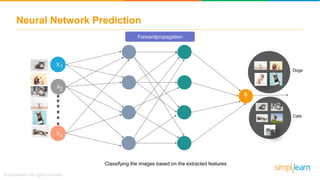
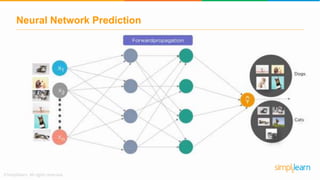
The document provides an overview of deep learning, focusing on its fundamentals such as neural networks, activation functions, and the process of image recognition. It explains the necessity of deep learning, highlighting its capabilities to handle large data sets and perform complex tasks, along with various applications including cancer detection, robot navigation, and autonomous driving. Additionally, it delves into the mechanics of neural networks, including the training process, backpropagation, and the challenges faced during training.