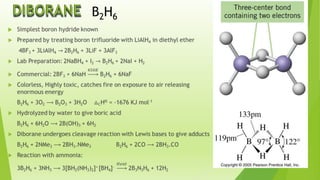
The document provides detailed information about the chemical properties and uses of boron and its compounds, including borax, boric acid, and diborane. Key characteristics such as atomic number, melting point, boiling point, and various applications in industries are highlighted. It also raises questions about the acid characteristics and behavior of boron compounds.