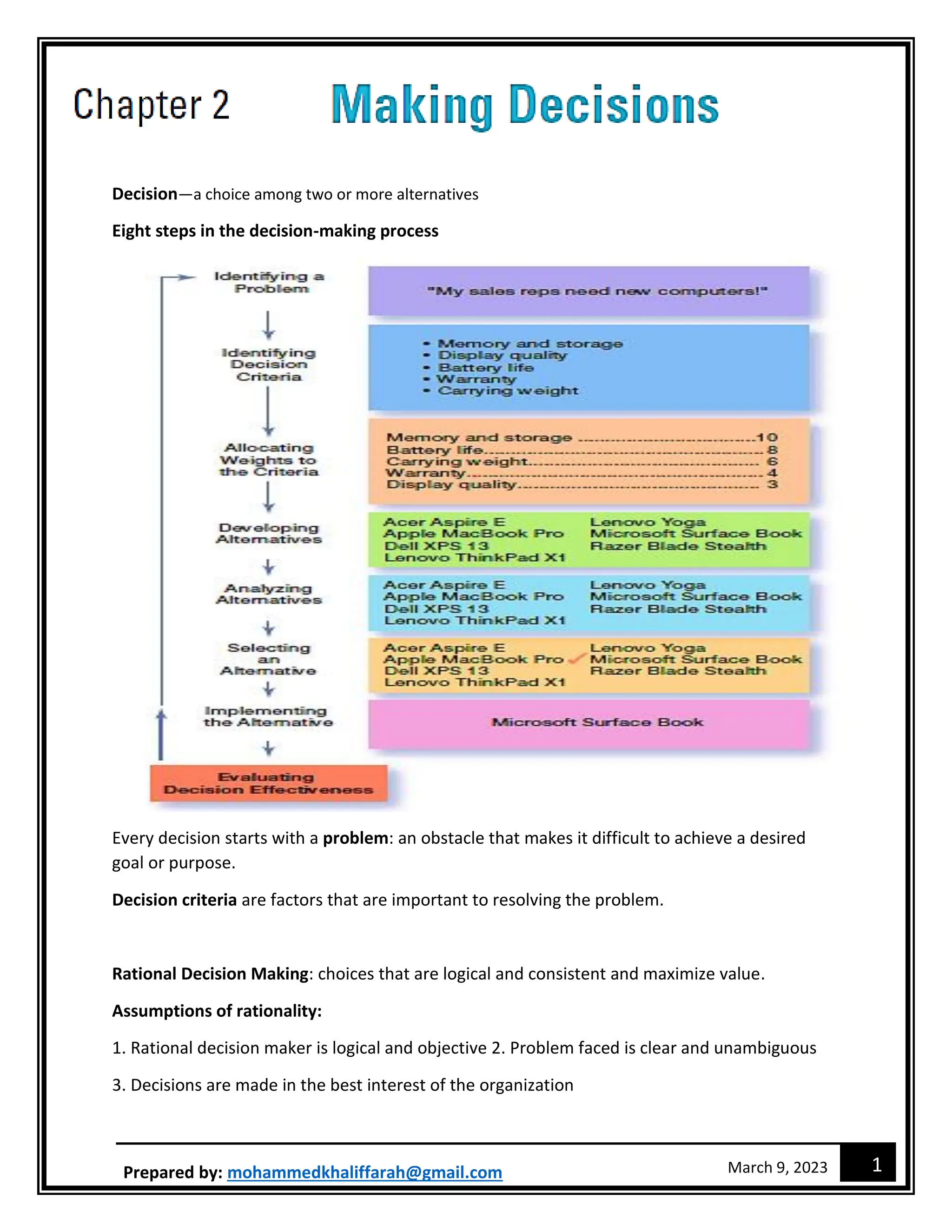
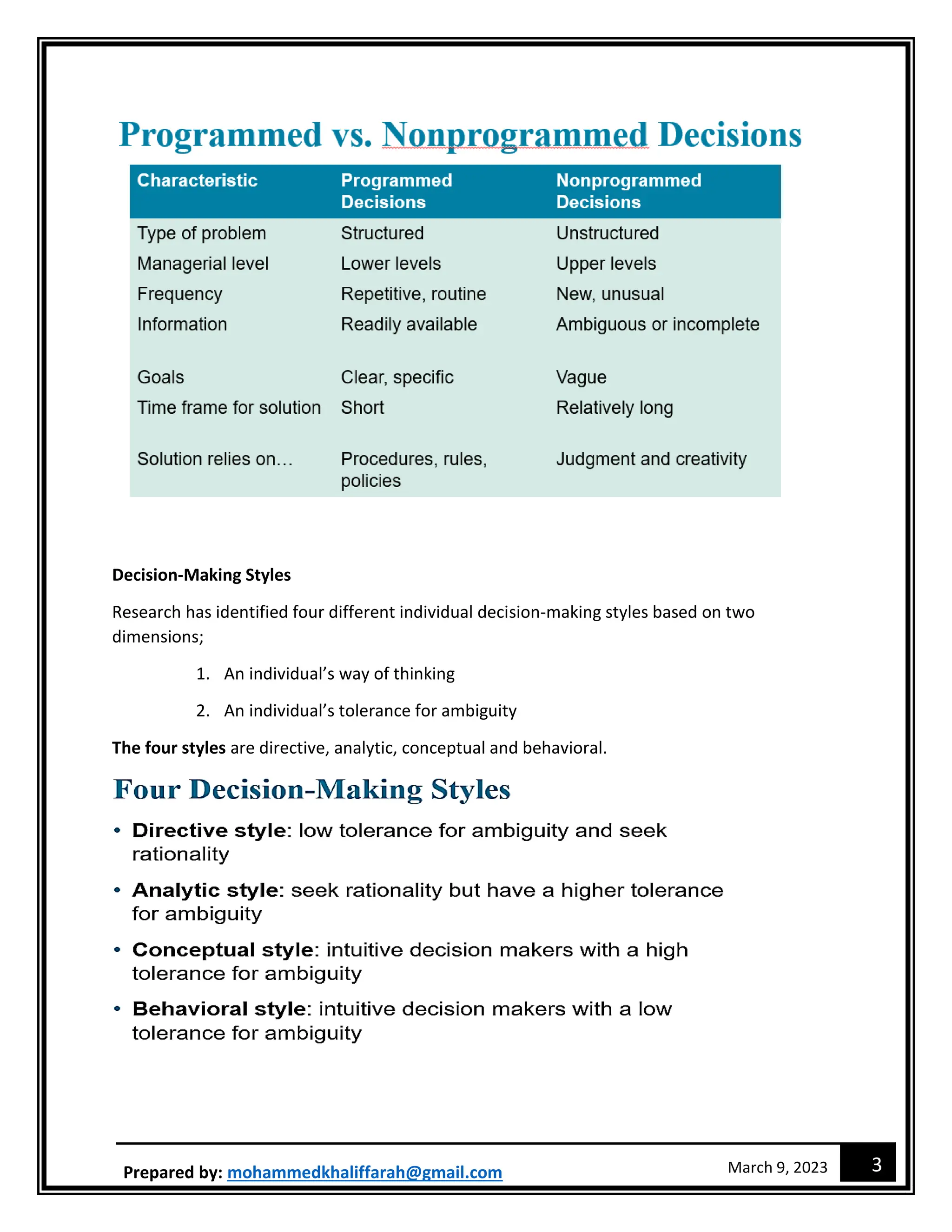
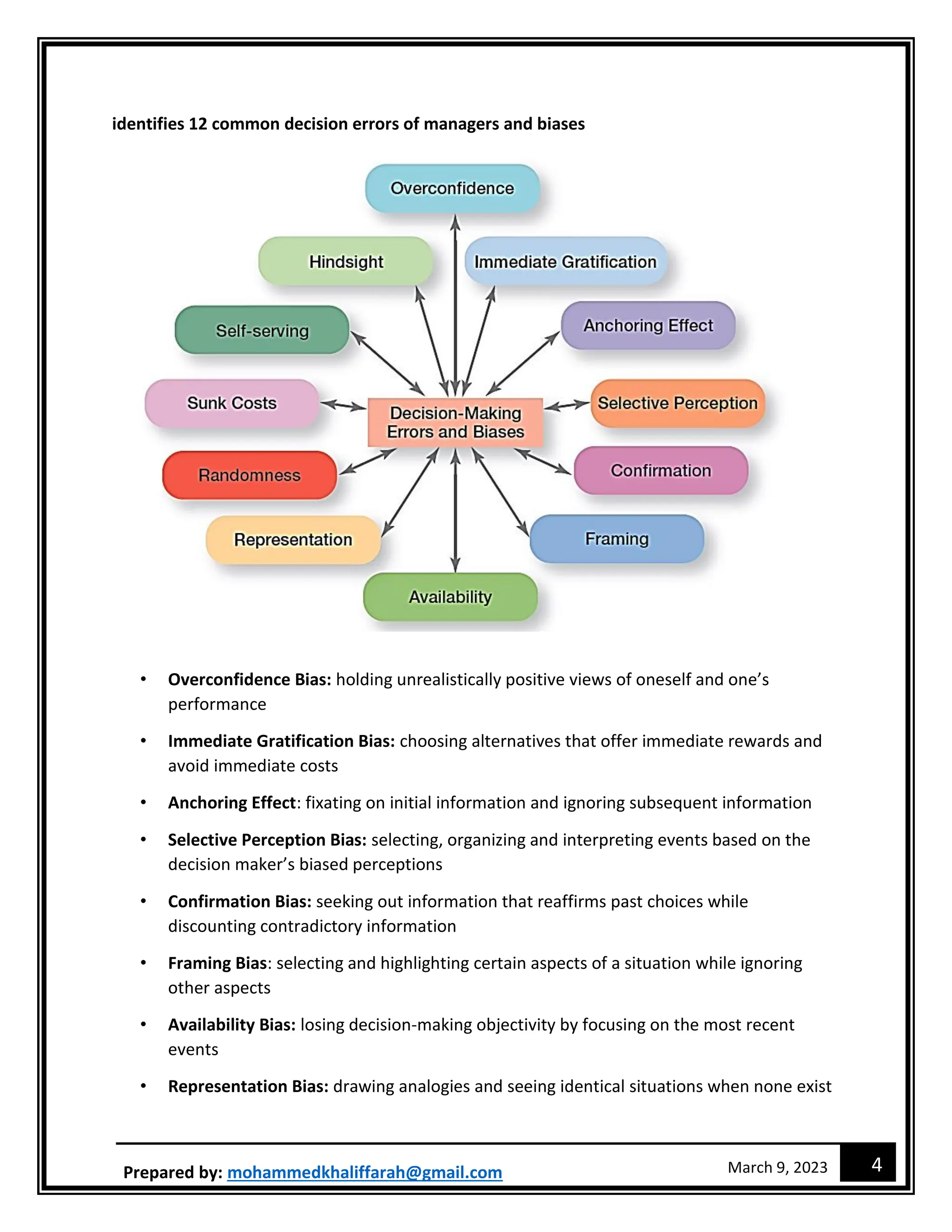
The document outlines the decision-making process and different approaches to decision making. It discusses the eight steps in the decision-making process, five approaches including rational decision making and bounded rationality. It also describes different types of decisions, decision-making styles, and common decision biases. New technologies like design thinking, big data, artificial intelligence, machine learning and analytics are changing how managers make decisions.