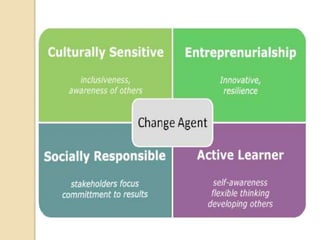
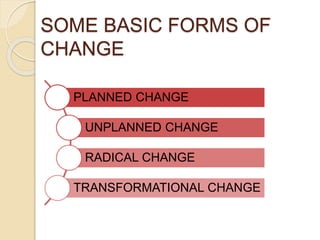
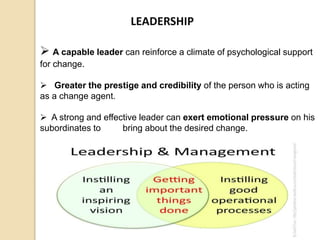
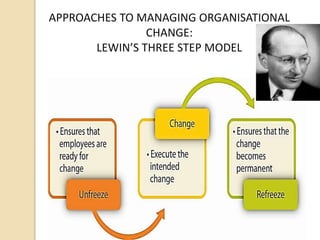
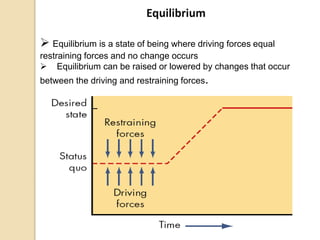
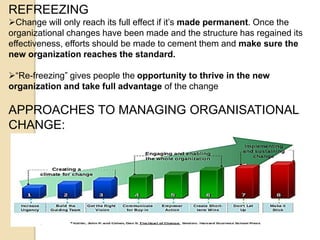
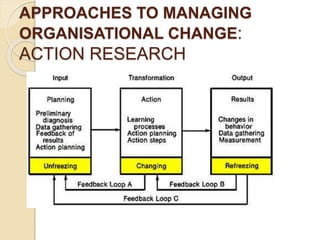
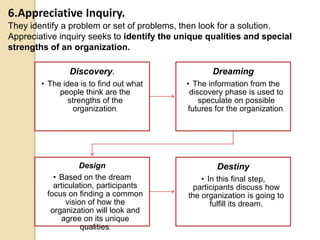
The document discusses various aspects of organizational change including defining organizational change, change management, forms of change (planned, unplanned, radical, transformational), forces for change (external and internal), resistance to change and strategies for managing resistance. It also summarizes approaches to managing organizational change including Lewin's three step model, Kotter's eight step model, action research and organizational development. Finally, it discusses creating a culture for change and innovation in organizations.