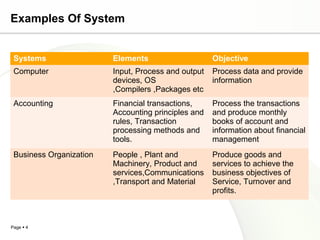
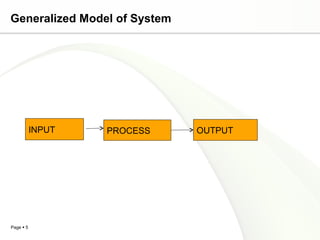
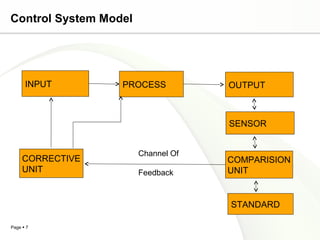
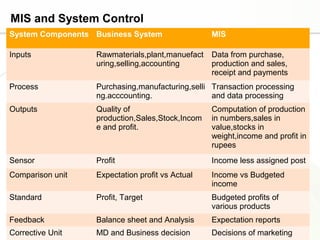
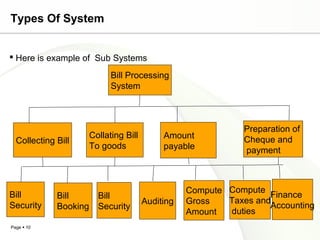
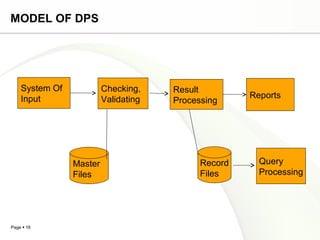
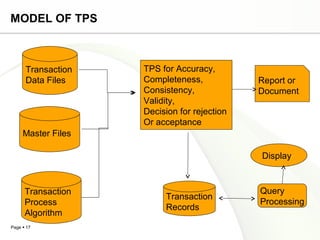
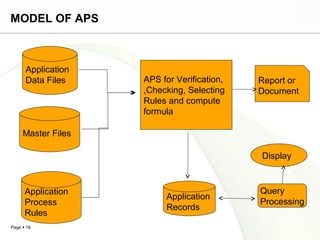
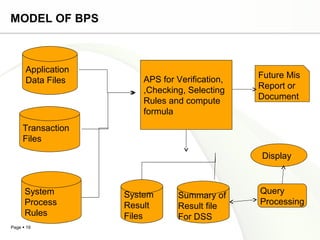
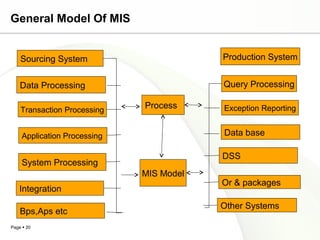
This document discusses system engineering concepts and provides examples of different types of systems. It describes a generalized model of a system with inputs, processes, and outputs. It also discusses system control using feedback loops, hierarchical system structures, and techniques for handling complex systems. The document provides examples of different system types and classes. It proposes general models for different information systems and discusses managing systems after implementation.