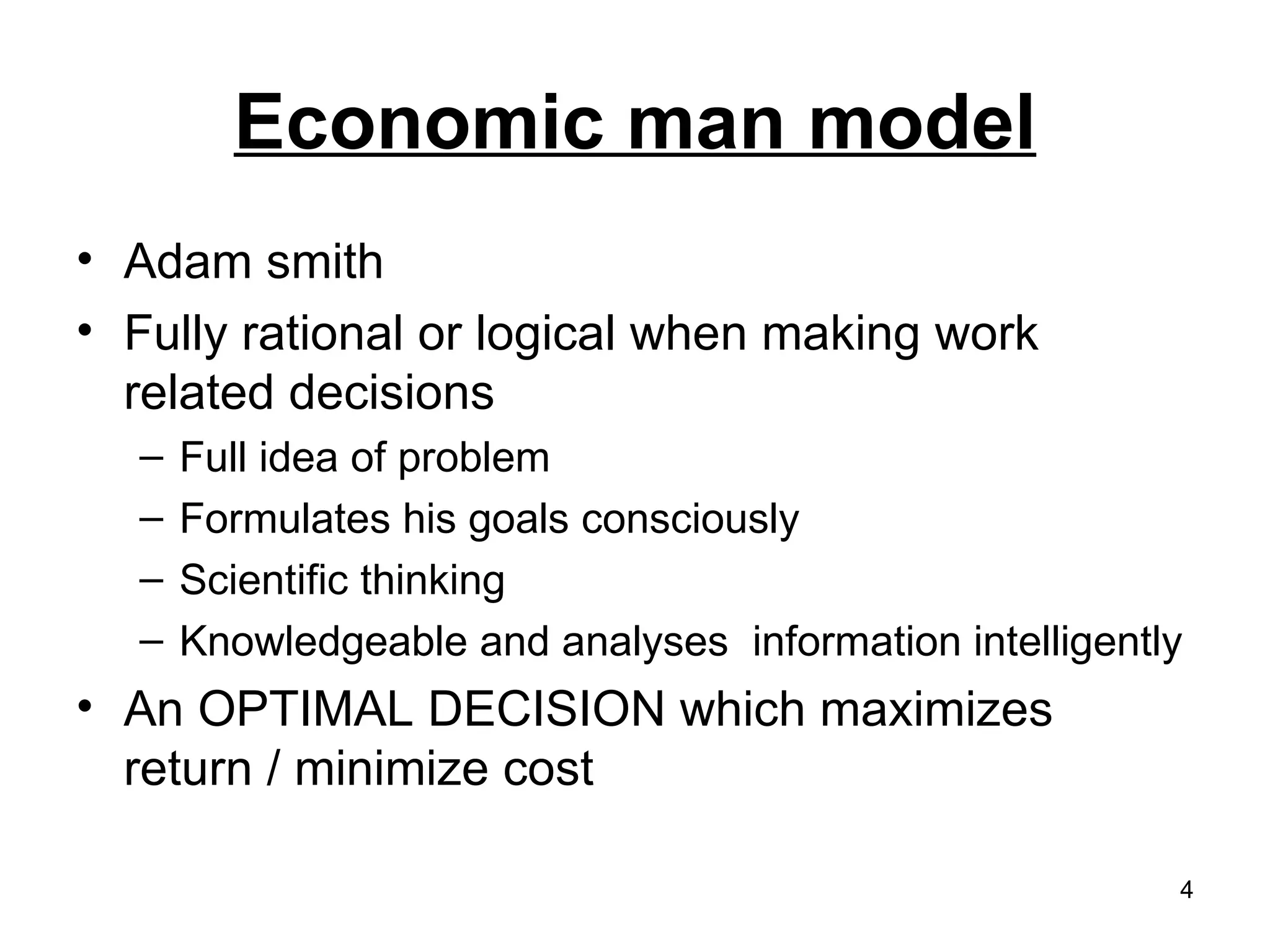
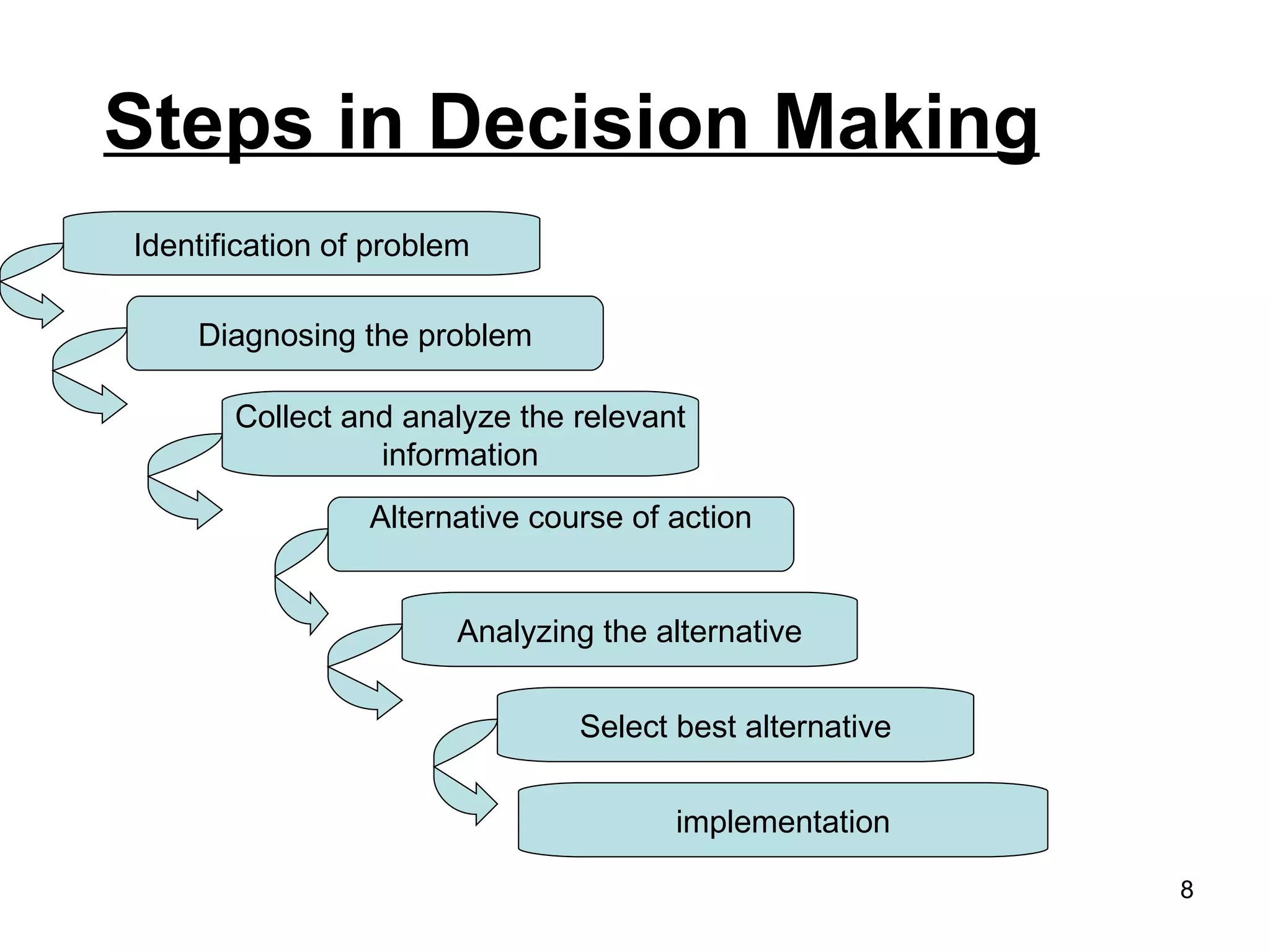
The document discusses different models and approaches to decision making. It describes the economic man model which involves fully rational decision making to maximize returns. However, it also introduces the administrative man model which recognizes that in reality, managers have bounded rationality due to limitations of time, information, and skills. The document also outlines different types of decisions like programmed vs non-programmed and strategic vs tactical vs operating decisions. Finally, it lists some typical steps involved in the decision making process.