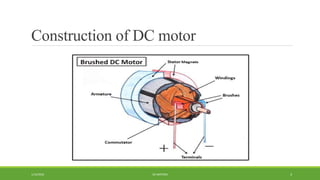
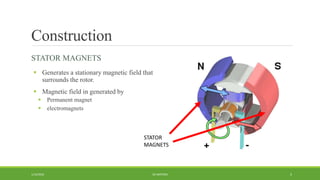
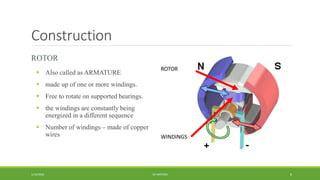
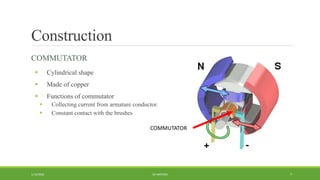
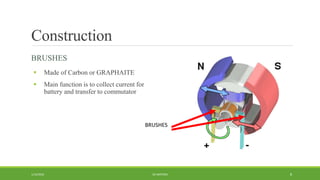
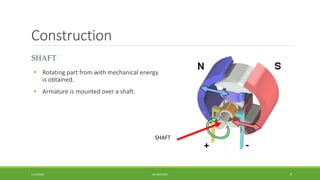
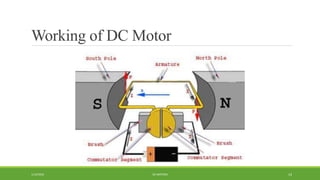
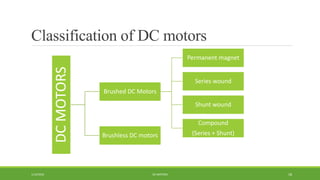
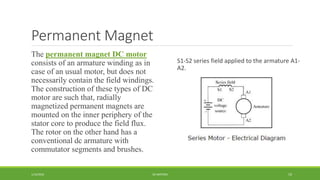
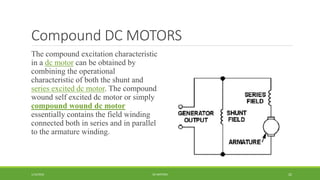
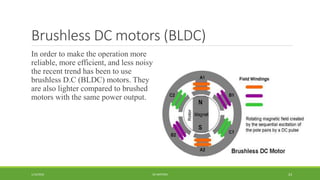
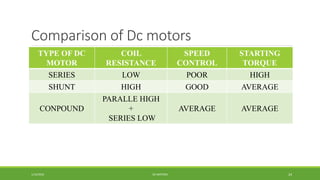
DC motors are used for applications requiring variable speed control and are inexpensive and easy to operate. A DC motor consists of a stator with magnets that produces a stationary magnetic field, a rotor or armature made of windings that rotates when power is applied, a commutator that changes the current direction in the windings, and brushes that conduct current from the commutator to an external circuit. When current passes through the rotor windings in the magnetic field, it produces a torque due to the Lorentz force, causing the rotor to rotate. DC motors are classified as permanent magnet, series wound, shunt wound, compound wound, and brushless types depending on how the field windings are connected.