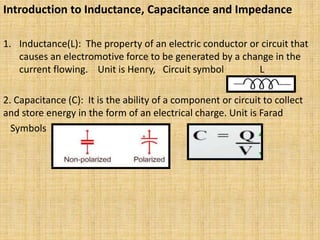
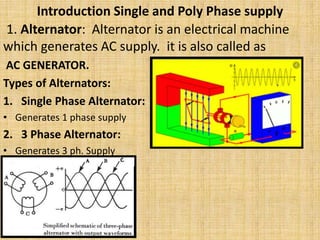
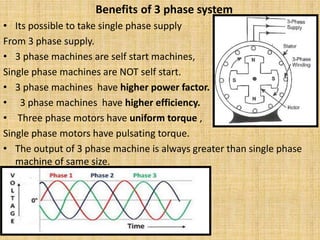
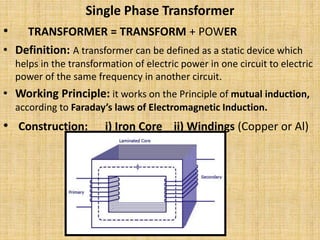
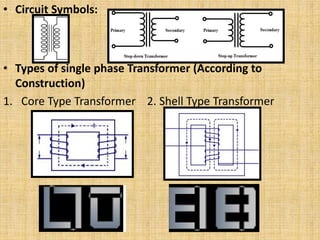
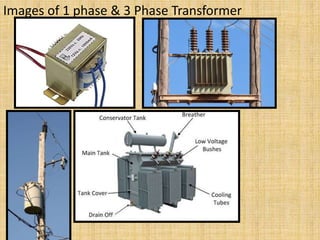
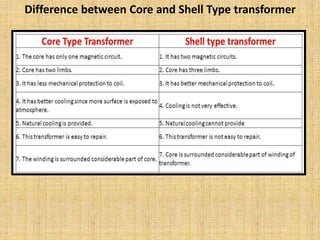
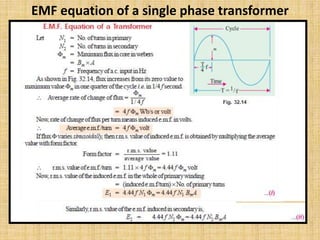
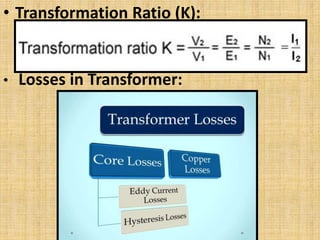
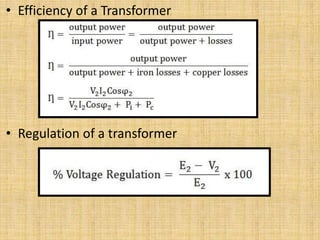
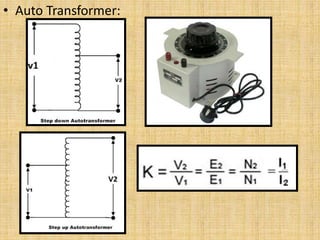
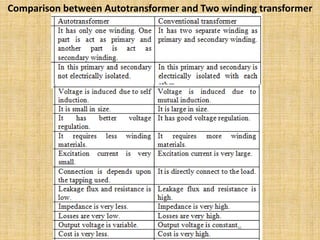
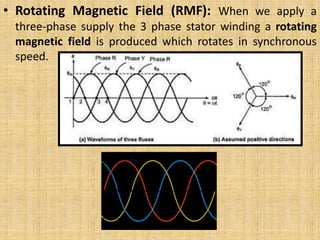
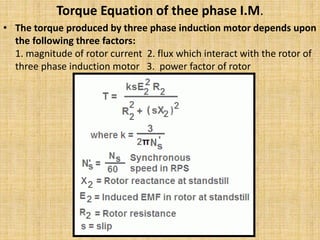
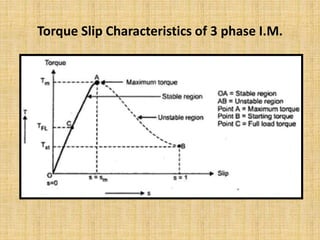
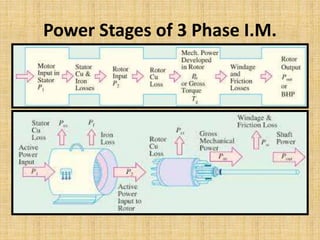
Unit 3 of the document covers principles of alternating current machinery, including inductance, capacitance, and impedance. It discusses types of electrical machines like alternators and transformers, their construction, working principles, and efficiency. Additionally, it outlines three-phase induction motors, detailing their construction, operating principles, and applications.