Embed presentation
Downloaded 42 times

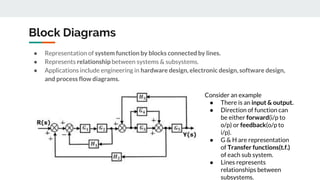
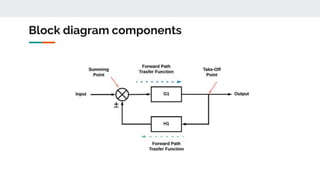
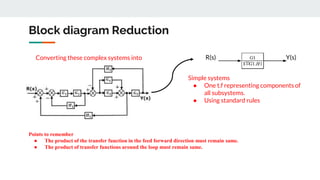
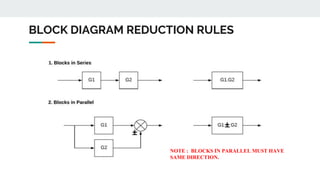
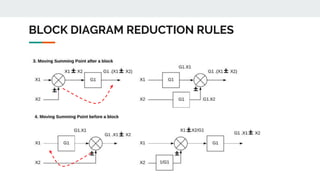
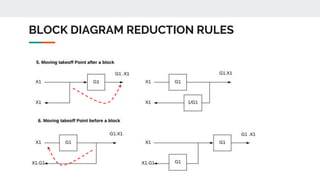
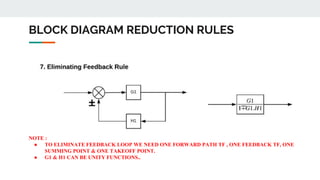


Block diagram reduction is a technique to simplify complex systems represented by block diagrams into simpler systems. A block diagram uses blocks and lines to represent the relationships between systems and subsystems. Block diagram reduction uses standard rules to convert the transfer functions of multiple subsystems into a single transfer function representing the entire system. The key points are that the product of transfer functions in the forward direction and around any feedback loops must remain the same after applying the reduction rules.








