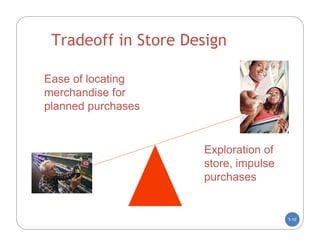
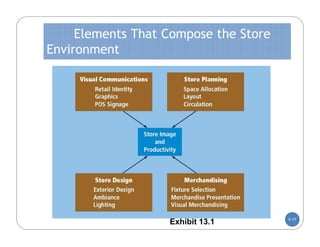
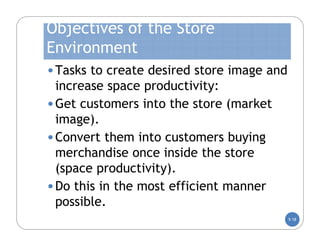
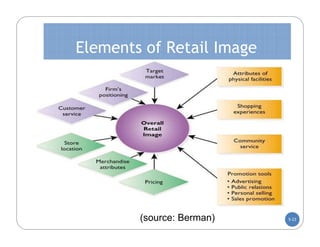
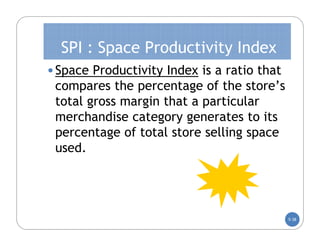
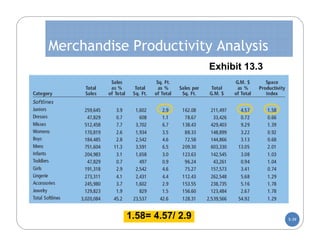
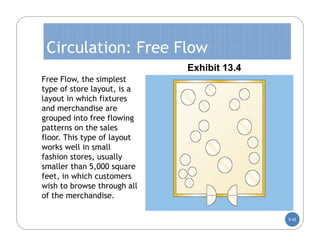
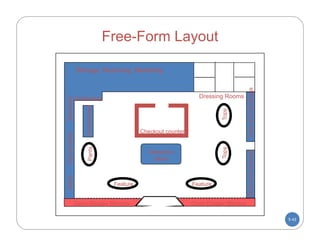
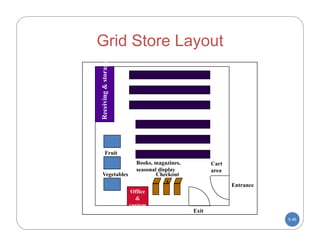
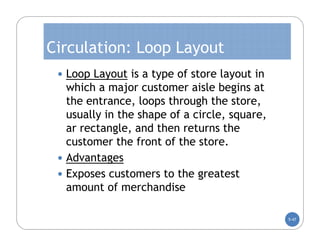
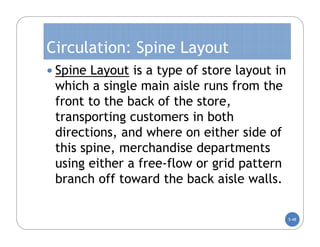
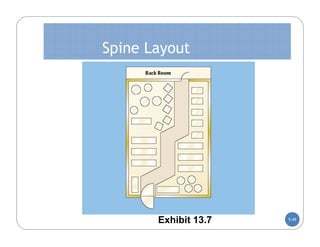
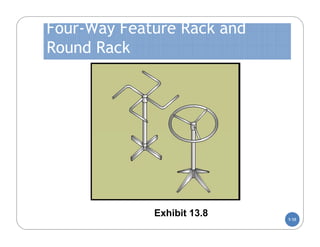
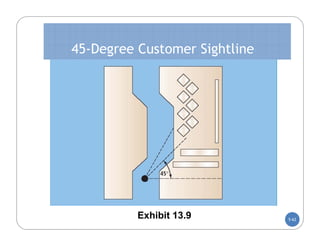
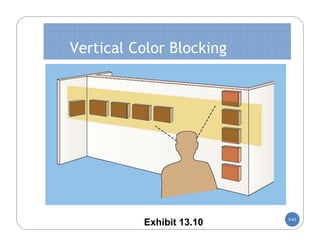
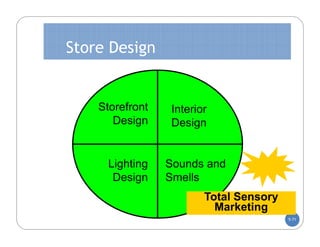
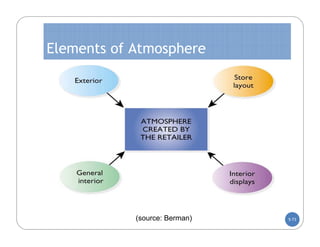
The document discusses store layout and design. It covers the objectives of store layout planning, which are to implement a retailer's strategy, influence customer buying behavior, control costs, provide flexibility, and meet legal requirements. The key elements of store layout that impact customers are store image, space allocation, merchandise placement, and aisle planning. Effective store layout and design can attract customers, help them find items, encourage spending more time and money in the store.