Embed presentation
Downloaded 91 times

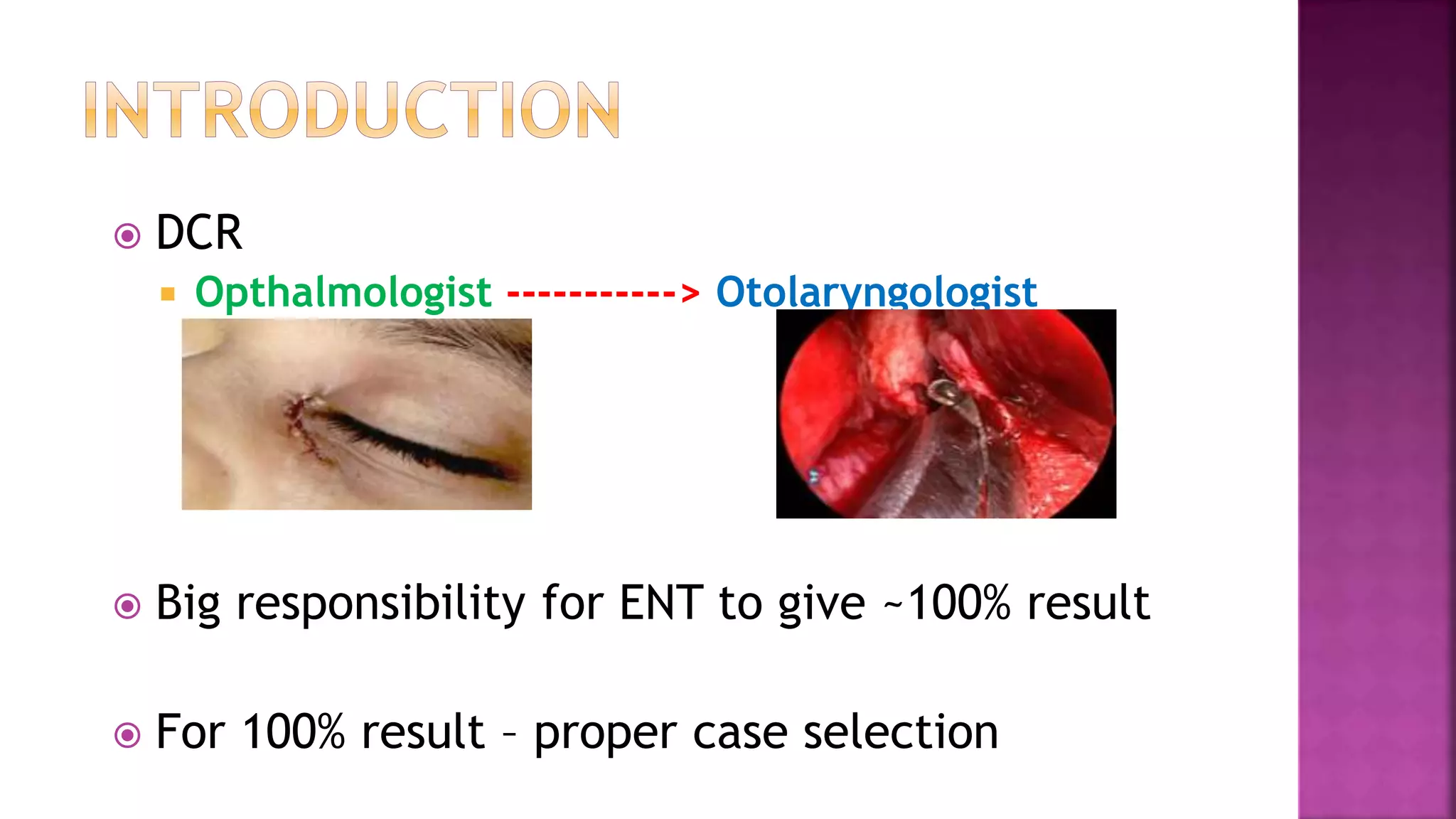

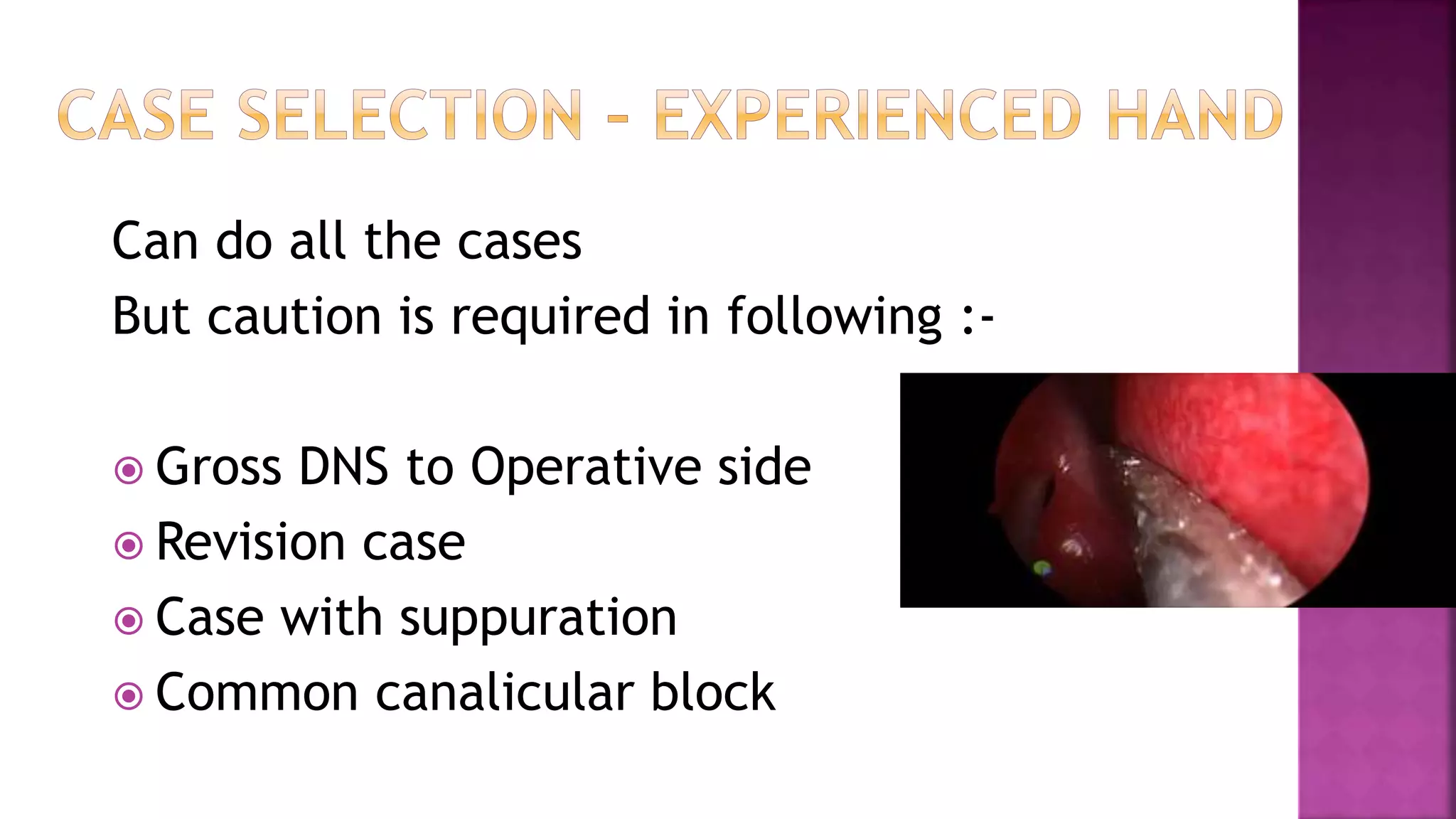

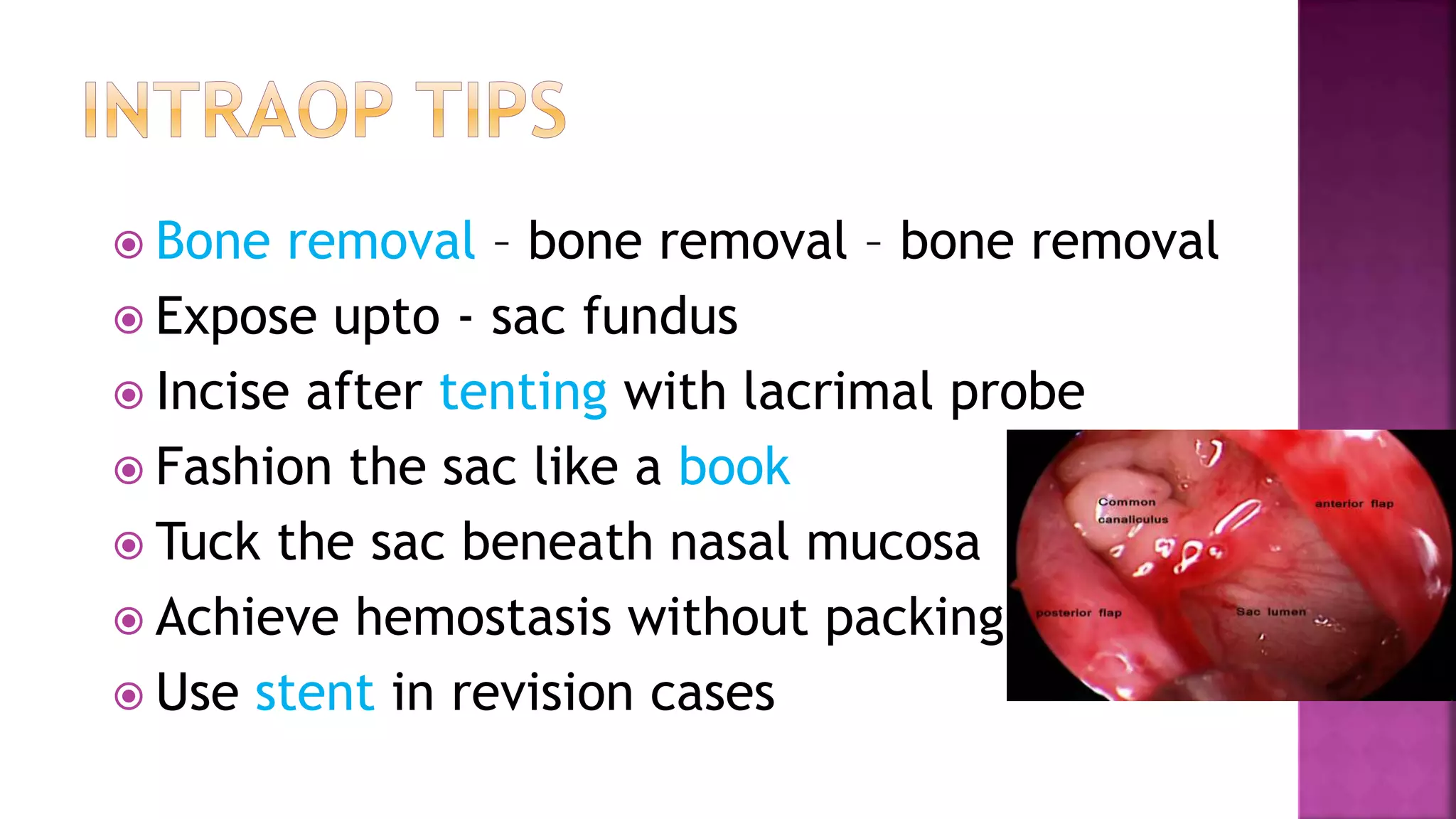




Dr. Zeeshan Ahmad discusses considerations for successful dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) surgery. Certain patient characteristics and test results help ensure success, such as epiphora duration under 1 year, positive regurgitation test, and distended sac on probing. Thorough bone removal from the lacrimal sac is emphasized. Post-operative care involves antibiotics, syringing, and controlling nasal allergy. The document outlines techniques for incising the sac, tucking it under the nasal mucosa, and achieving hemostasis without packing. It notes that DCR has become more of an ENT procedure due to scar advantage and better epistaxis control. The author's series showed a success rate of









