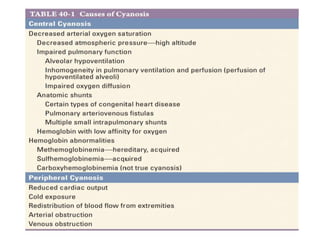
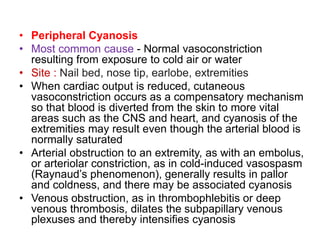
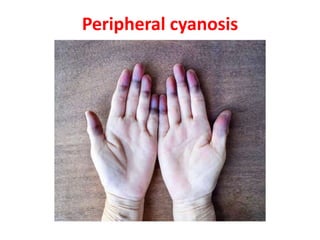
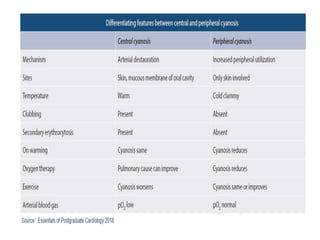
Cyanosis is a bluish discoloration of the skin or mucous membranes due to excessive amounts of deoxygenated hemoglobin. It can be central or peripheral in origin. Central cyanosis occurs when oxygen saturation in arterial blood is low, such as in congenital heart defects causing right-to-left shunts. Peripheral cyanosis is caused by slowed blood flow and high oxygen extraction from normally saturated blood, as seen in cold exposure, shock, or peripheral vascular disease. Differential cyanosis may present with cyanosis isolated to certain limbs depending on anatomy. Methemoglobinemia and sulfhemoglobinemia can also cause cyanosis and require specific treatments.