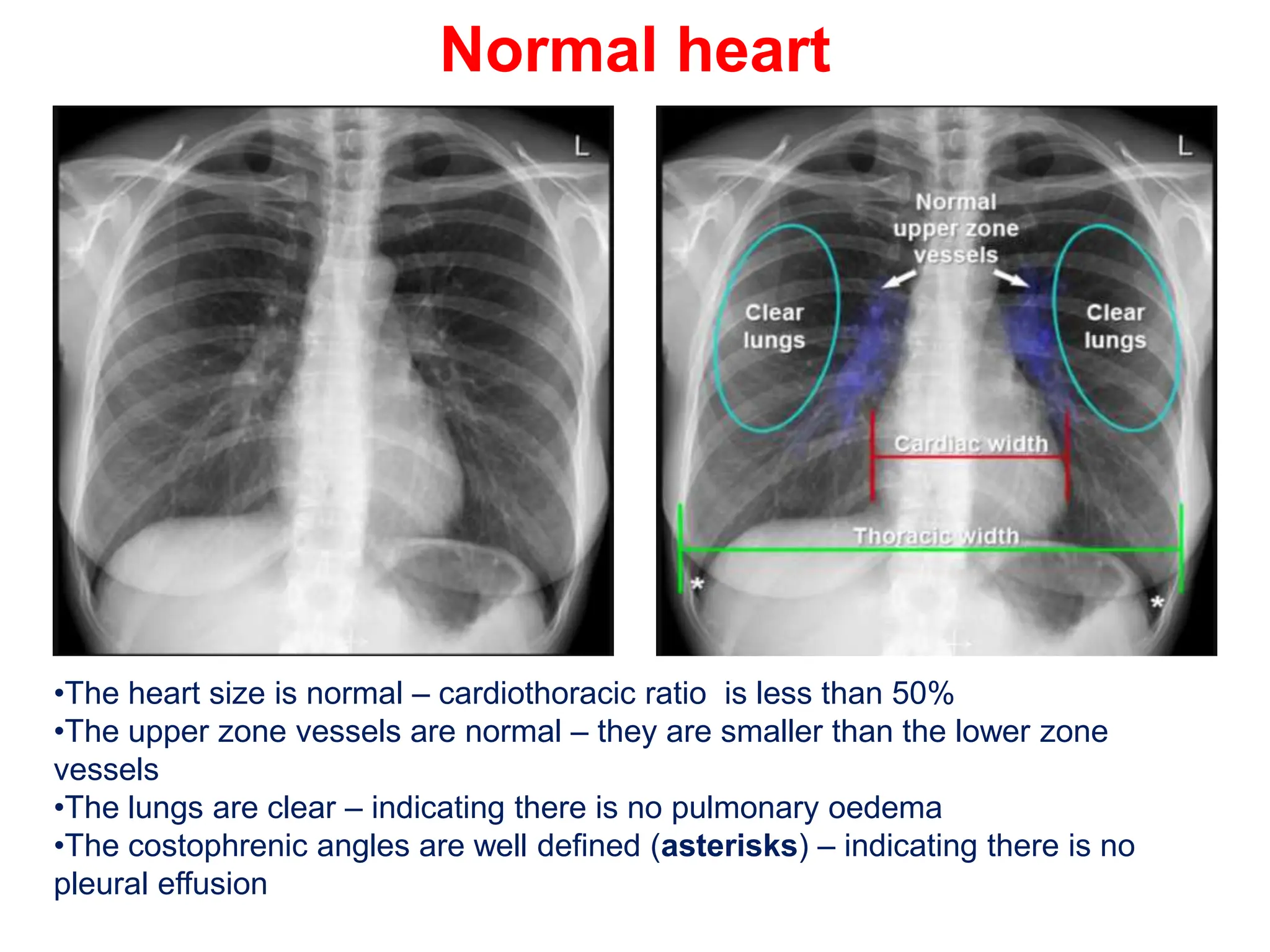
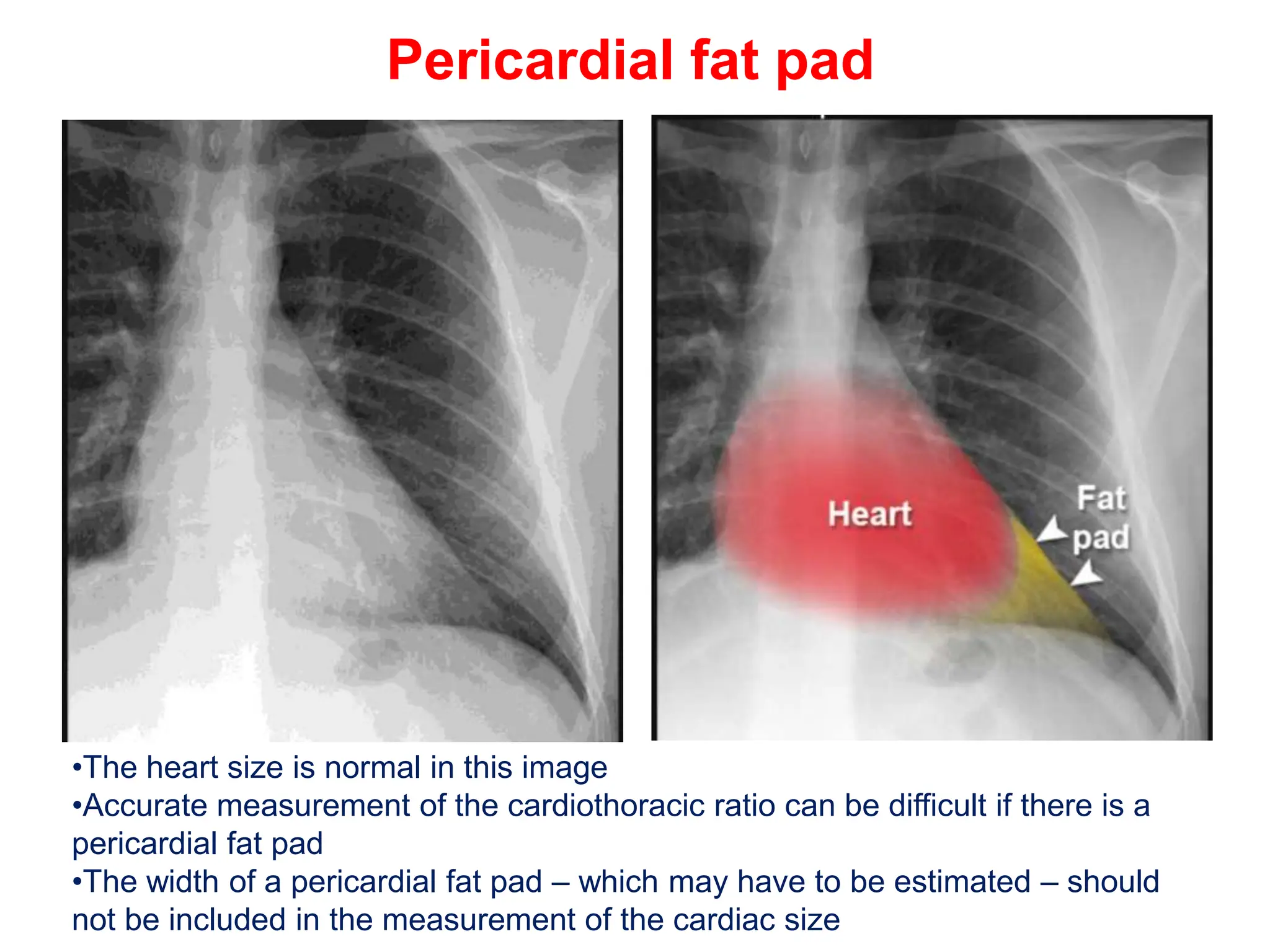
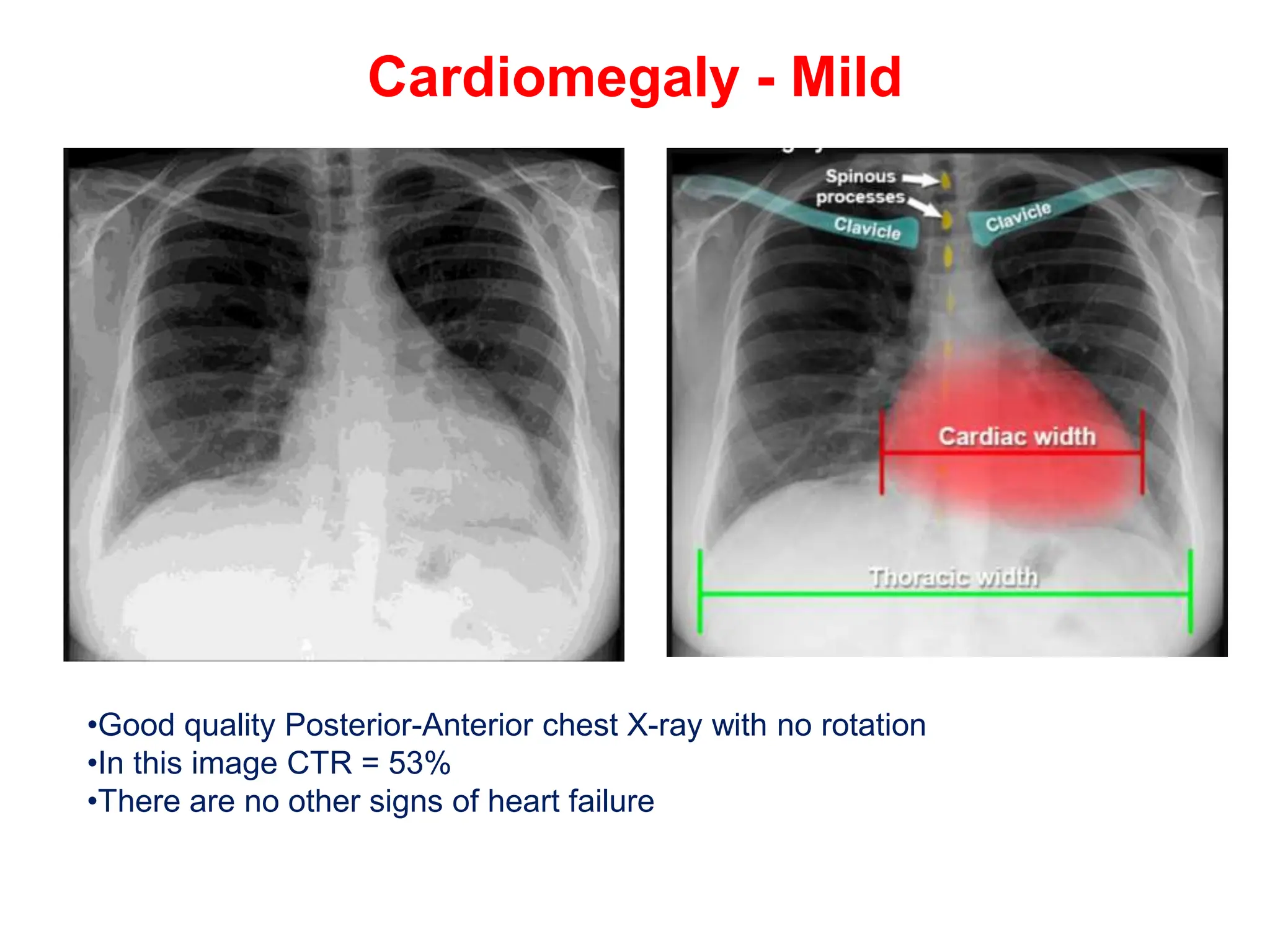
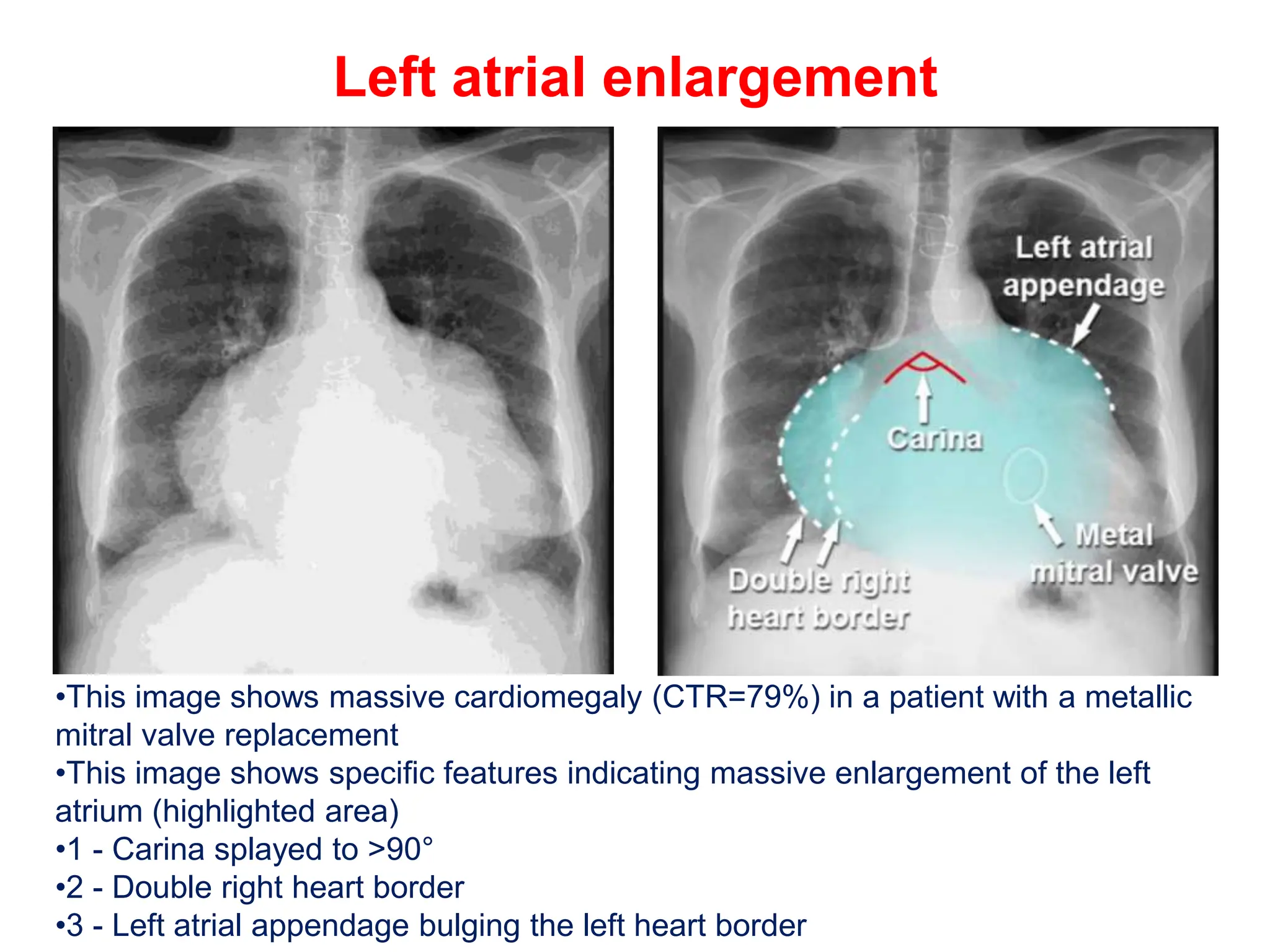
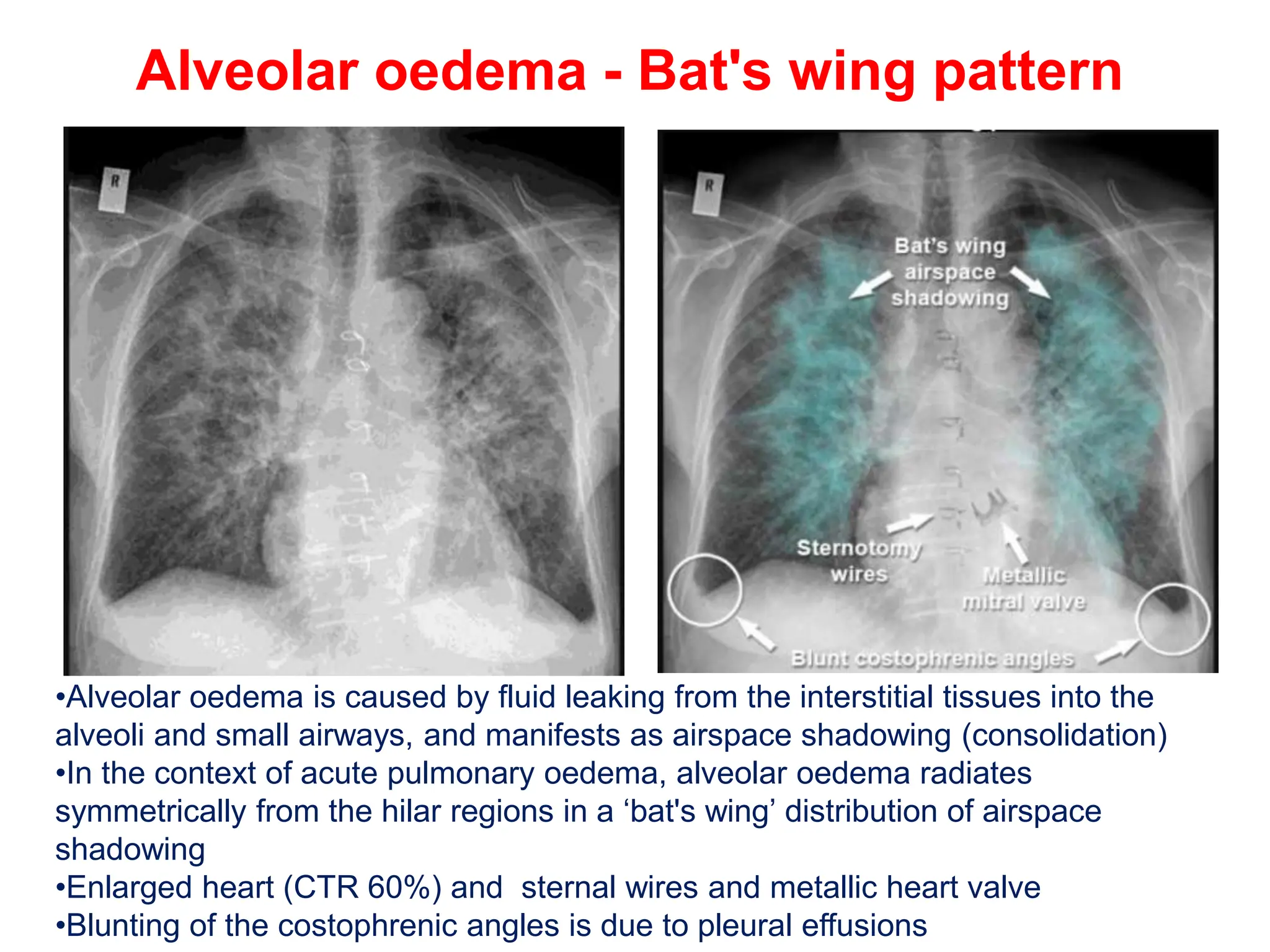
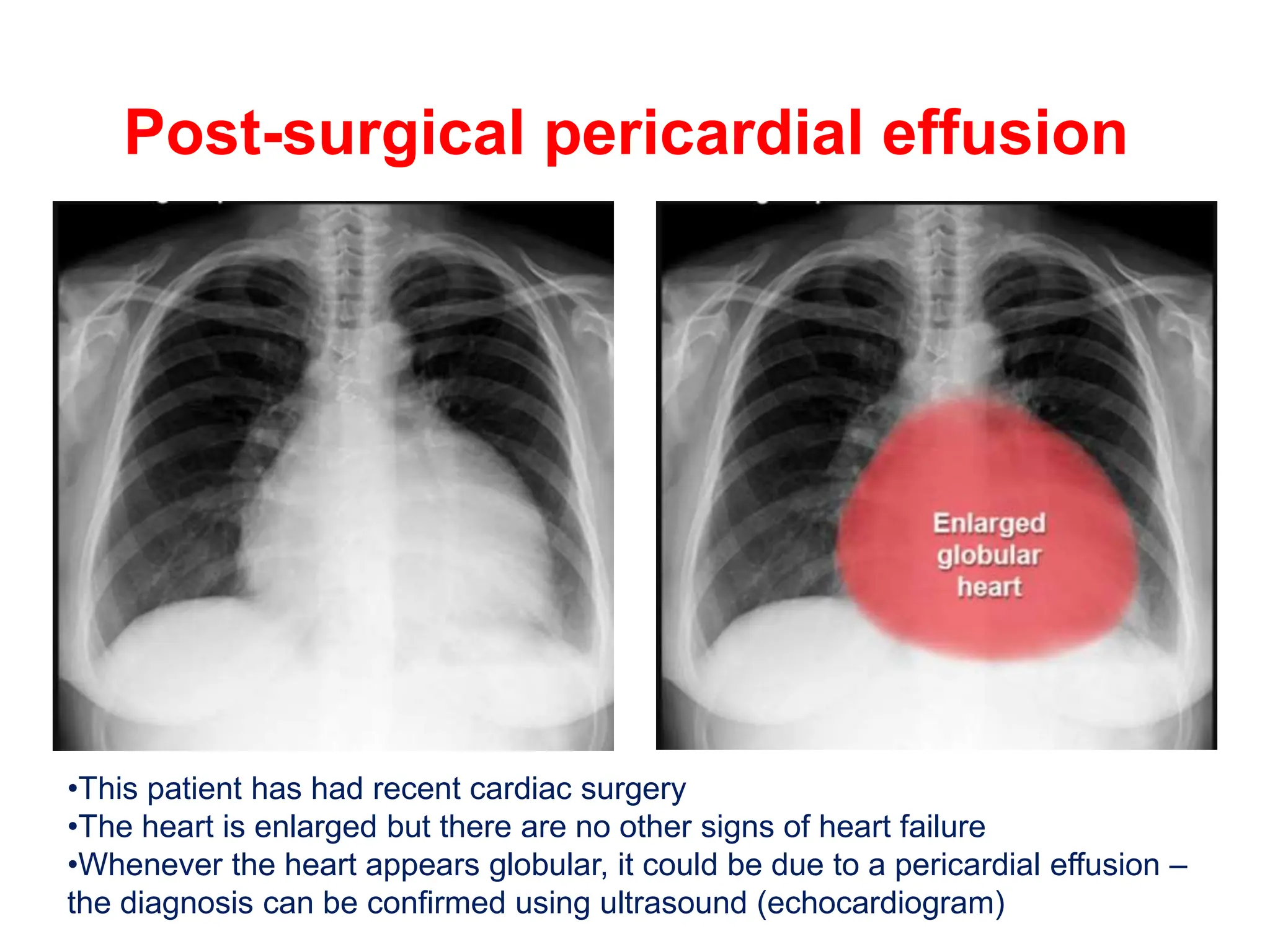
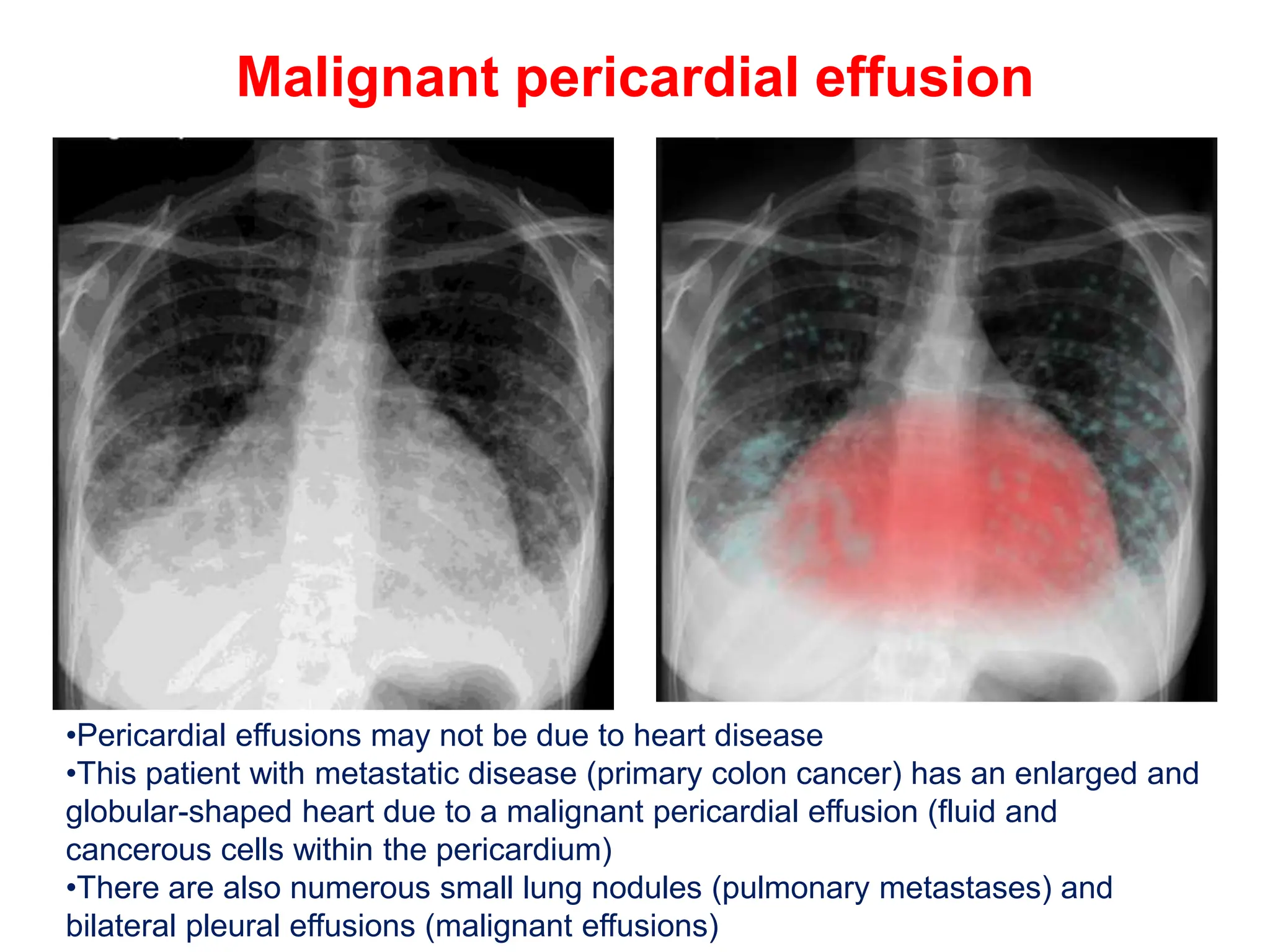
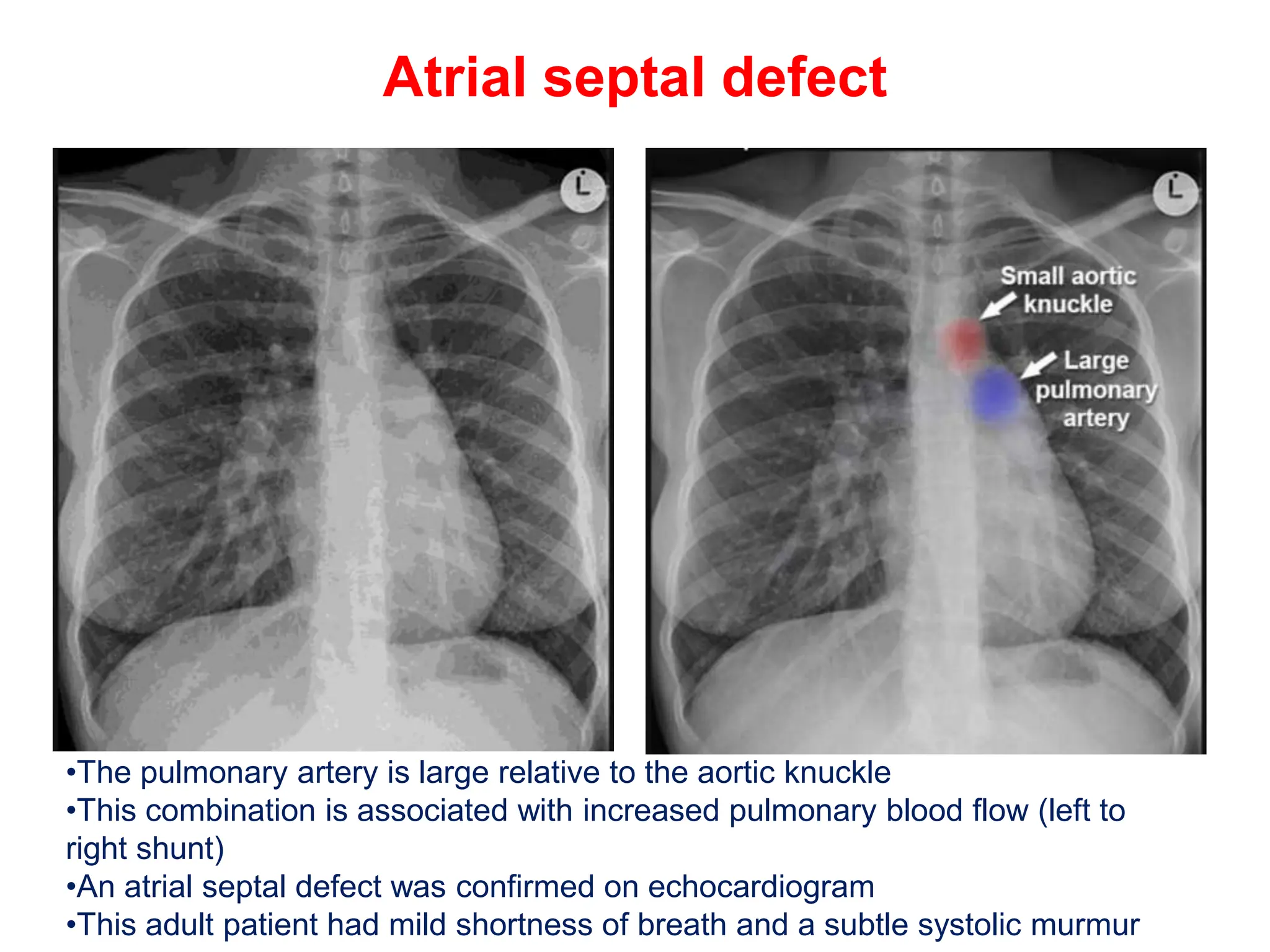
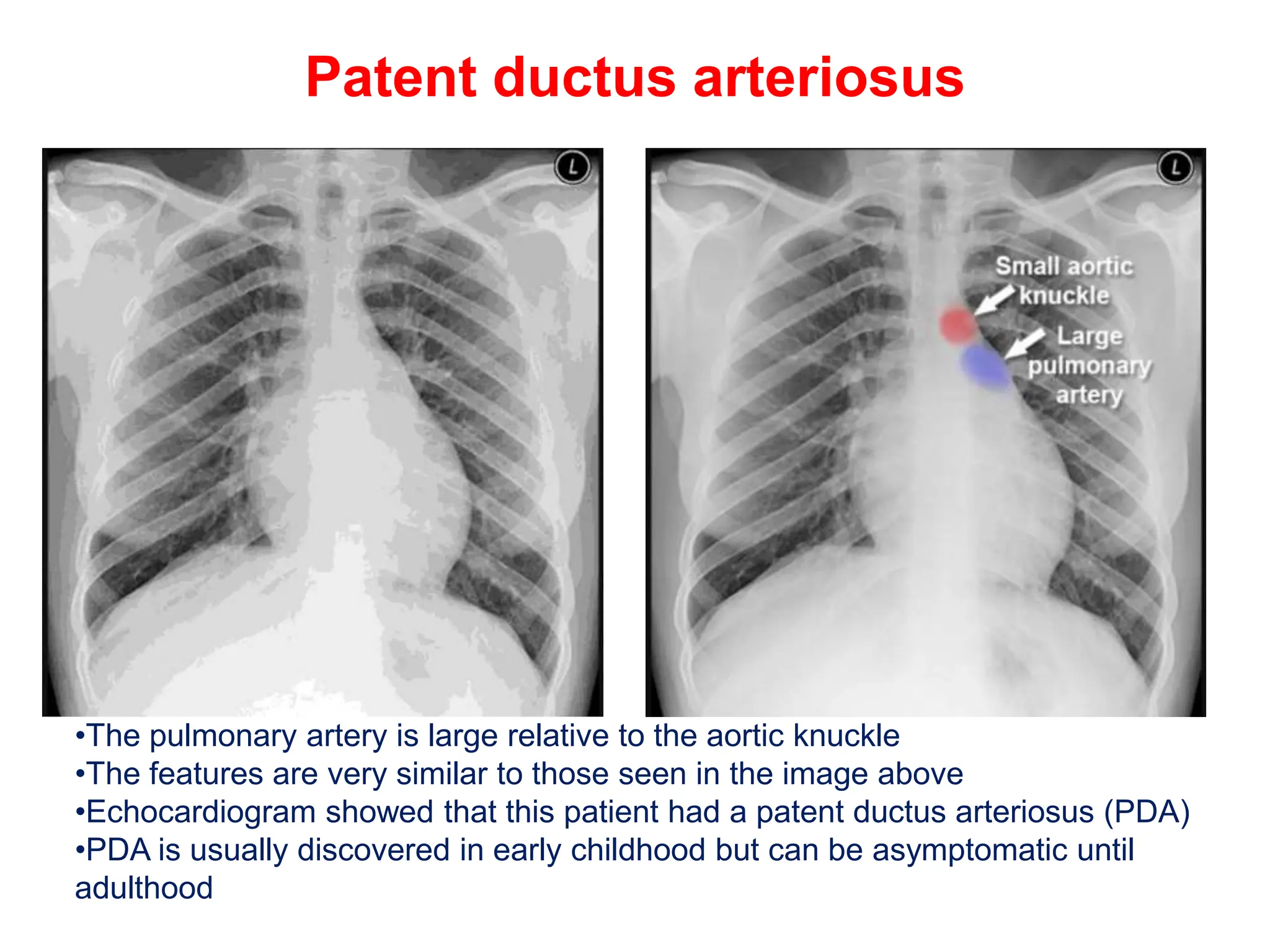
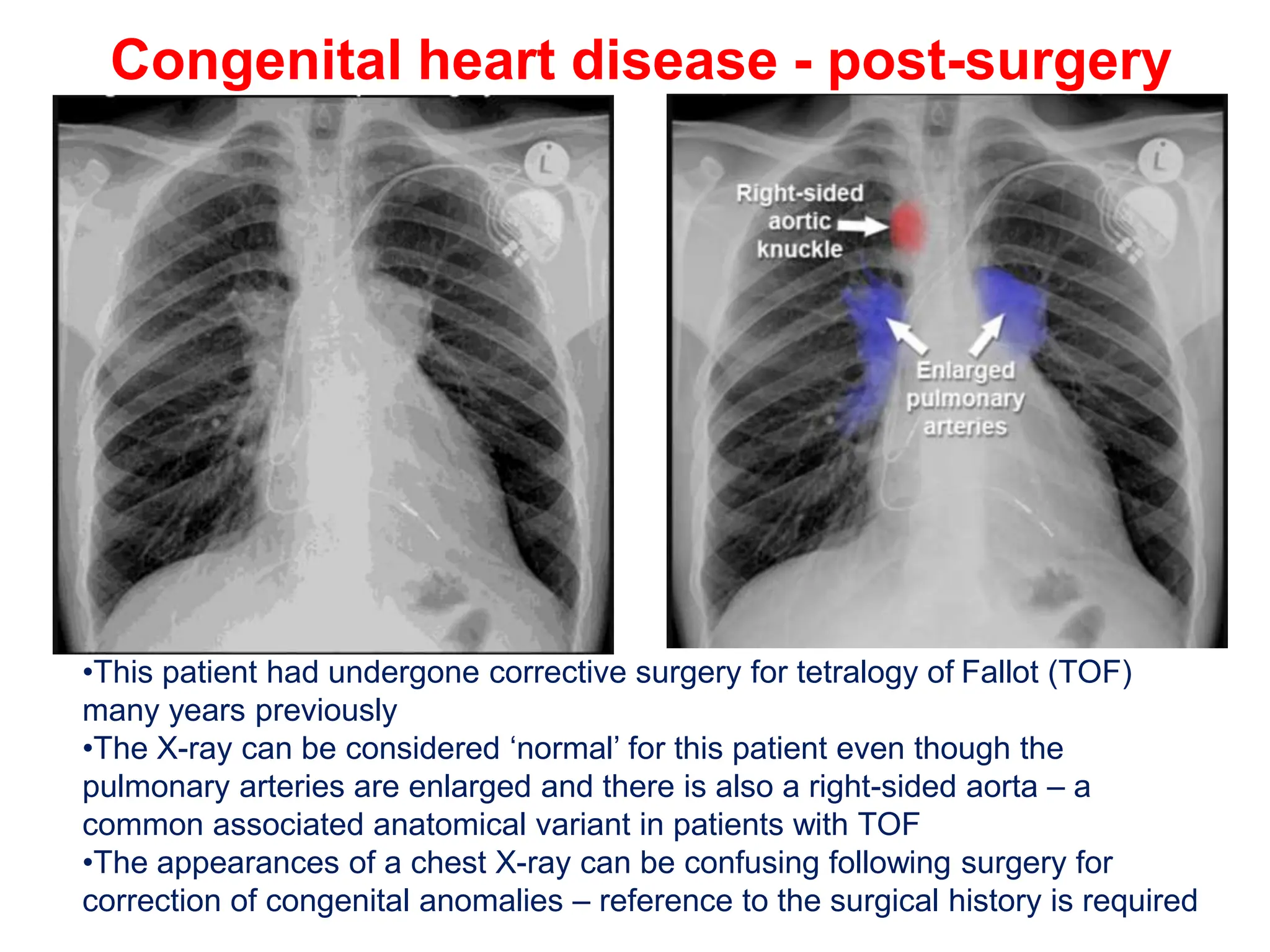
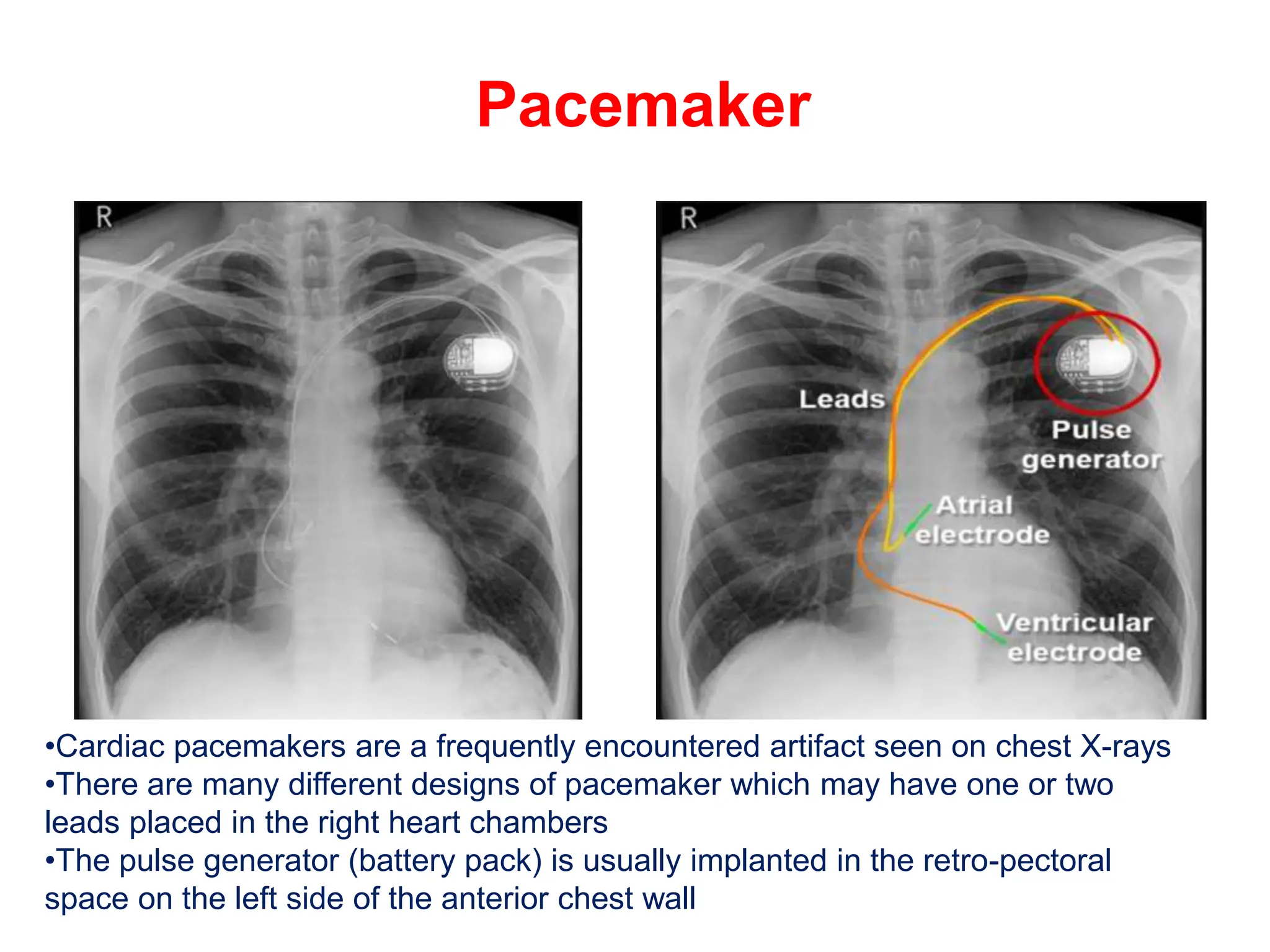
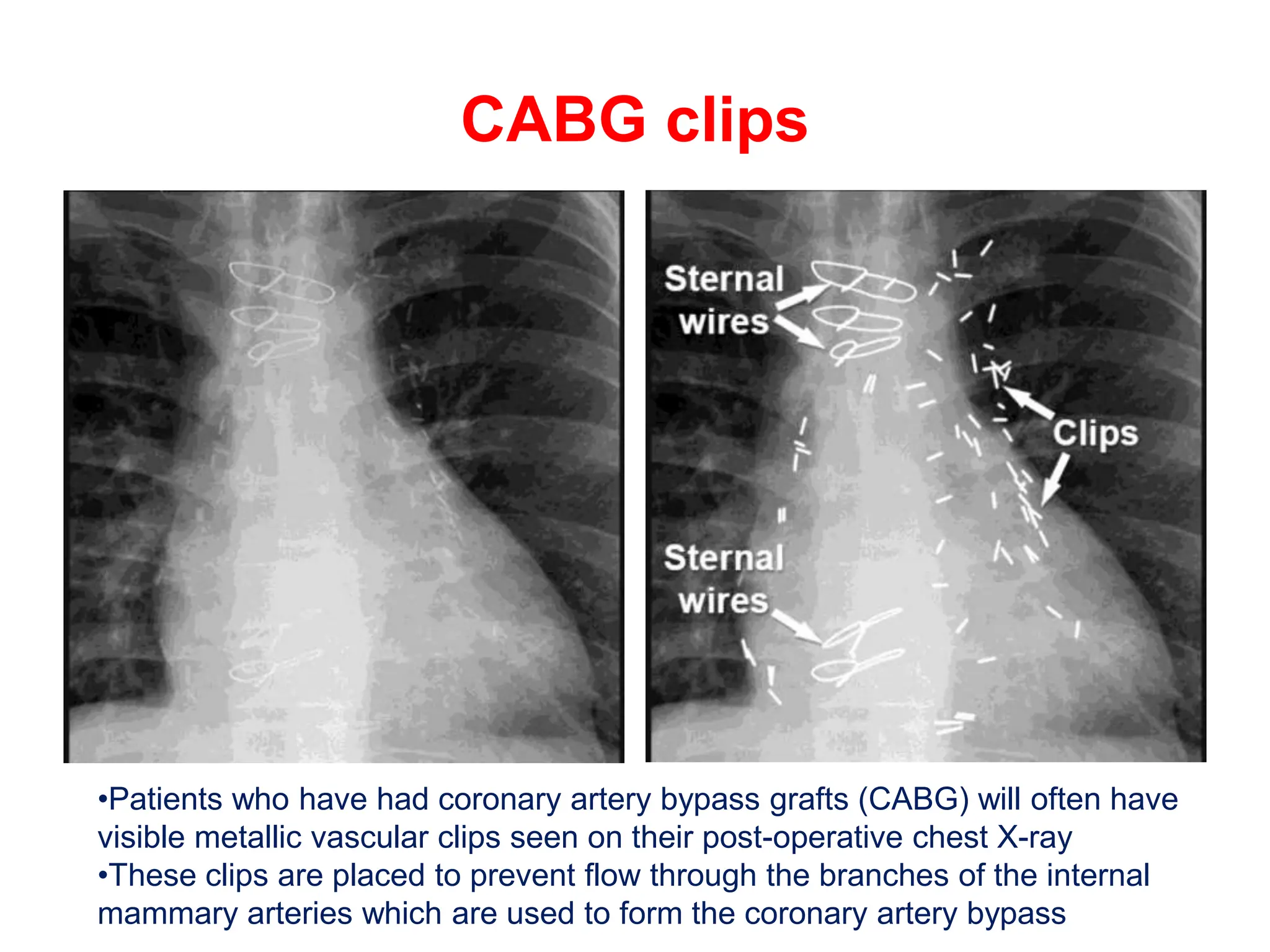
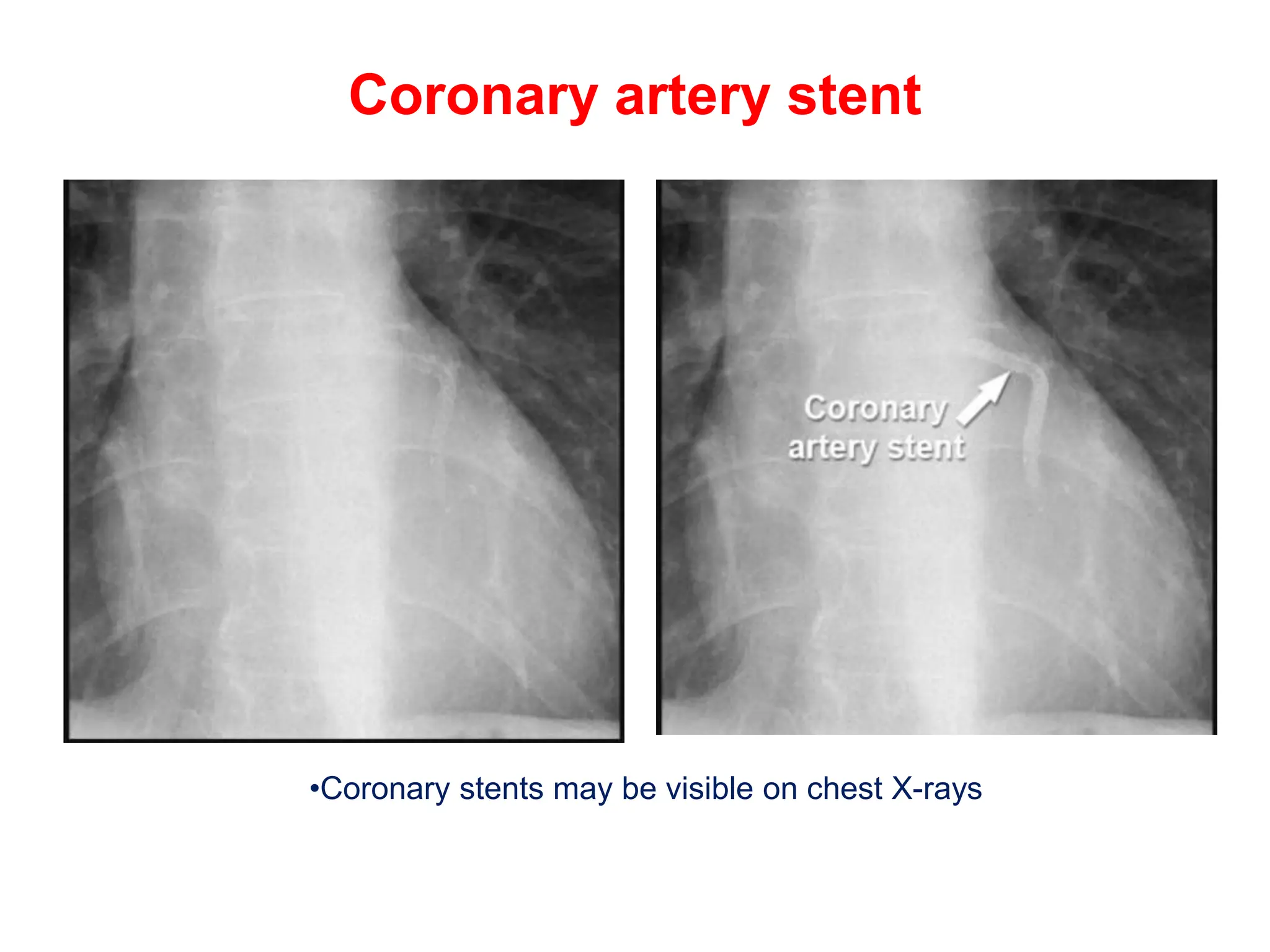
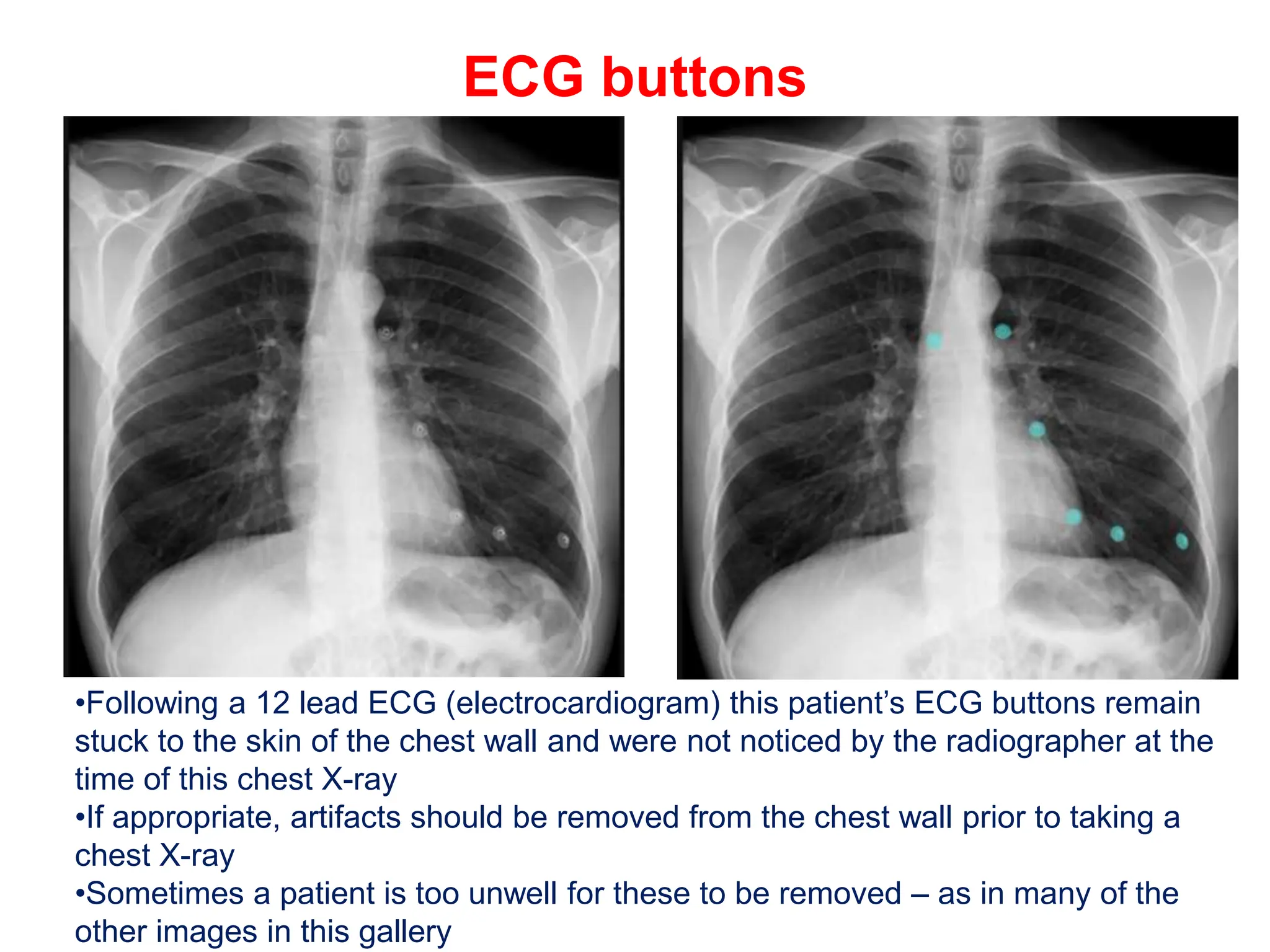
The document provides a comprehensive overview of various chest X-ray findings related to cardiac diseases, including normal and abnormal heart sizes, signs of cardiomegaly, pulmonary edema, and pleural effusions. It details specific indicators such as septal lines and alveolar edema, as well as artifacts from cardiac devices like pacemakers and stents. The document emphasizes the importance of clinical context when interpreting X-ray results, especially concerning heart conditions.