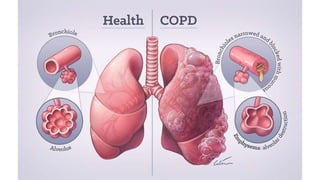
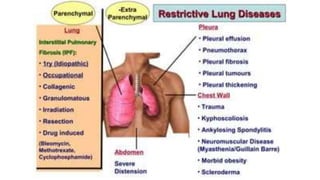
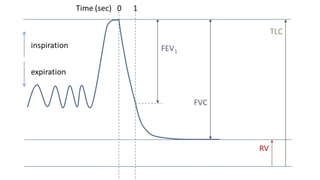
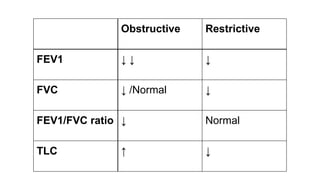
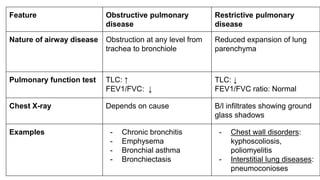
This document discusses the differences between obstructive and restrictive lung diseases. Obstructive lung diseases involve obstruction in the airways from the trachea to the bronchioles, causing increased resistance to airflow. Restrictive lung diseases involve reduced expansion of the lung parenchyma and decreased total lung capacity. Pulmonary function tests can help distinguish the two, as obstructive diseases typically show decreased FEV1 and FVC with increased TLC, while restrictive diseases show decreased FEV1, FVC and TLC with a normal FEV1/FVC ratio. Common examples of each type of disease are also provided.