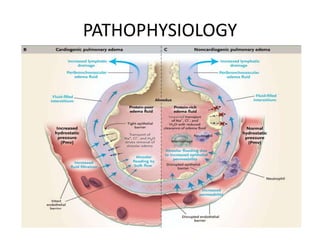
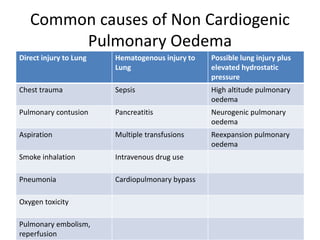
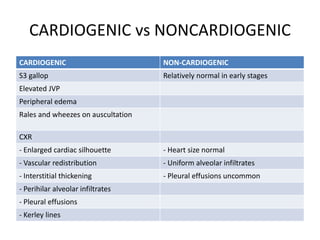
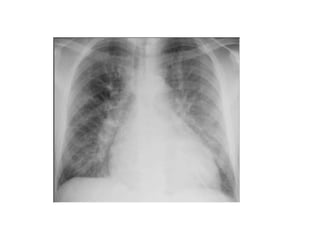
This document provides an overview of pulmonary edema, including its definition, causes, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Pulmonary edema is fluid accumulation in the lungs caused by increased pulmonary capillary pressure or decreased plasma oncotic pressure. It can be cardiogenic or non-cardiogenic in origin. Diagnosis involves physical exam, imaging, and labs. Treatment focuses on oxygen therapy, reducing preload with diuretics and vasodilators, and supporting ventilation if needed. Prognosis depends on severity but mortality can be up to 20% for cardiogenic pulmonary edema.