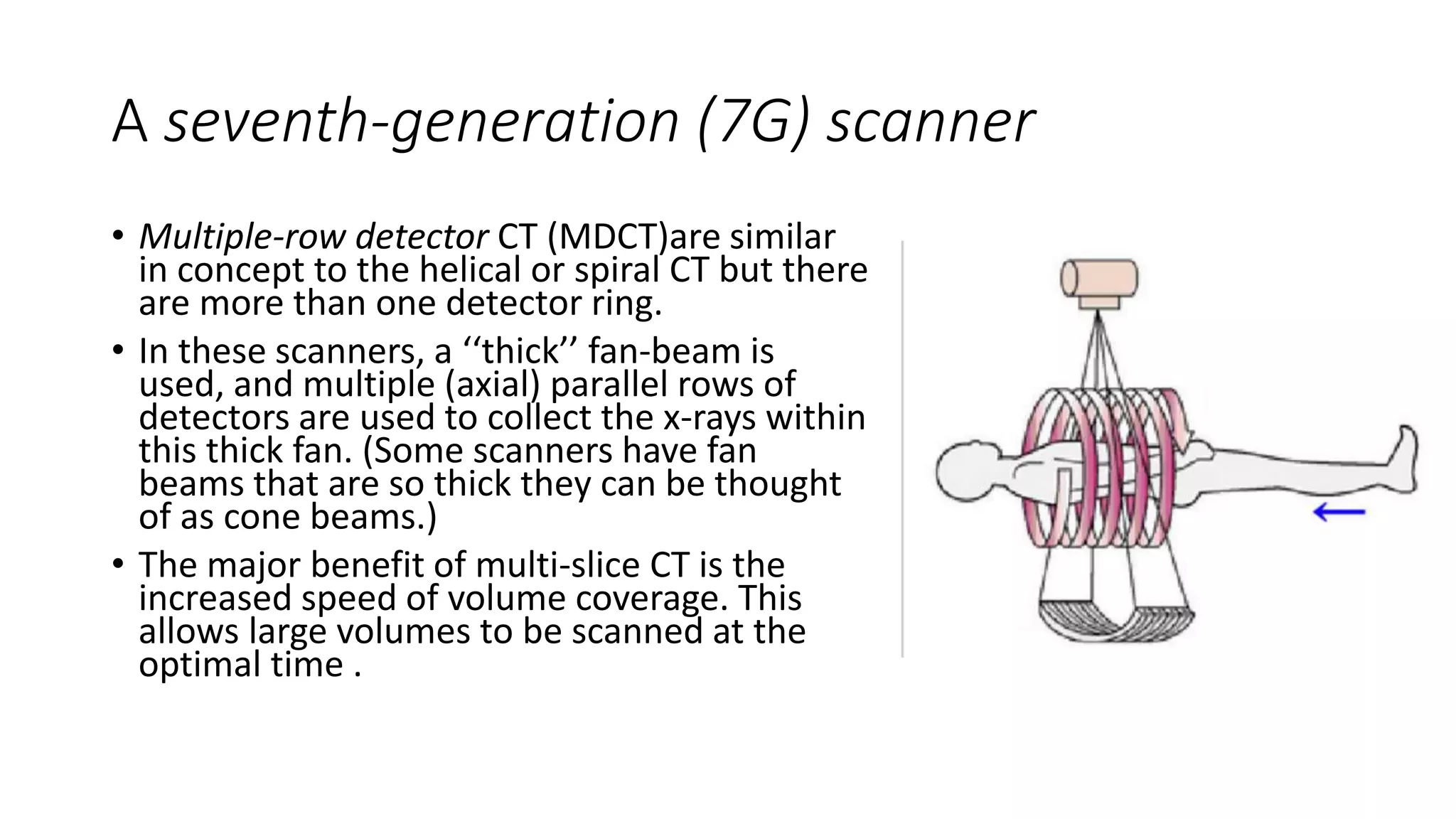
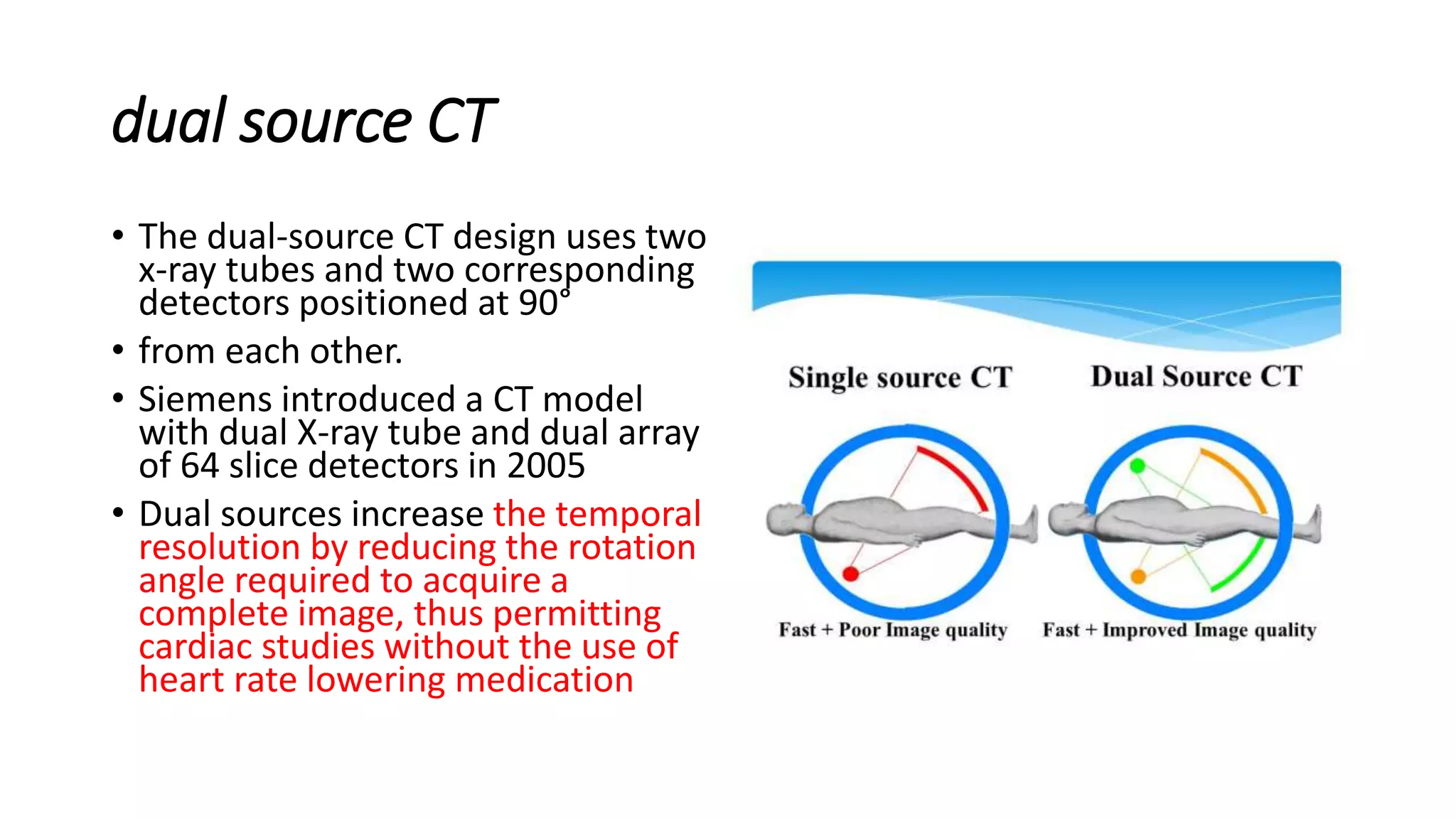
This document provides an overview of computed tomography (CT) technology. It describes the basic components and evolution of CT scanners from first to seventh generation machines. Key points include: CT uses X-rays and computers to produce 3D images of the body's soft tissues and organs. Early scanners moved in a linear path, while newer scanners allow continuous rotation. Detector arrays have expanded from single to multi-row designs for faster image acquisition. Helical and volume scanning allow imaging of entire regions rather than individual slices.