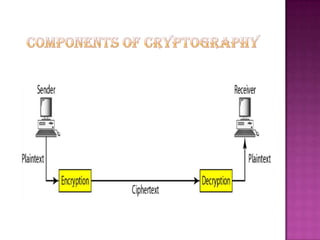
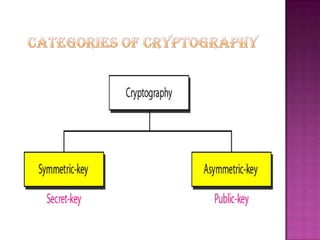
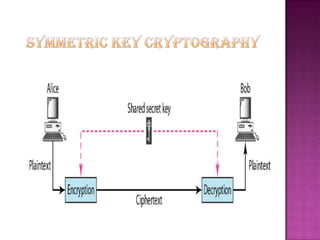
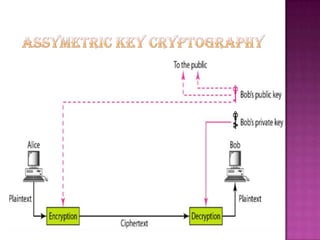
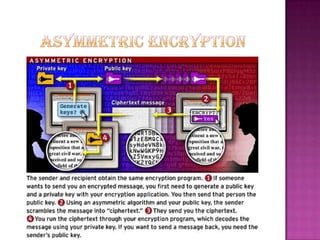
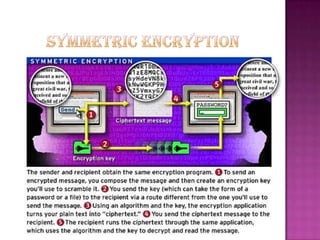
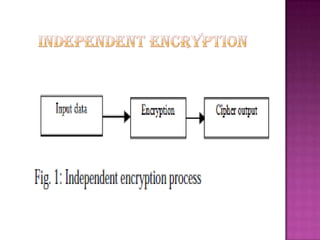
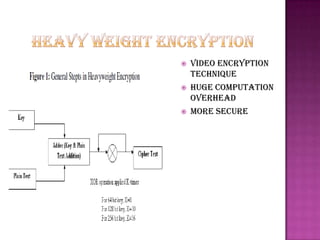
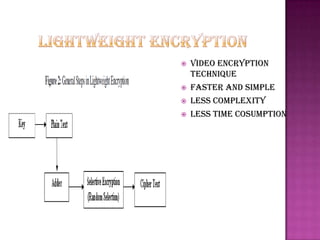
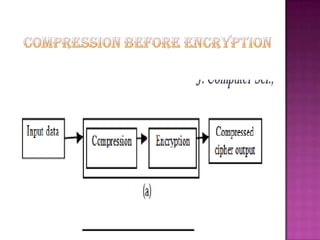
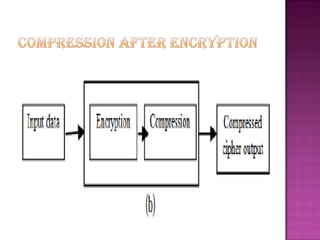
Cryptography is the science of securing information and communication through techniques like encryption. The document discusses various cryptography concepts like encryption algorithms, symmetric and asymmetric key encryption, objectives of cryptography like confidentiality and integrity, and applications of encryption like web browsing, email, and video encryption. It also compares independent encryption with joint compression and encryption techniques for securing video data.