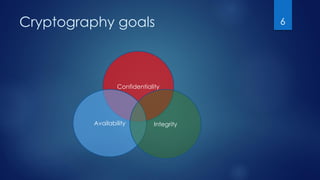
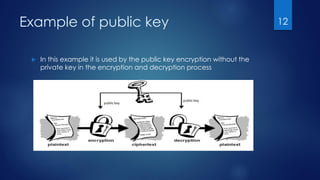
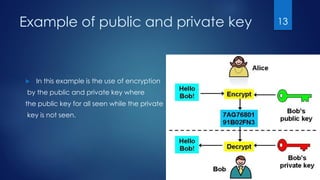
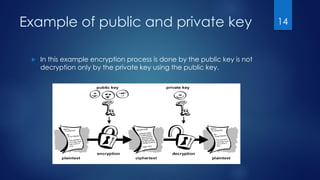
The document serves as an introduction to cryptography, detailing its historical context, definitions, and key goals such as confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It explains the processes of encryption and decryption and highlights the importance of cryptographic keys, distinguishing between public and private keys. The document sets the stage for further discussion on types of encryption in subsequent sections.