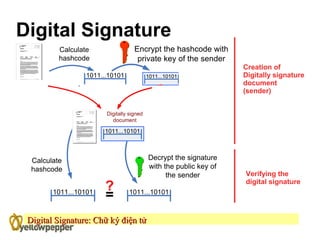
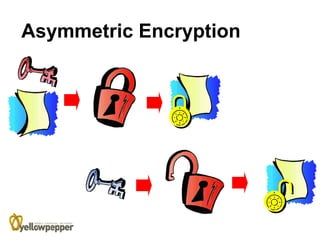
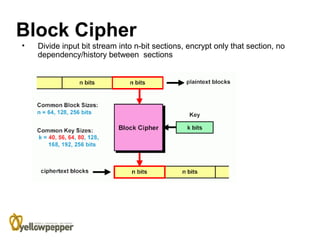
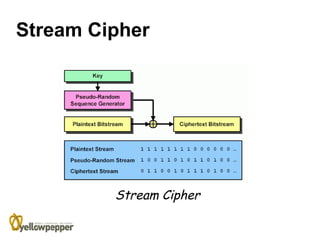
This document provides an overview of cryptography. It begins with background information, defining cryptography as using mathematics to encrypt and decrypt data to enable secure transmission. The main purposes of cryptography are then outlined as authentication, privacy/confidentiality, integrity, and non-repudiation. The methodology section describes symmetric and asymmetric encryption methods. Symmetric encryption uses the same key for encryption and decryption while asymmetric uses mathematically related public/private key pairs. Specific symmetric algorithms like block and stream ciphers are then defined along with concepts like padding schemes. The document concludes with sections on key exchange and digital signatures, which enable practical uses of cryptography.














![Code Example
TDES ENCRYPTION:
public string SimpleTripleDes(string Data)
{
byte[] key = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("passwordDR0wSS@P6660juht");
byte[] iv = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("password");
byte[] data = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(Data);
byte[] enc = new byte[0];
TripleDES tdes = TripleDES.Create();
tdes.IV = iv;
tdes.Key = key;
tdes.Mode = CipherMode.CBC;
tdes.Padding = PaddingMode.PKCS7;
ICryptoTransform ict = tdes.CreateEncryptor();
enc = ict.TransformFinalBlock(data, 0, data.Length);
return ByteArrayToString(enc);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cryptographyv1-1-121024044551-phpapp01/85/Cryptography-Fundamentals-20-320.jpg)
![Code Example
AES ENCRYPTION:
public static string EncryptData( byte[] plainText , byte[] keyBytes )
{
RijndaelManaged rijndaelCipher = new RijndaelManaged();
rijndaelCipher.Mode = CipherMode.CBC;
rijndaelCipher.Padding = PaddingMode.PKCS7;
rijndaelCipher.KeySize = 128;
rijndaelCipher.BlockSize = 128;
rijndaelCipher.Key = keyBytes;
rijndaelCipher.IV = keyBytes;
ICryptoTransform transform = rijndaelCipher.CreateEncryptor();
byte[] cipherBytes = transform.TransformFinalBlock(plainText, 0, plainText.Length);
return Convert.ToBase64String(cipherBytes);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cryptographyv1-1-121024044551-phpapp01/85/Cryptography-Fundamentals-21-320.jpg)





![Code Example
MD5 ENCRYPTION:
public string CalculateMD5Hash(string input) {
// step 1, calculate MD5 hash from input
MD5 md5 = System.Security.Cryptography.MD5.Create();
byte[] inputBytes = System.Text.Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(input);
byte[] hash = md5.ComputeHash(inputBytes);
// step 2, convert byte array to hex string
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < hash.Length; i++) {
sb.Append(hash[i].ToString("X2"));
}
return sb.ToString();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cryptographyv1-1-121024044551-phpapp01/85/Cryptography-Fundamentals-28-320.jpg)