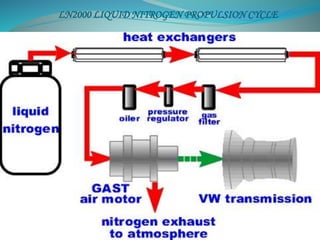
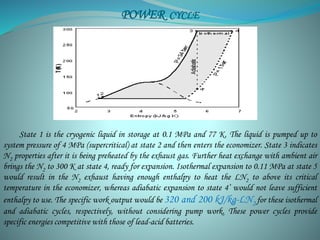
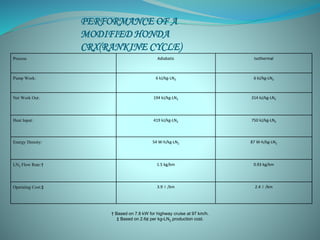
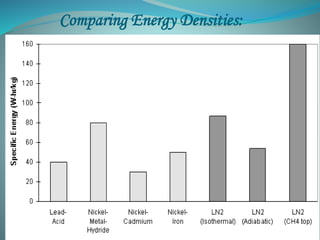
This document presents the CryoCar, which utilizes liquid nitrogen in an open Rankine cycle for automotive propulsion. Liquid nitrogen offers advantages over batteries in performance and cost. The system works like a steam engine, using a heat exchanger to boil liquid nitrogen which is then expanded in an engine to produce power. Analysis shows the liquid nitrogen cycle can provide competitive specific energies to lead-acid batteries. A modified Honda CRX using the liquid nitrogen cycle could achieve an energy density of 54-87 W-h/kg of nitrogen with a operating cost of $0.039-0.024 per km. The document concludes liquid nitrogen propulsion warrants further consideration due to advantages in refueling time compared to batteries.