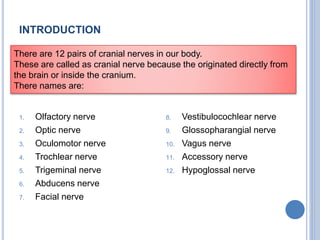
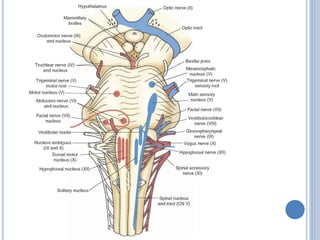
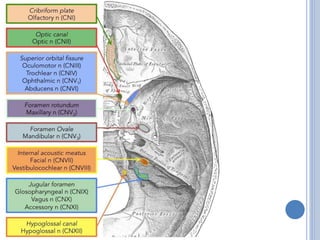
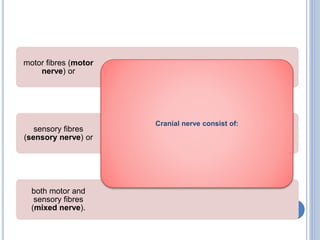
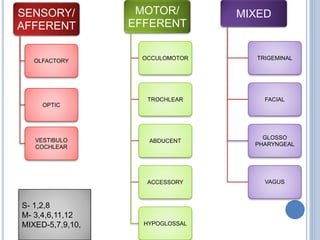
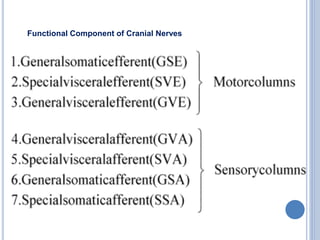
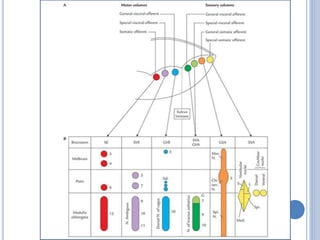
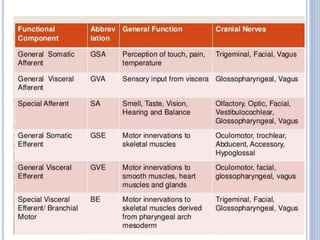
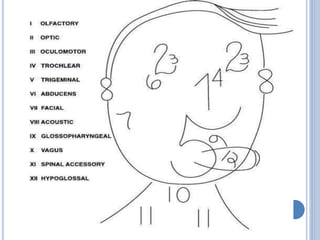
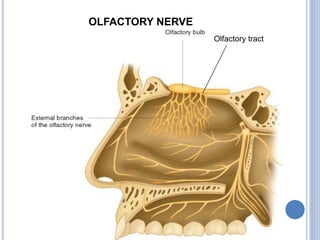
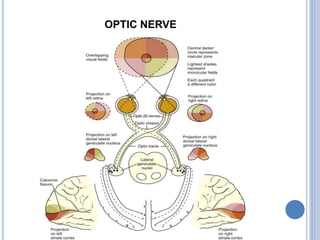
There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves that originate directly from the brain or inside the cranium. The first two cranial nerves, the olfactory and optic nerves, originate from the forebrain. Cranial nerves 3 through 12 arise from the brainstem, with nerves 3-4 originating from the midbrain, nerves 5-8 from the pons, and nerves 9-12 from the medulla oblongata. The cranial nerves consist of sensory nerves, motor nerves, or mixed nerves and are involved with functions like vision, facial movements, hearing, balance, taste, and internal organ control.