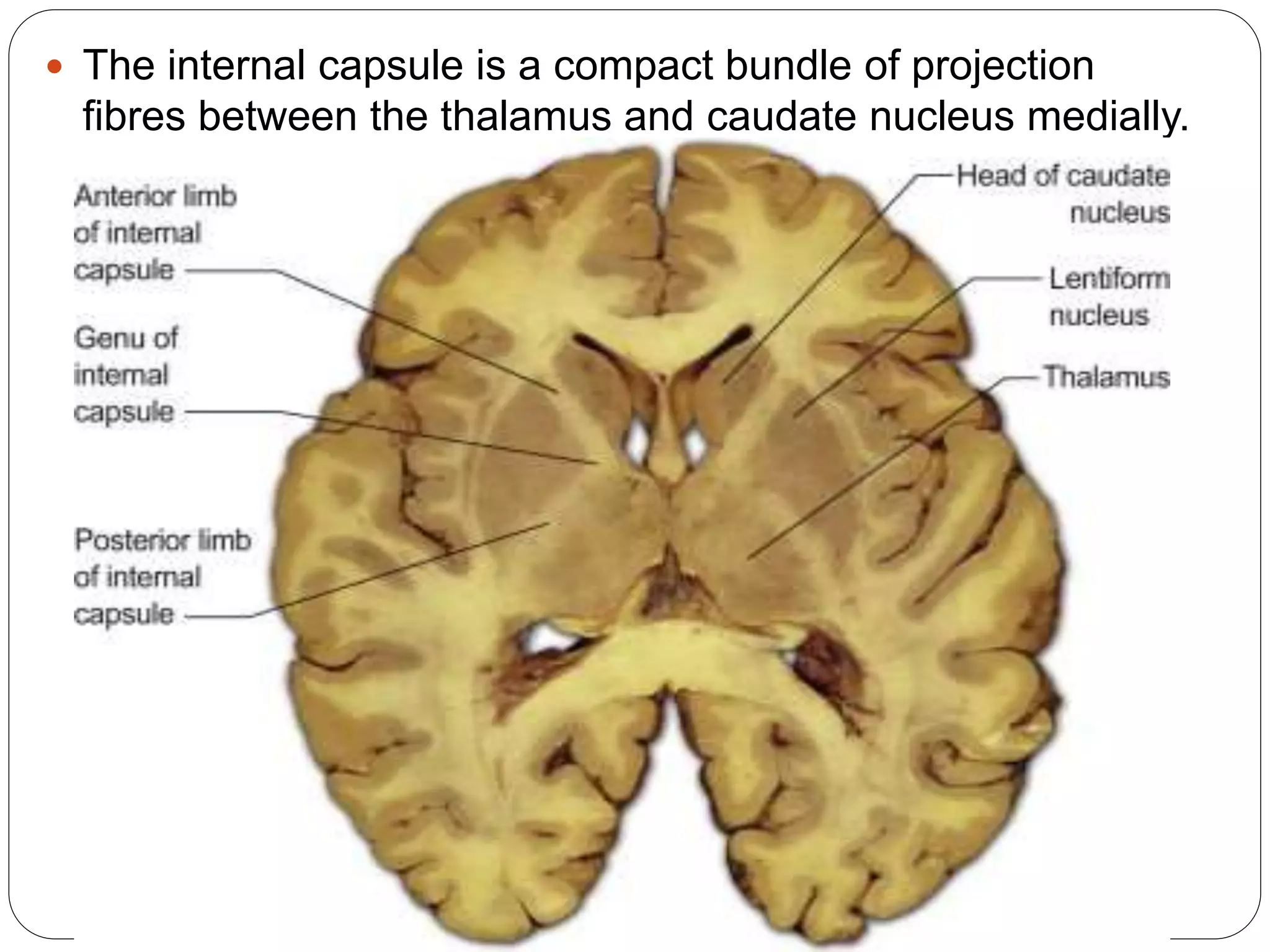
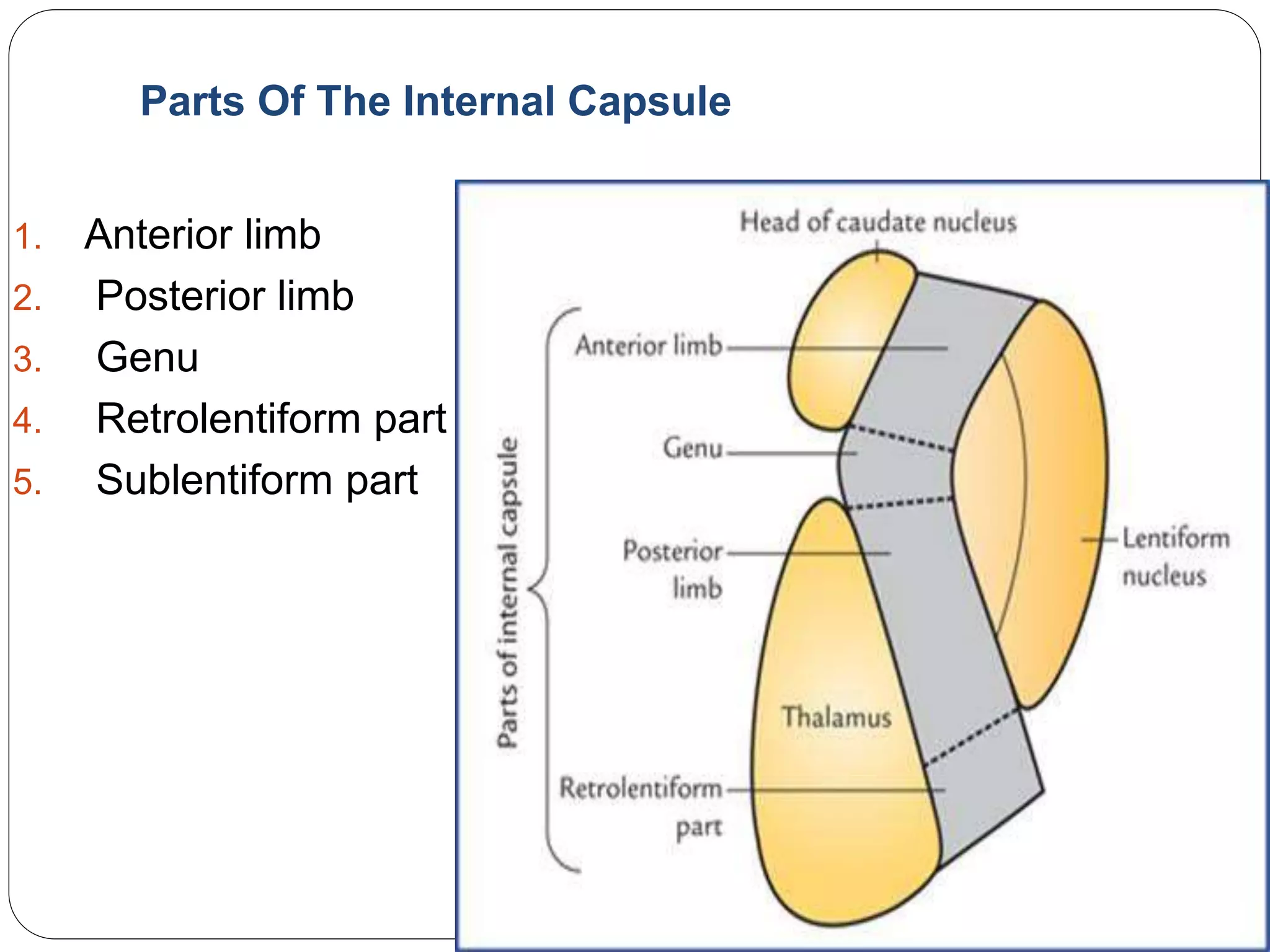
The internal capsule is a bundle of fibres between the thalamus and caudate nucleus medially, and the lentiform nucleus laterally. It contains motor and sensory fibres connecting the cerebral cortex with the brainstem and spinal cord. Damage to the internal capsule from hemorrhage or infarction can cause spastic paralysis on the opposite side of the body due to disruption of these fibre tracts. The most common cause is rupture of the artery of cerebral hemorrhage, which supplies the posterior limb of the internal capsule.