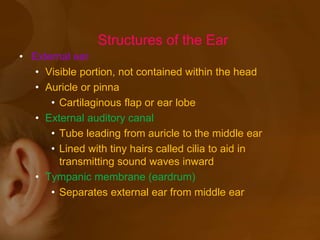
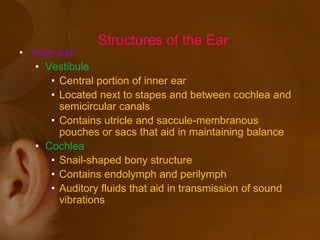
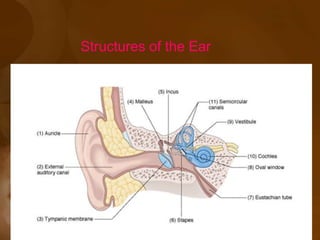
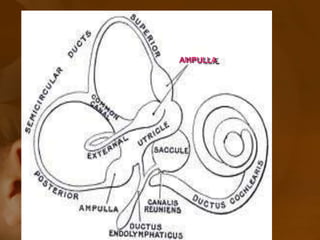
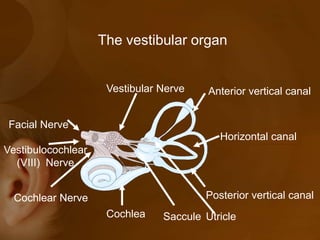
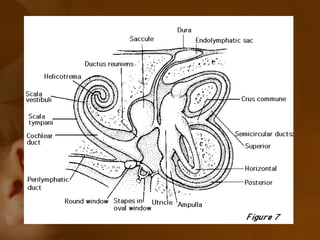
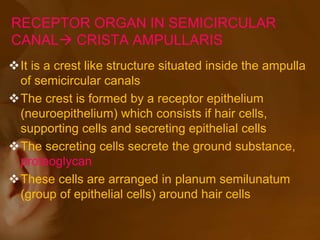
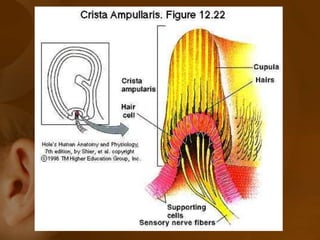
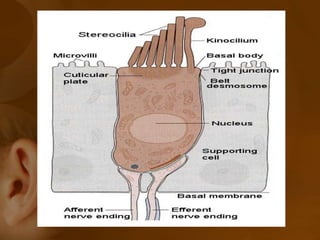
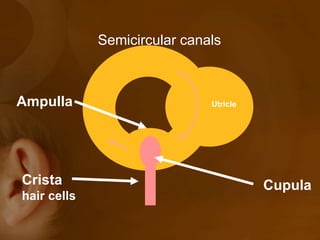
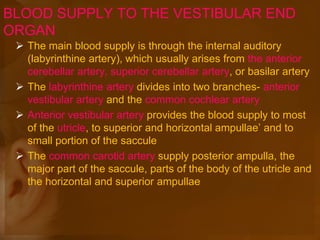
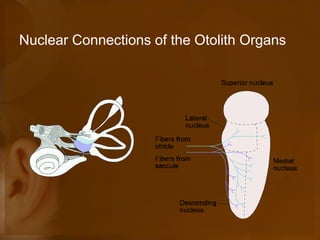
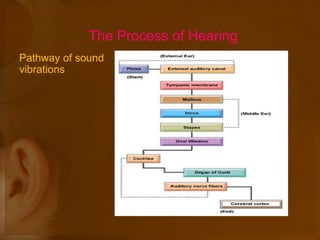
The document discusses the vestibular apparatus, which is part of the inner ear and functions as a sensory organ for balance and equilibrium. It contains three semicircular canals oriented at right angles to detect rotational movement, as well as the utricle and saccule which contain the maculae and detect linear acceleration. Hair cells within the crista ampullaris of the semicircular canals and within the maculae transmit signals about movement and acceleration to the brainstem via the vestibular nerve. The vestibular nuclei integrate this sensory information and coordinate motor responses to maintain balance and posture.