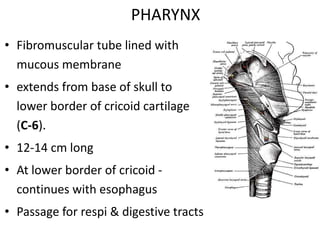
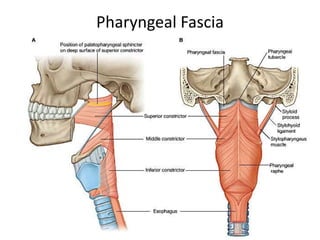
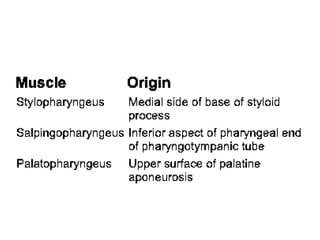
1. A 33-year-old woman presented with a foreign body sensation in her throat for two days. Upon examination, an orange seed was found embedded in her piriform fossa.
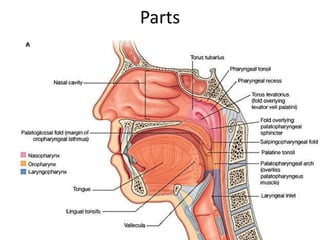
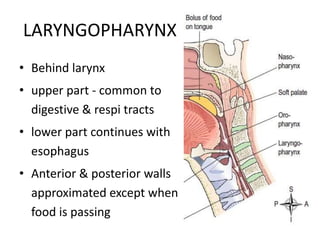
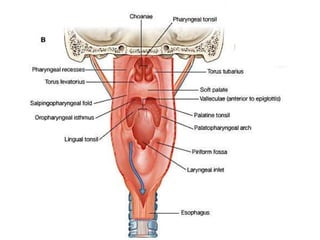
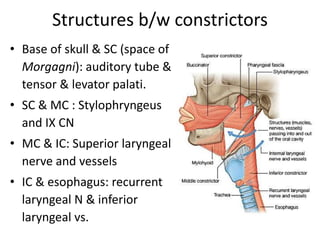
2. The piriform fossa is located on the anterior wall of the laryngopharynx. When removing the orange seed, precautions must be taken due to the location and structures in the area such as the epiglottis and aryepiglottic folds.
3. Careful and gentle removal of the embedded seed is needed to avoid damaging local structures like the vocal cords or triggering a gag reflex.