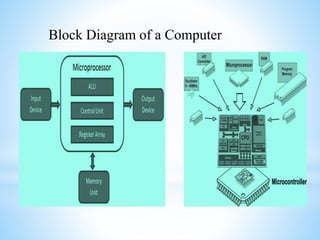
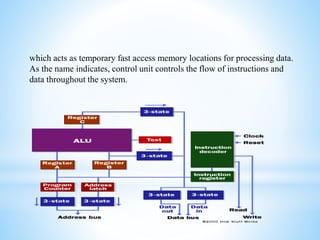
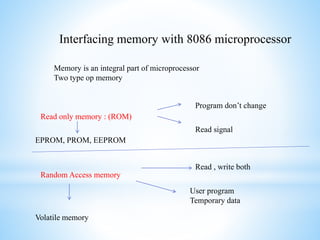
This presentation provides an introduction to microprocessors. It defines a microprocessor as an integrated circuit that incorporates the core functions of a computer's central processing unit. The presentation discusses how a microprocessor works, including that it consists of an arithmetic logic unit, control unit, and register array. Advantages of microprocessors are listed as low cost, high speed, small size, versatility, low power consumption, reliability, and portability. Examples of important microprocessors are provided, from early models like the Intel 4004 to current processors like the Intel Core i7. Memory interfacing and the functions of the timing and control unit are also summarized.