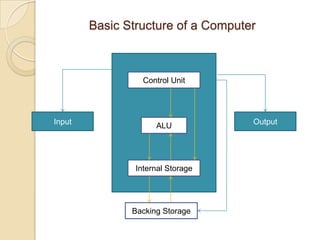
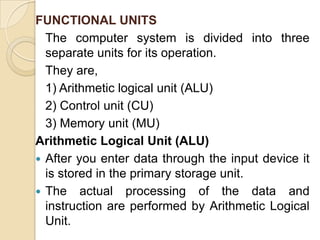
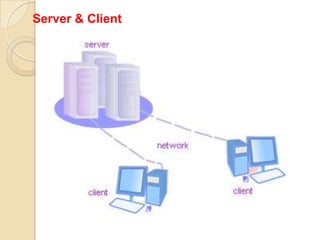
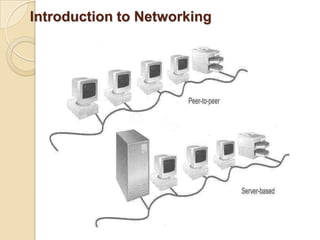
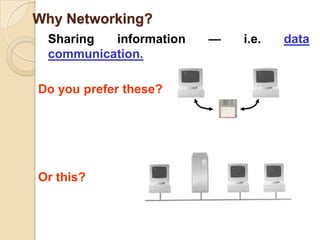
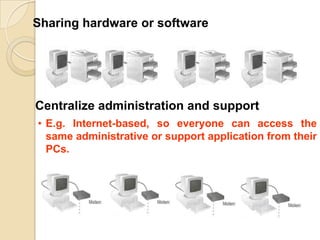
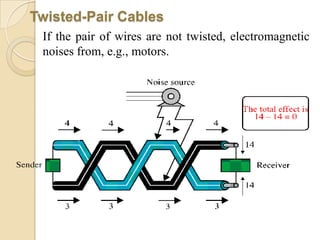
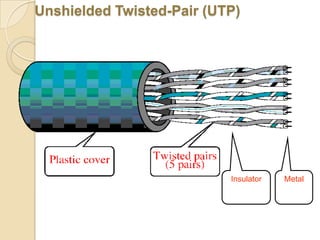
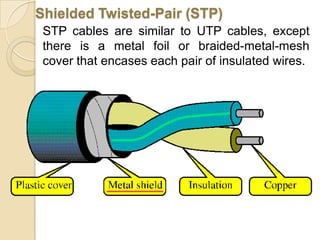
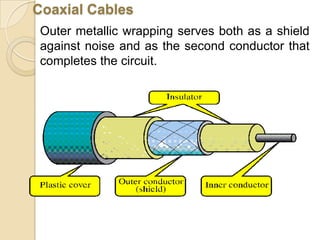
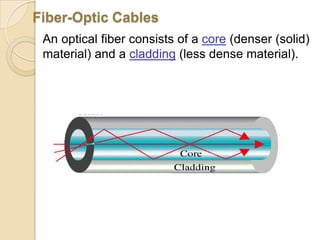
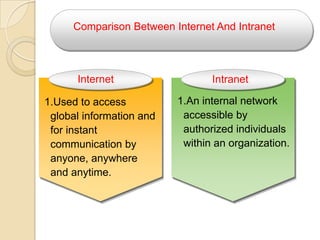
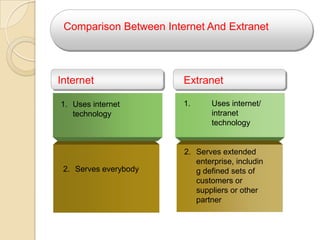
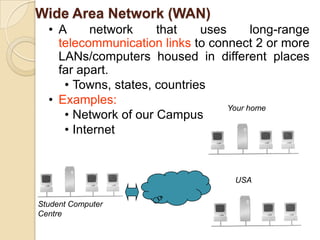
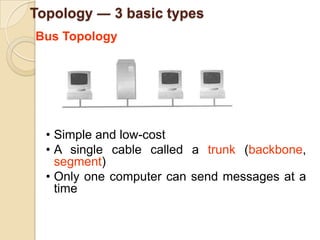
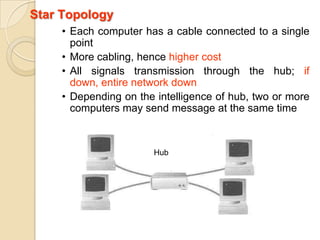
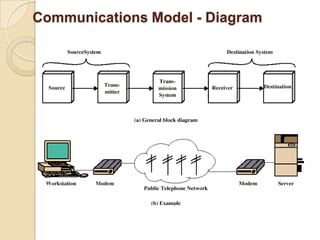
The document provides an overview of principles of information technology. It discusses what IT is and its role in economic and social development. It also covers the rapid evolution of IT and benefits in areas like education, healthcare, and government efficiency. The document then discusses basic computer concepts including hardware components, data organization, number systems, and storage capacities. It covers computer generations from first to fifth generation and concludes with an introduction to networking, discussing different network types, transmission media, and examples of internet, intranet, and extranet networks.