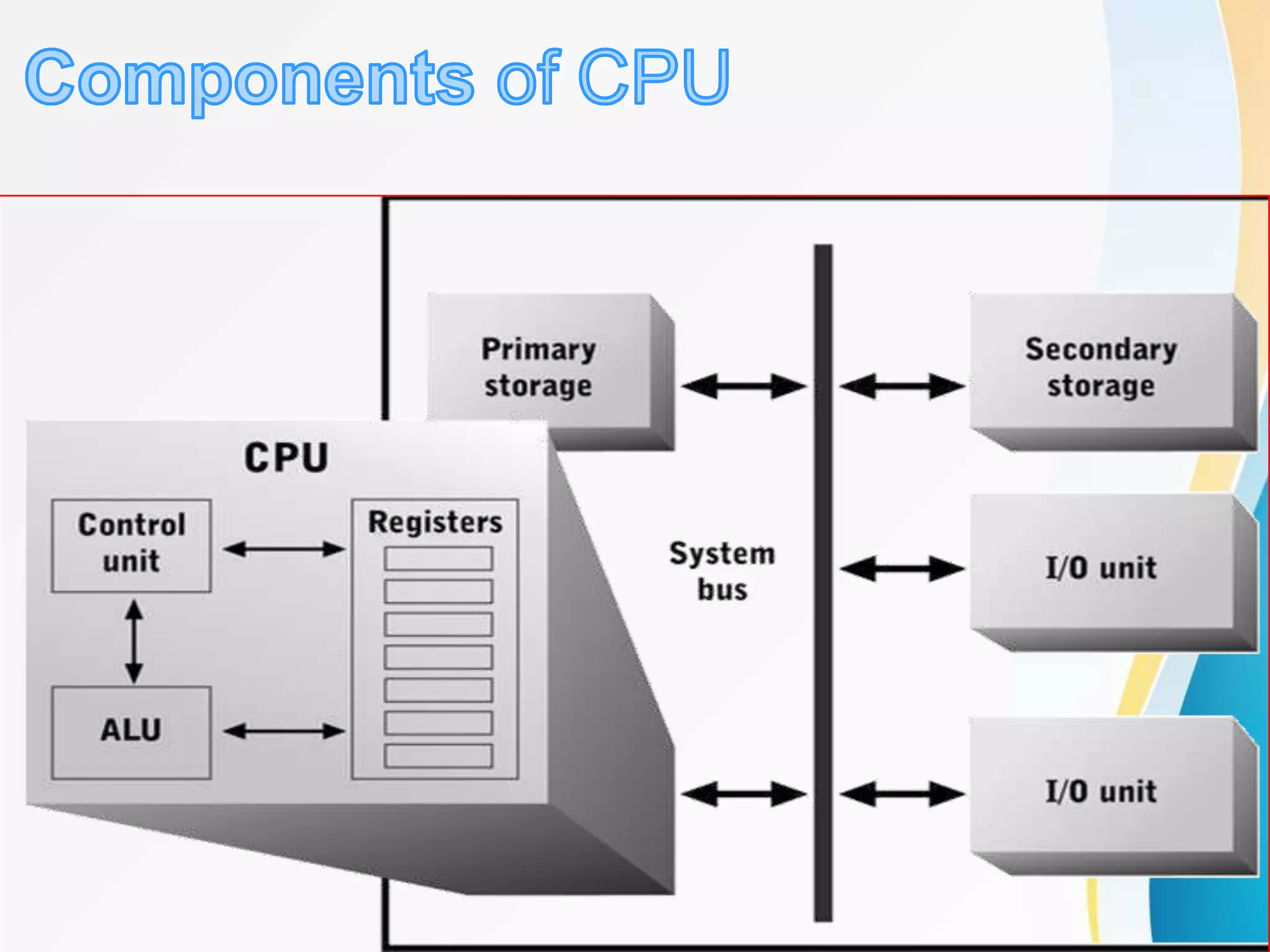
The document discusses the central processing unit (CPU) and its components. It describes the CPU as the brain of the computer that carries out instructions. The key components of the CPU are the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) for calculations, control unit for managing instruction fetching and execution, and registers for temporary storage. The document also discusses the fetch-decode-execute cycle of instruction processing and different types of processors, storage devices, and the basic input/output system (BIOS) that initializes hardware during startup.