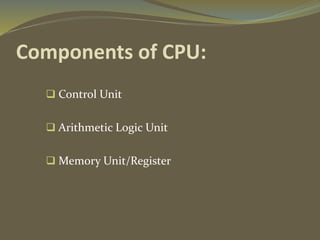
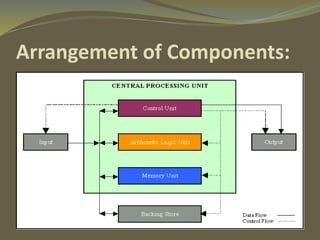
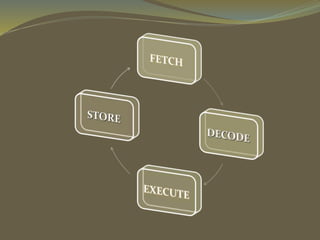
The document discusses the history and components of the CPU. It notes that the CPU was invented in the 1940s and evolved from room-sized mainframes in the 1970s to microchips. The CPU contains a control unit to direct operations, an arithmetic logic unit to perform calculations, and memory/registers to store data and instructions. It fetches instructions from memory, decodes them, executes the calculations or functions, and stores the results.