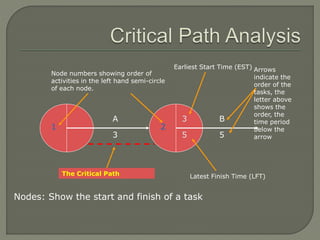
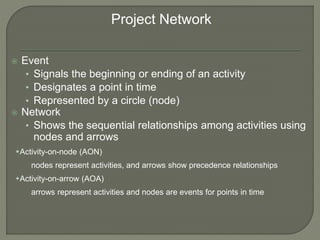
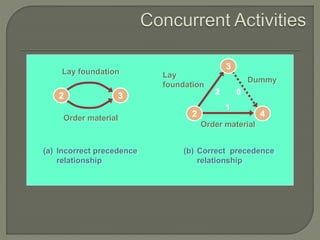
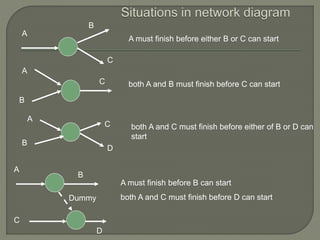
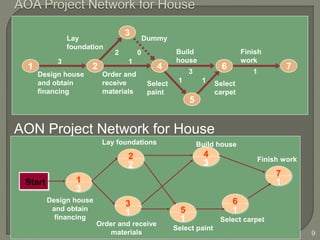
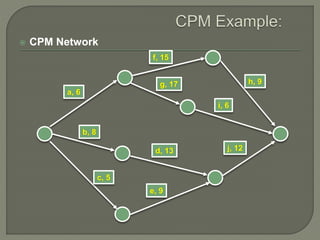
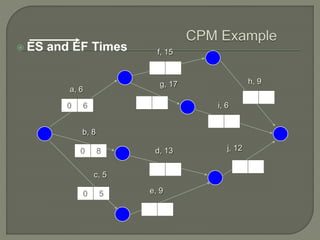
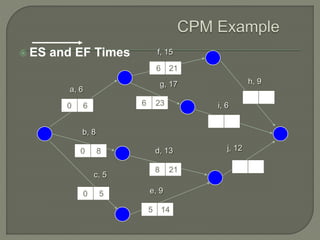
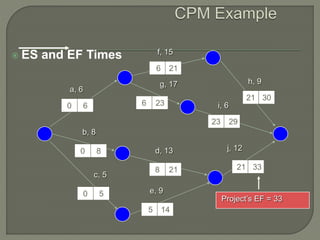
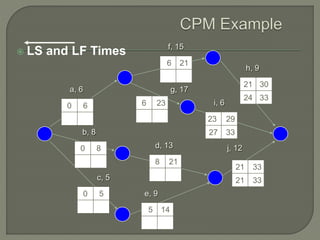
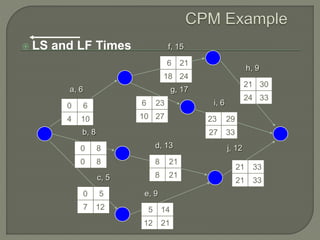
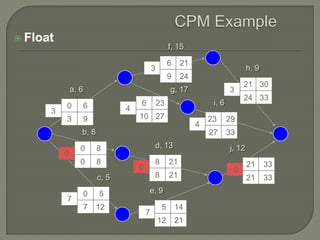
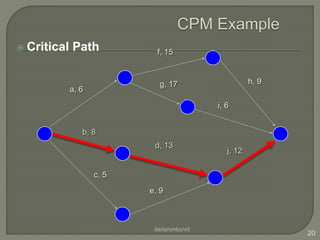
The document discusses critical path method (CPM) network analysis for project planning. CPM was developed in 1957 to plan construction and maintenance projects. It involves identifying all tasks, durations, dependencies and calculating earliest and latest start/finish times to determine the critical path that dictates the project duration. An example CPM network is provided and analyzed to identify the critical path.