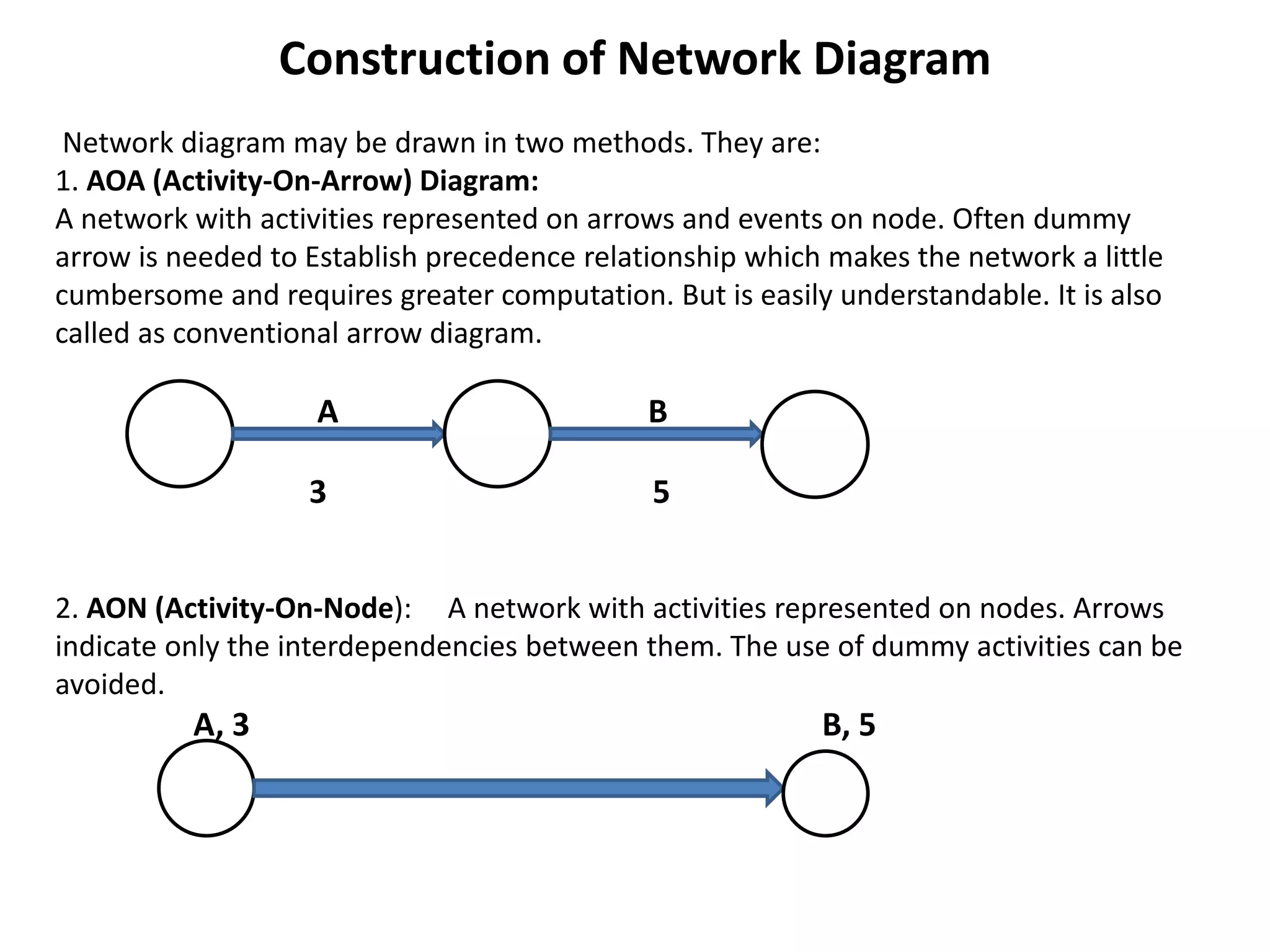
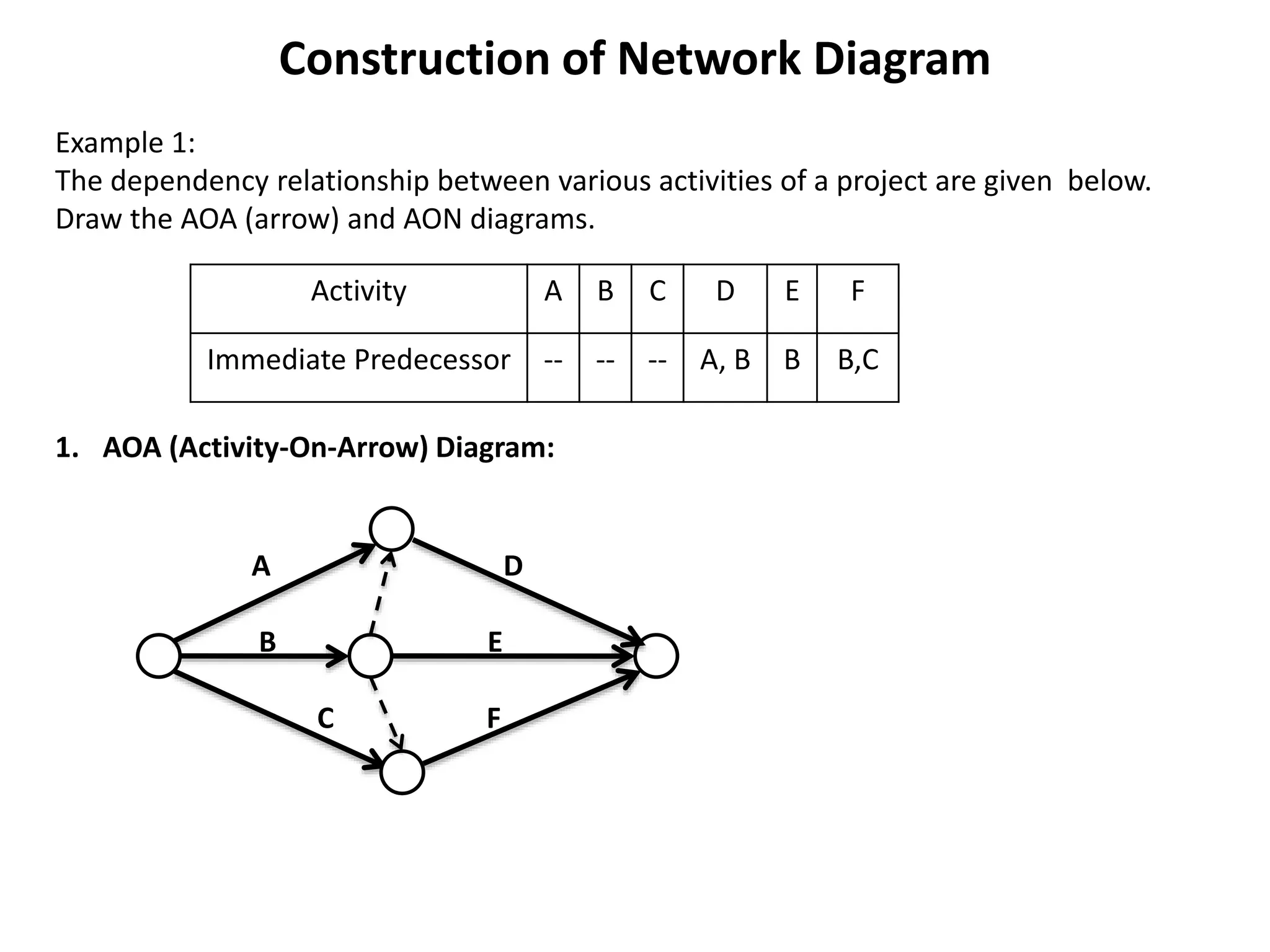
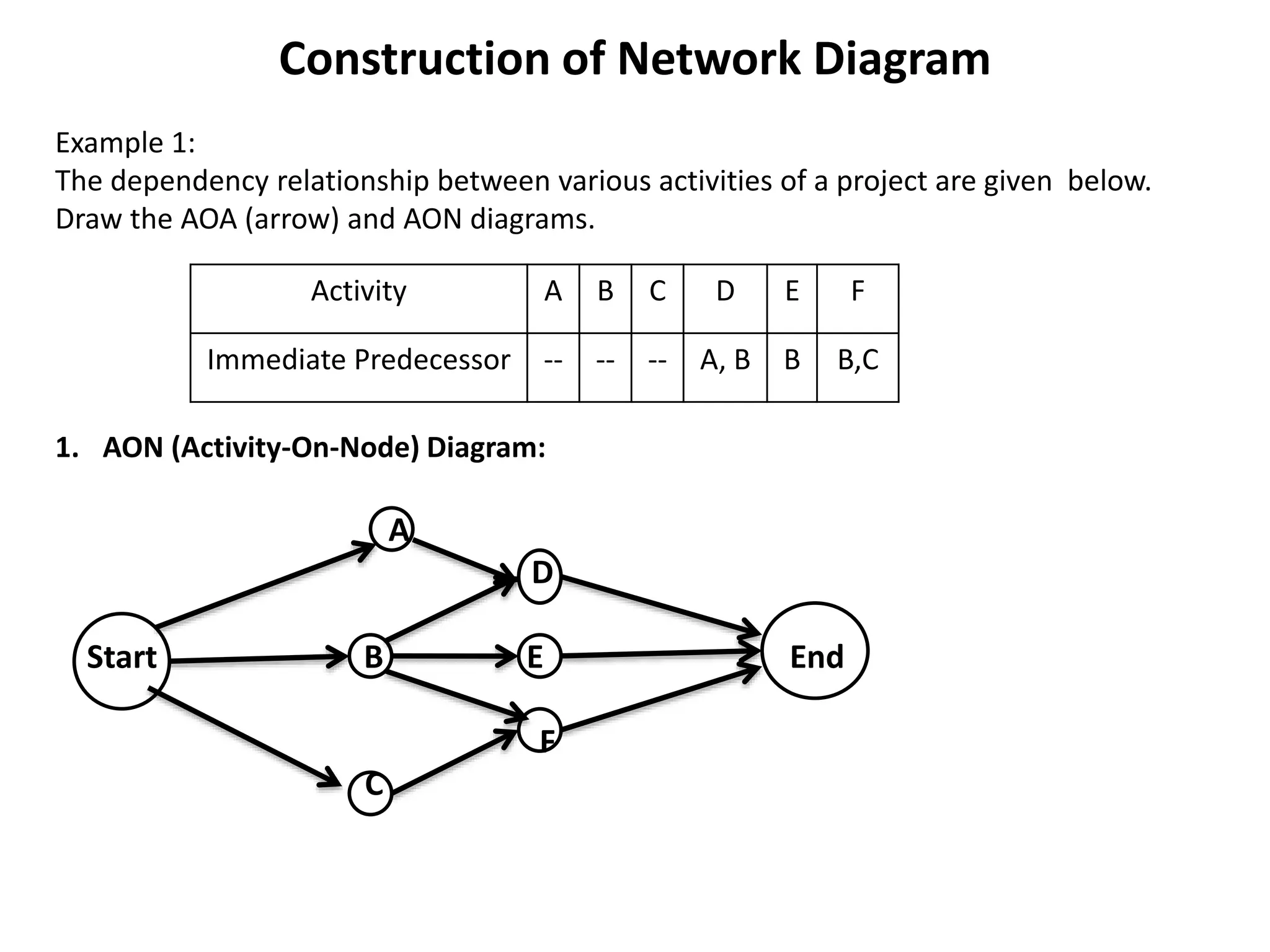
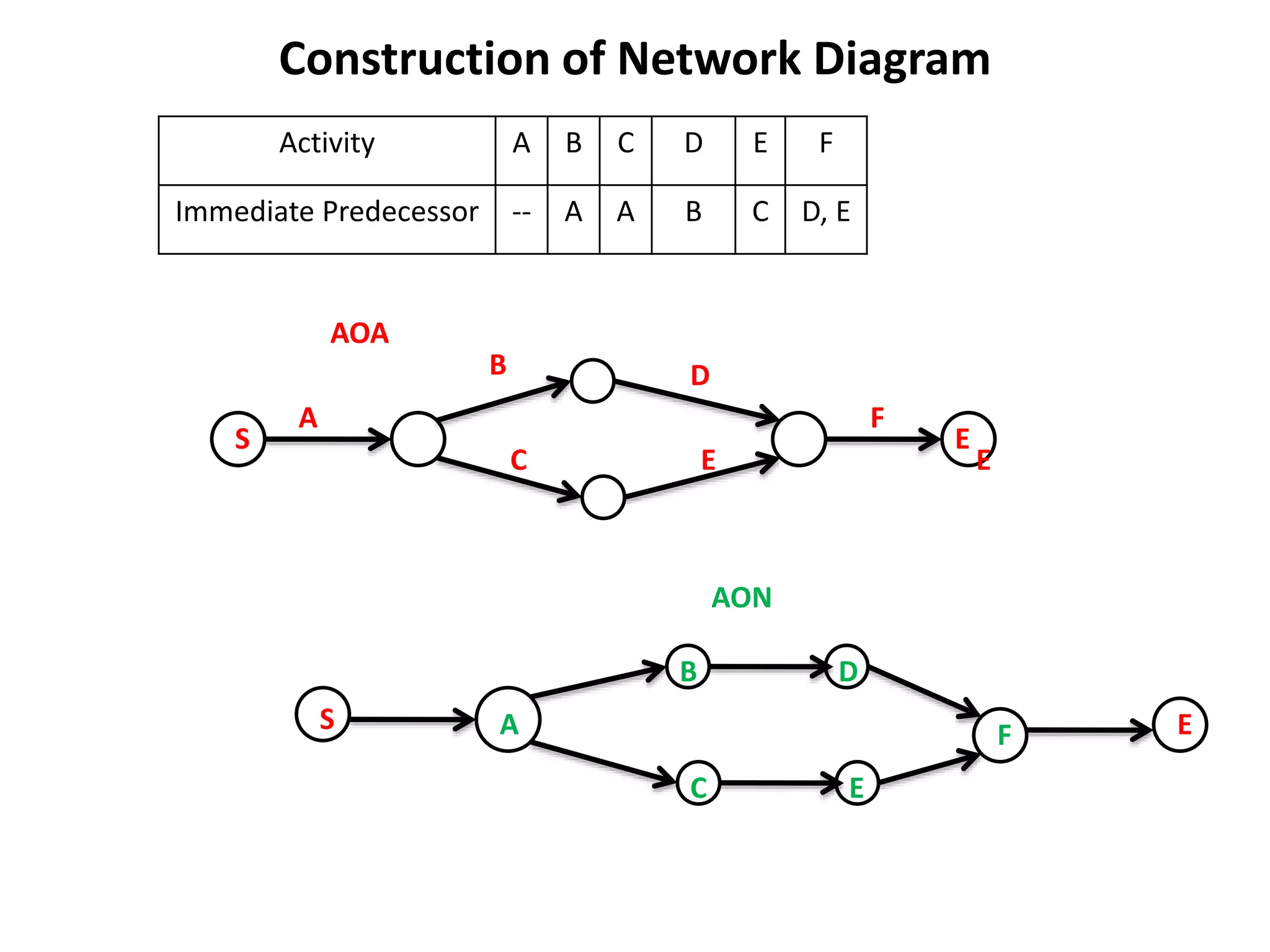
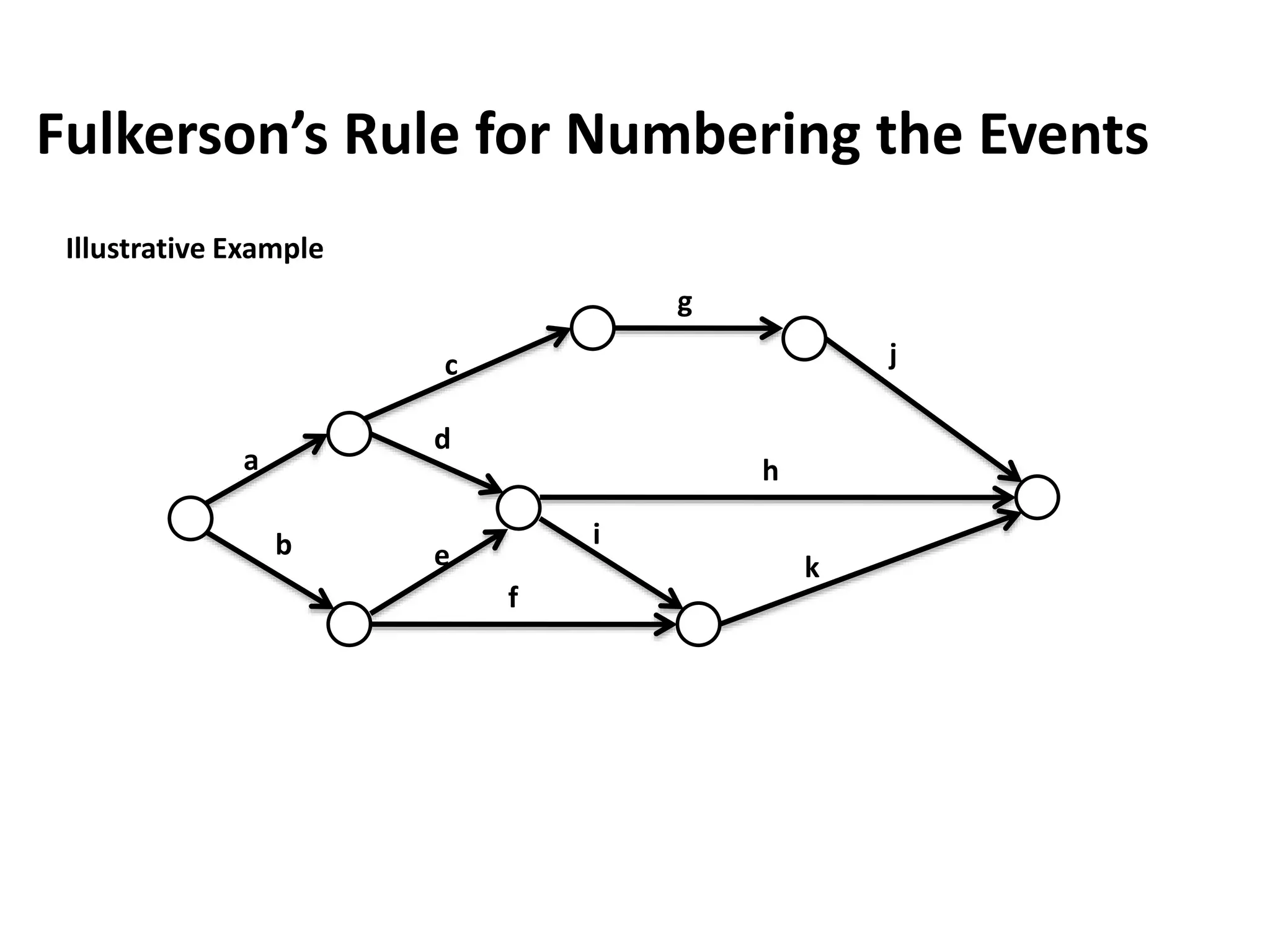
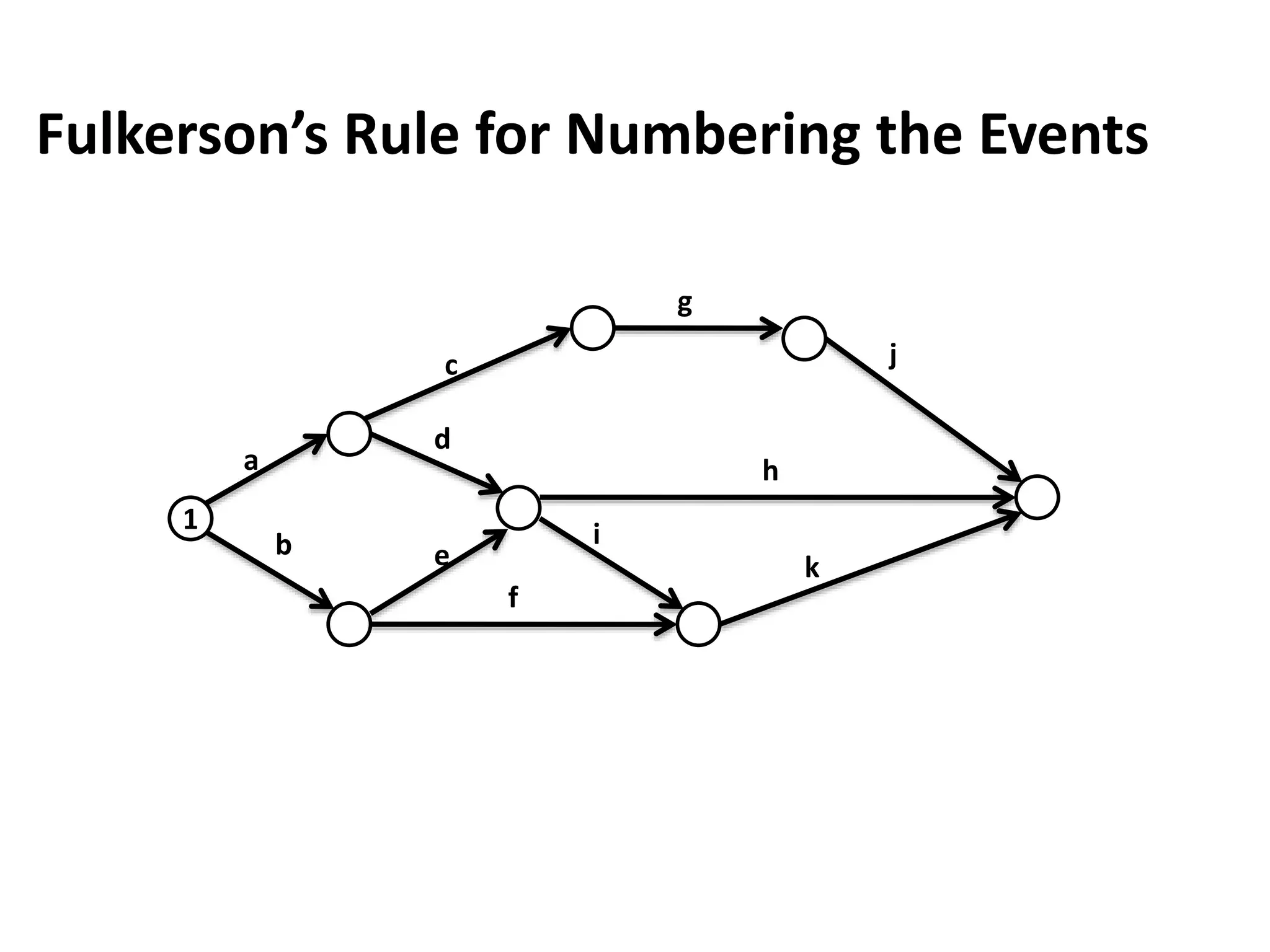
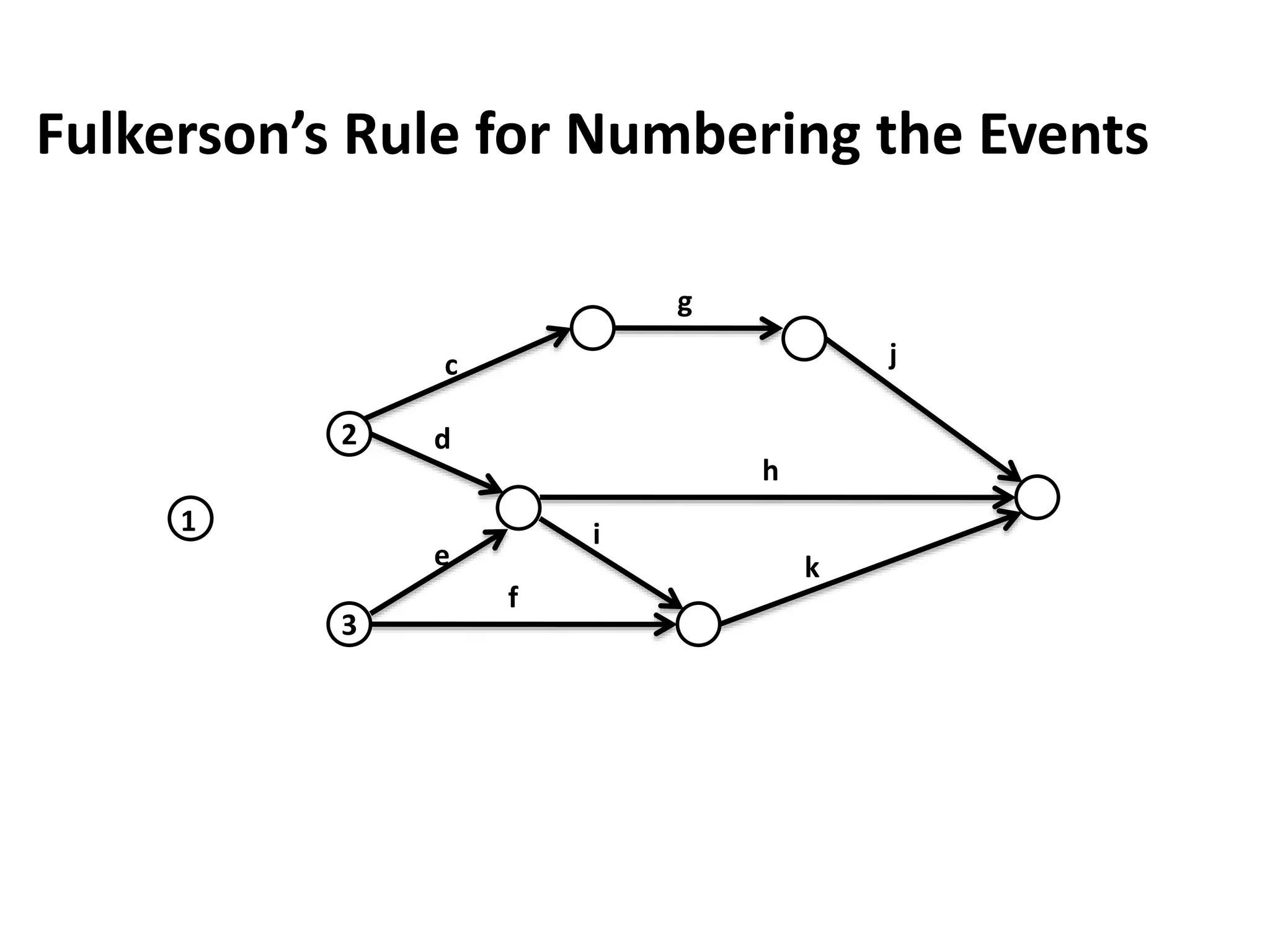
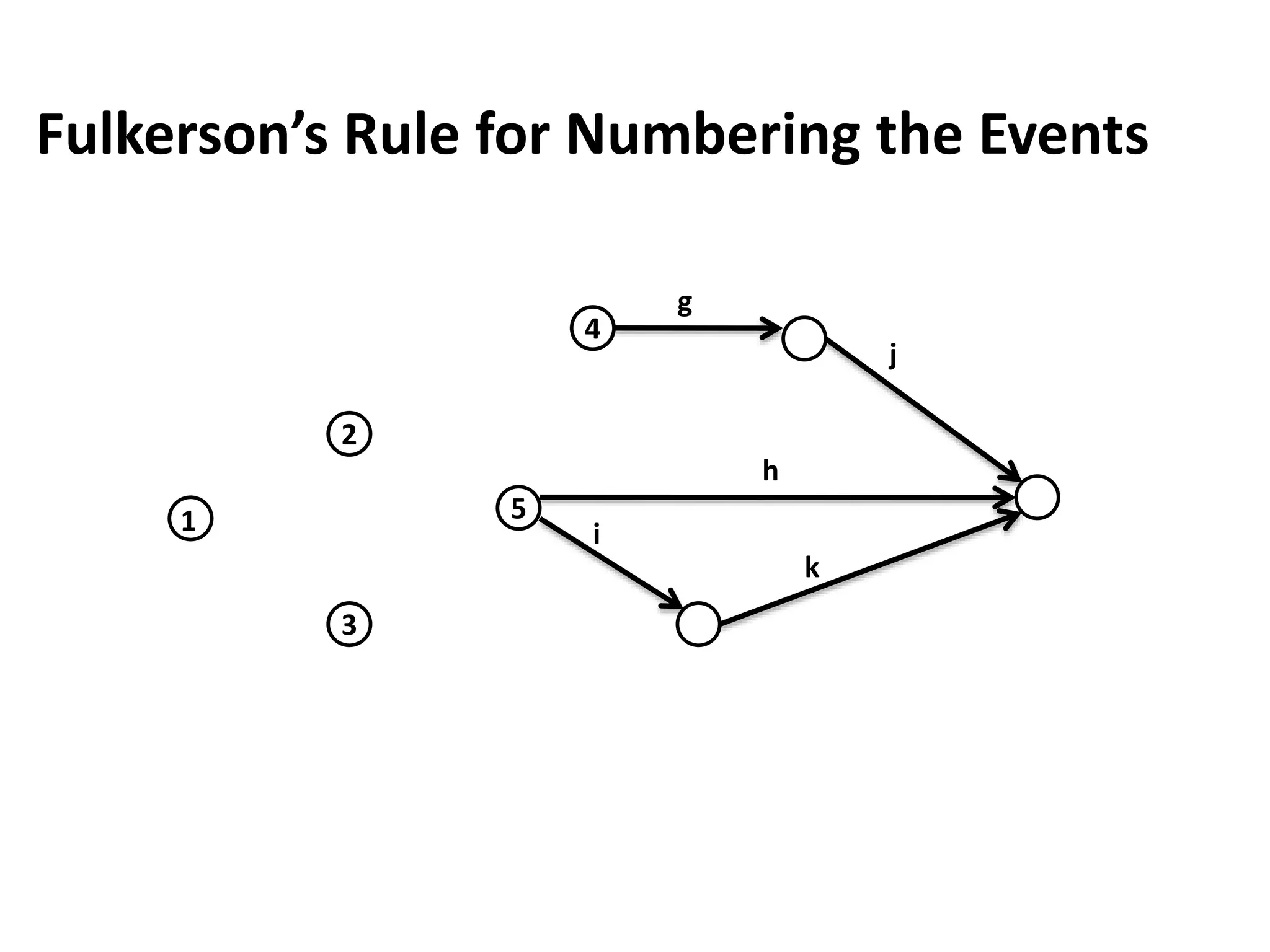
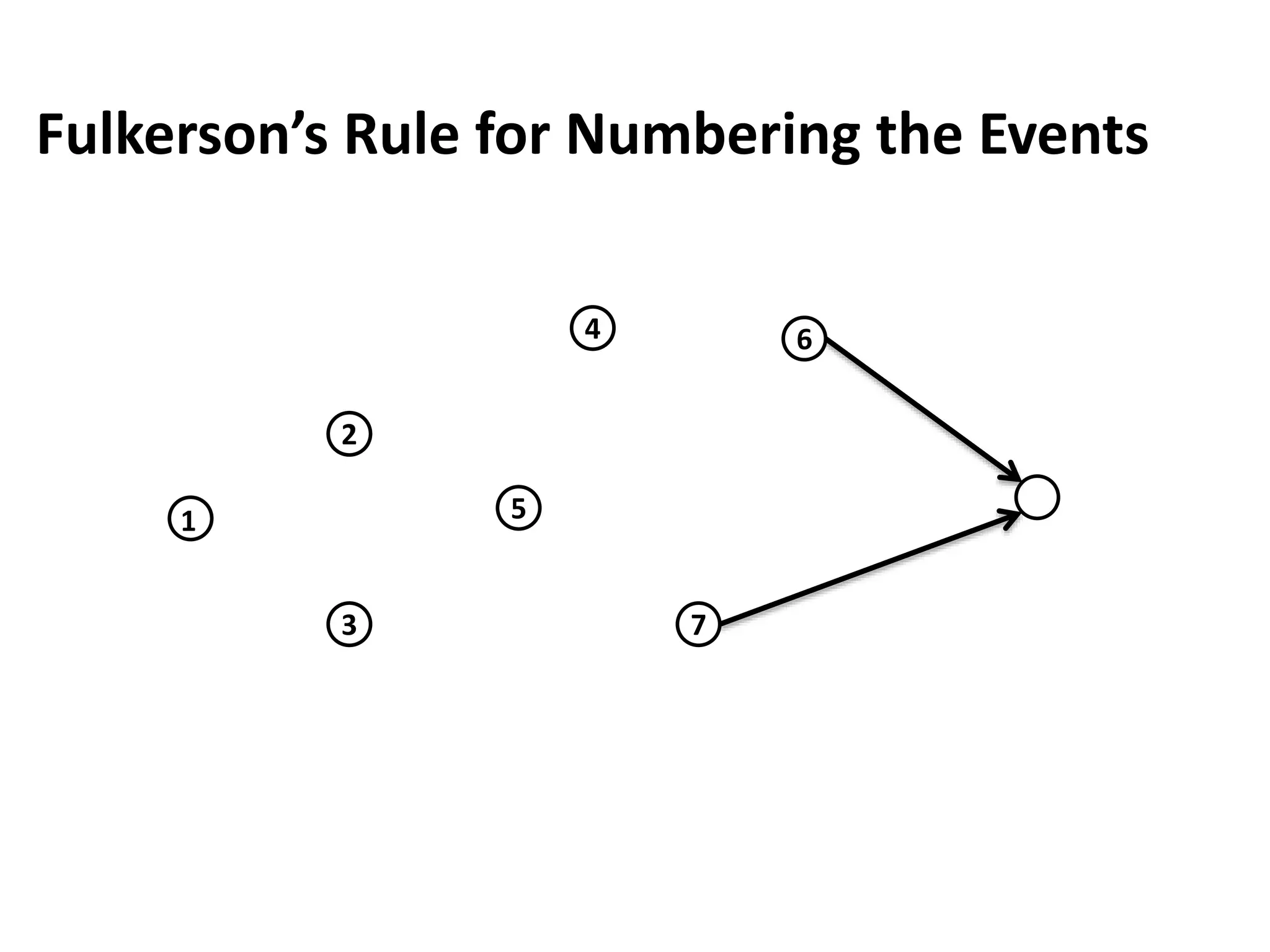
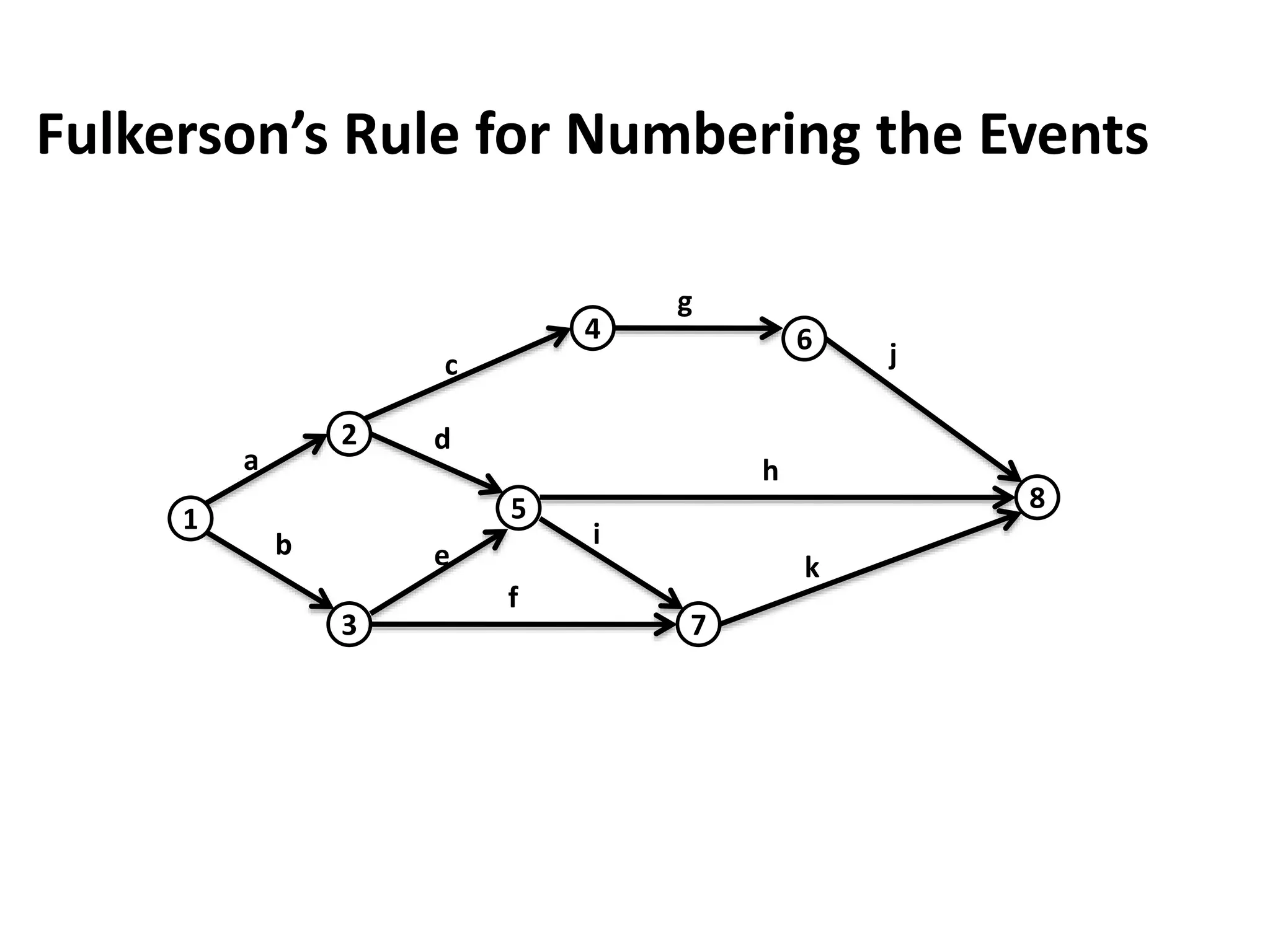
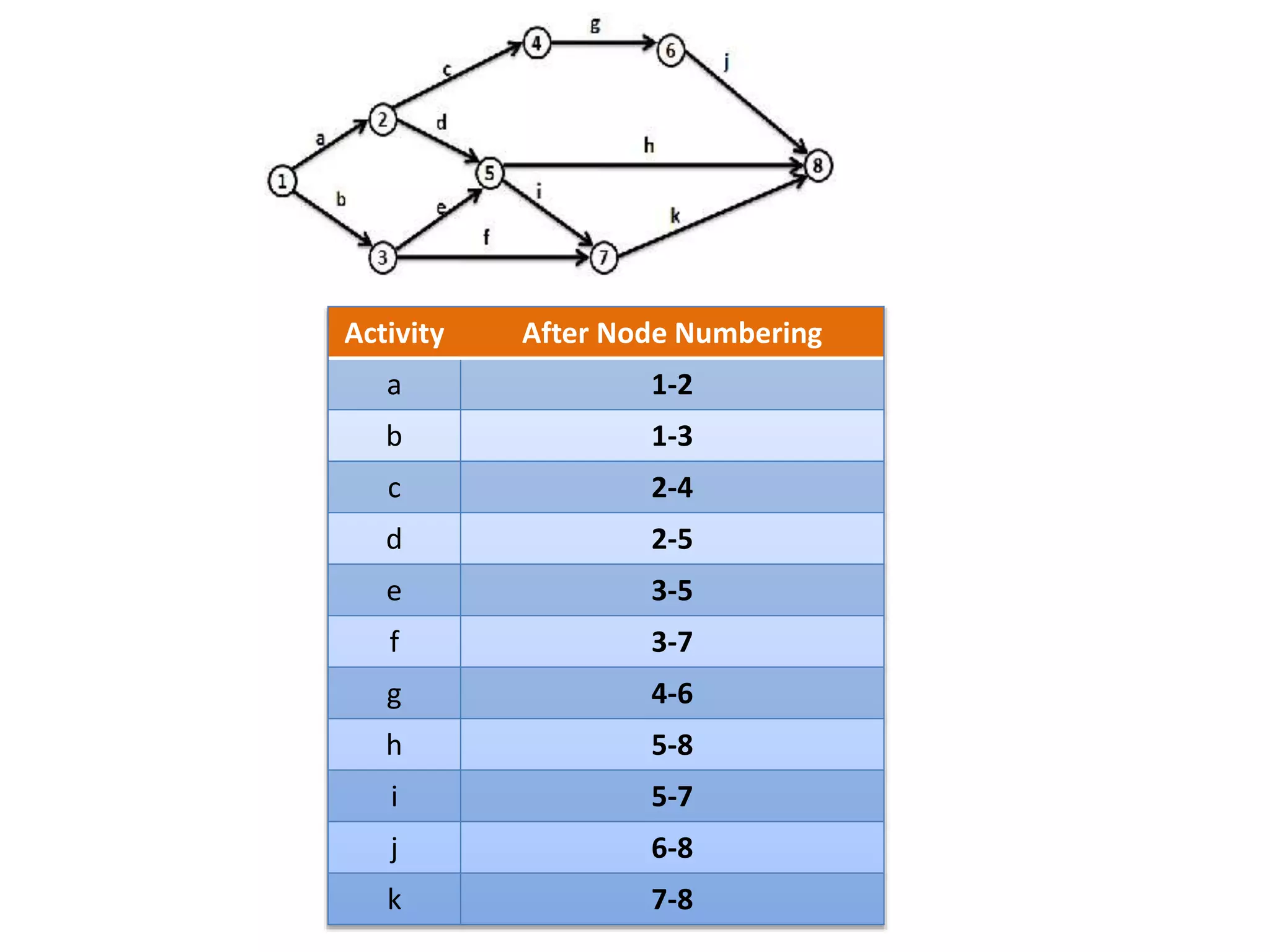
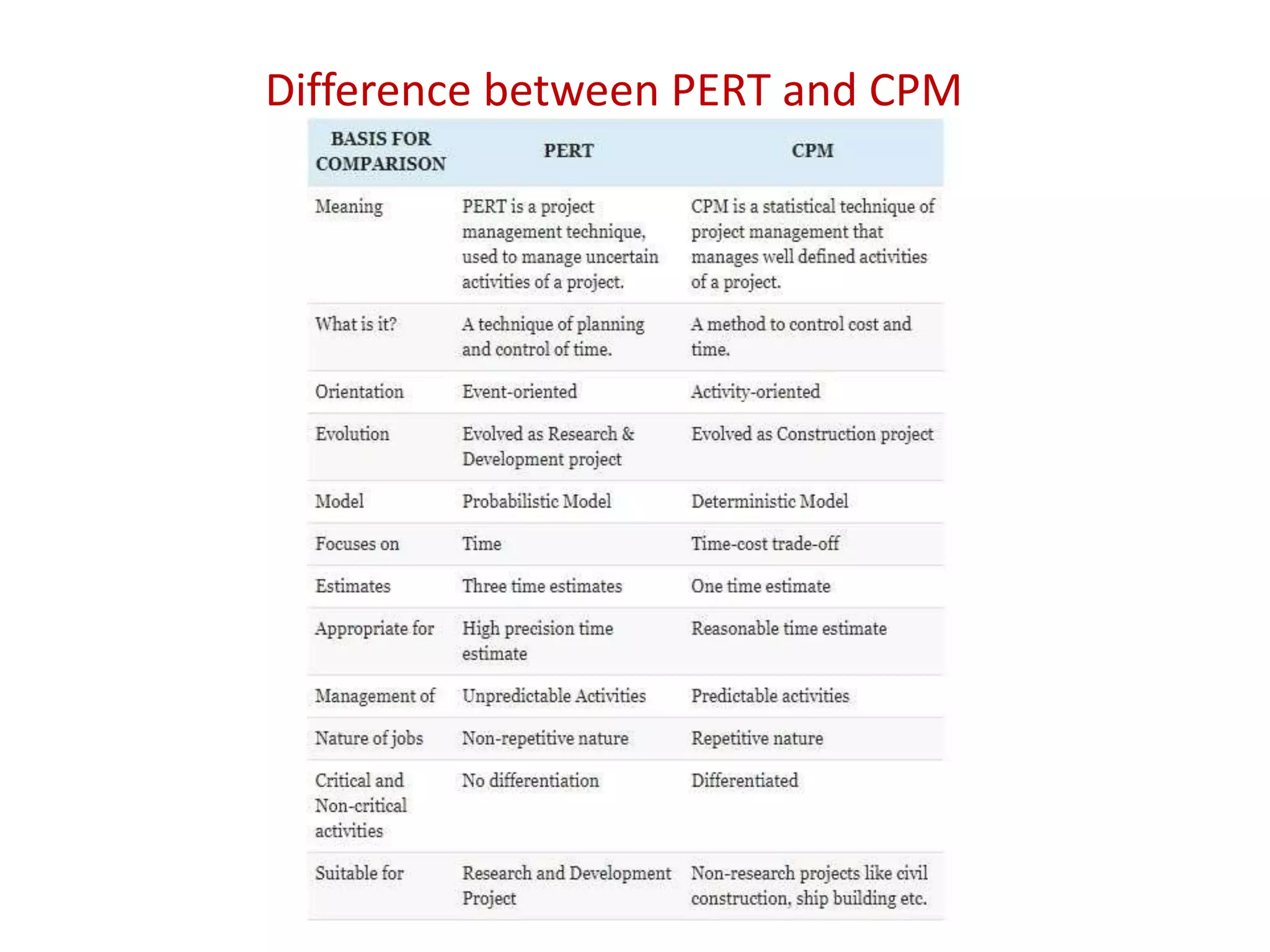
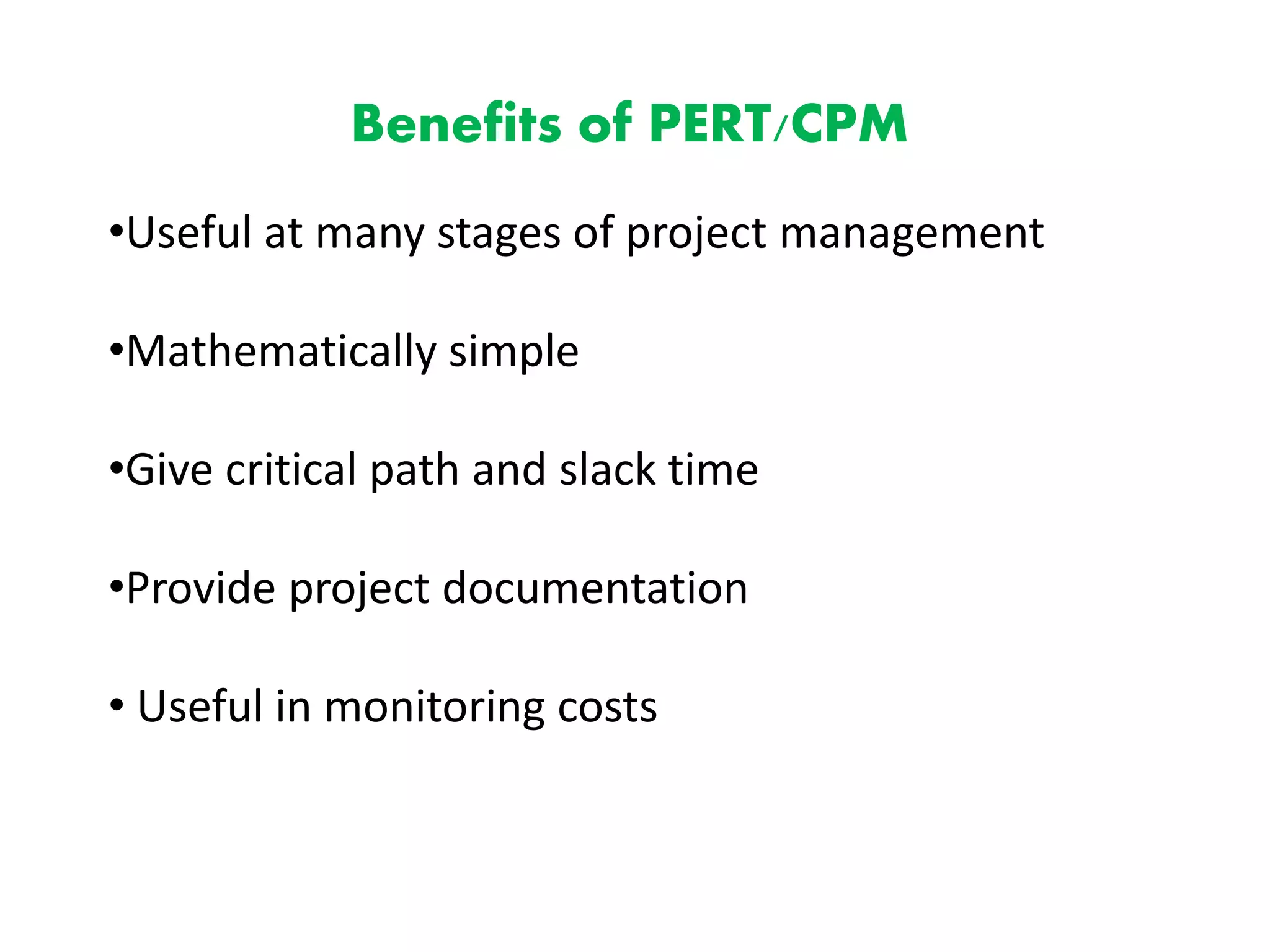
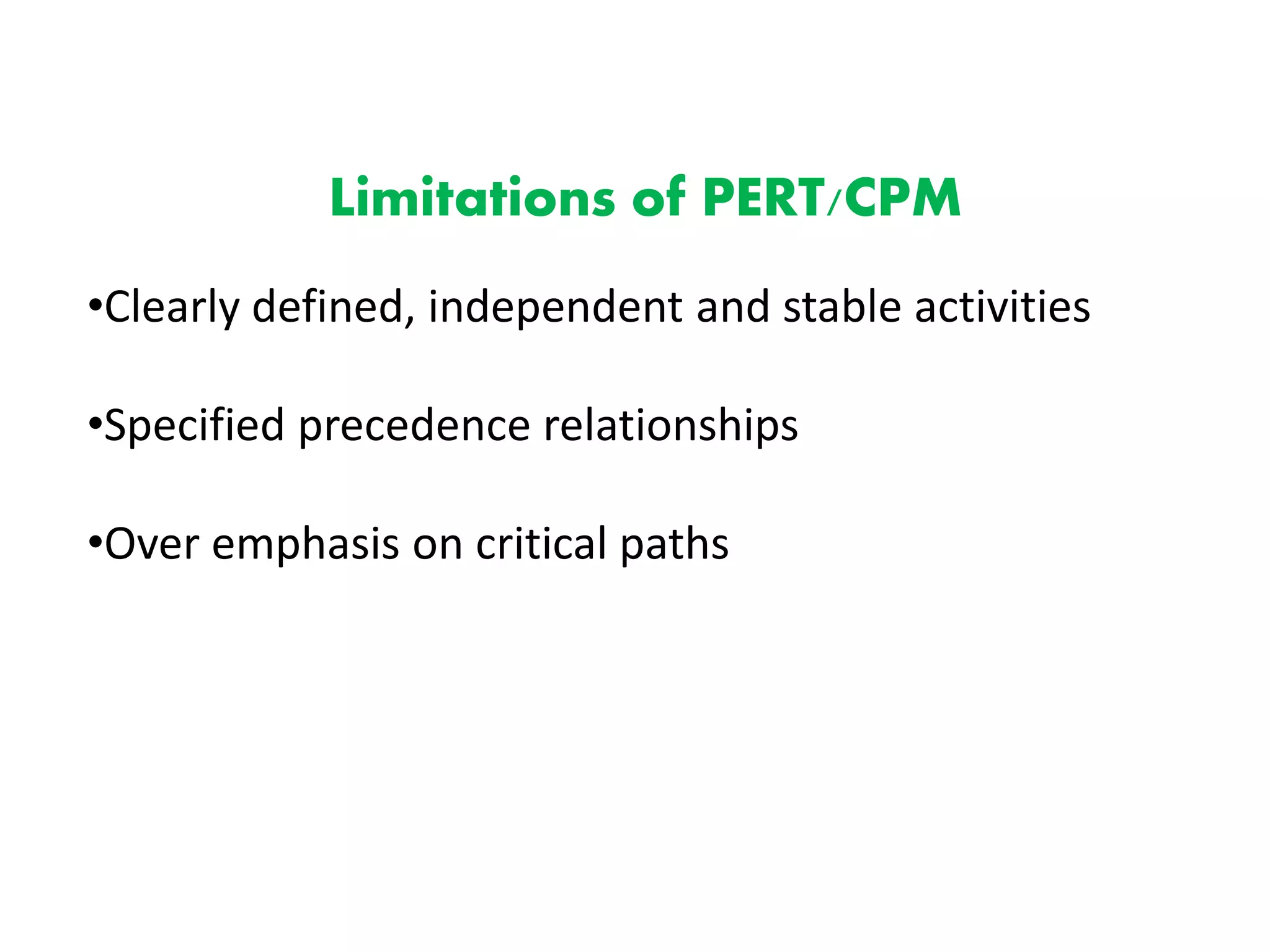
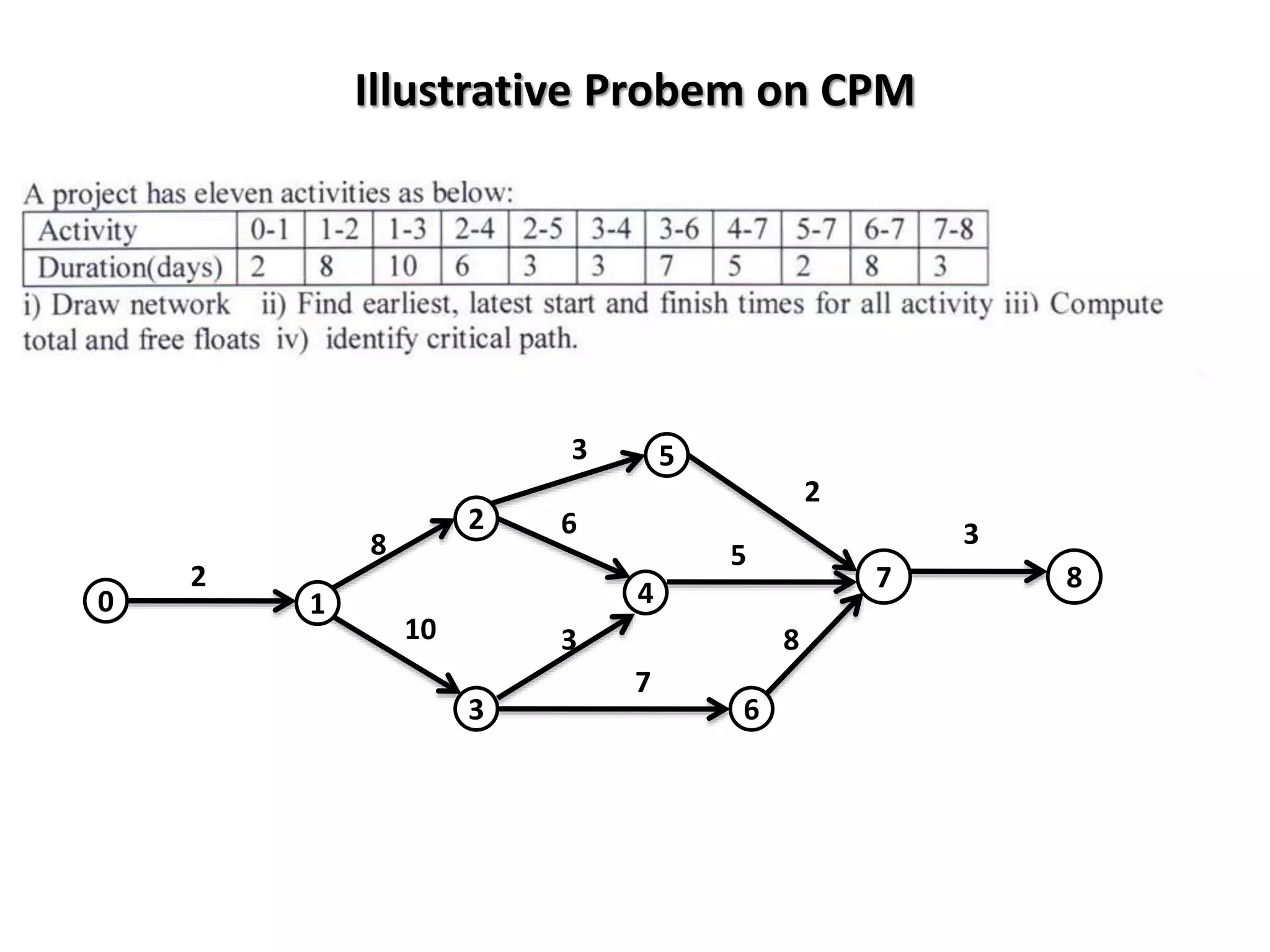
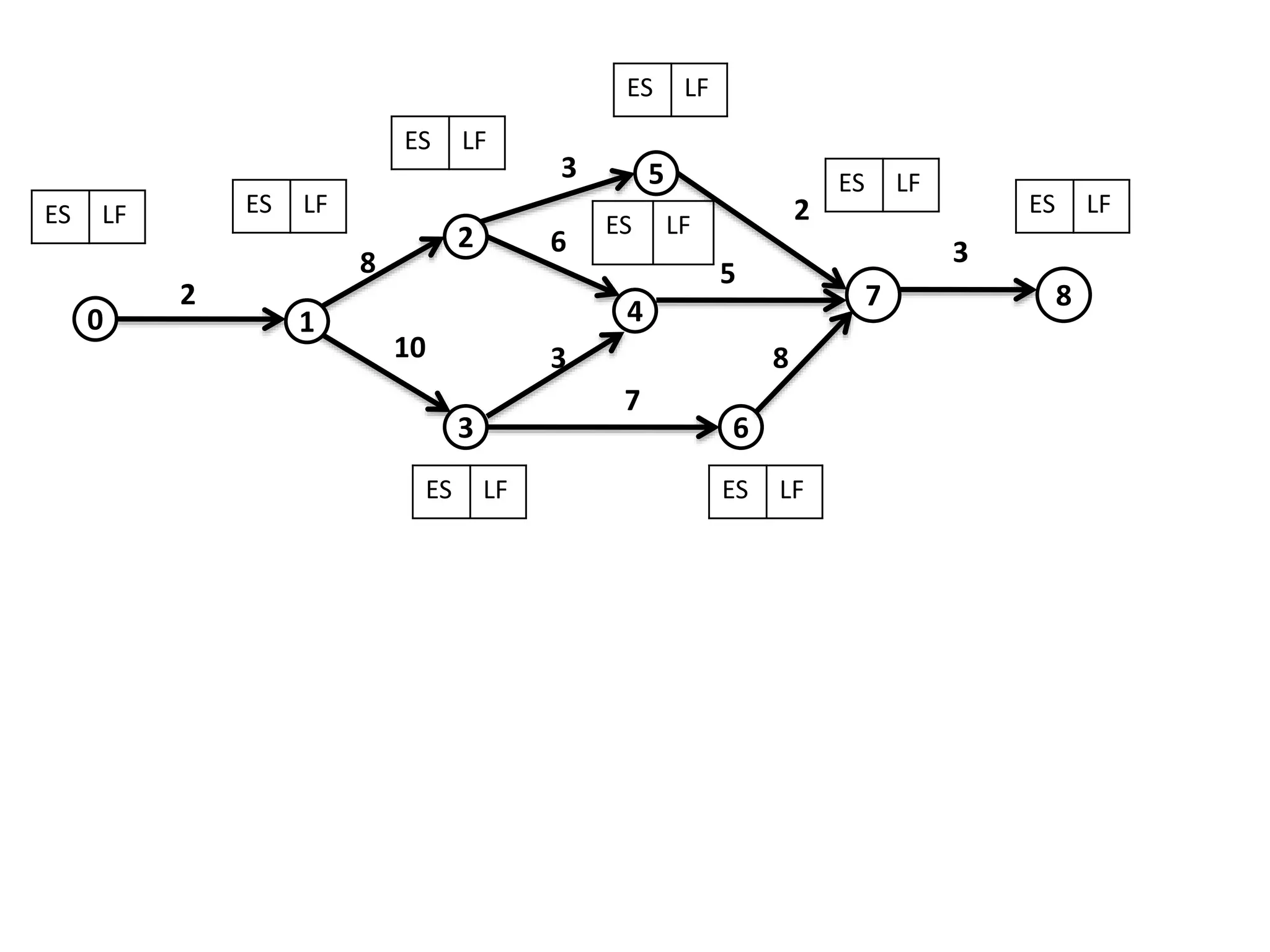
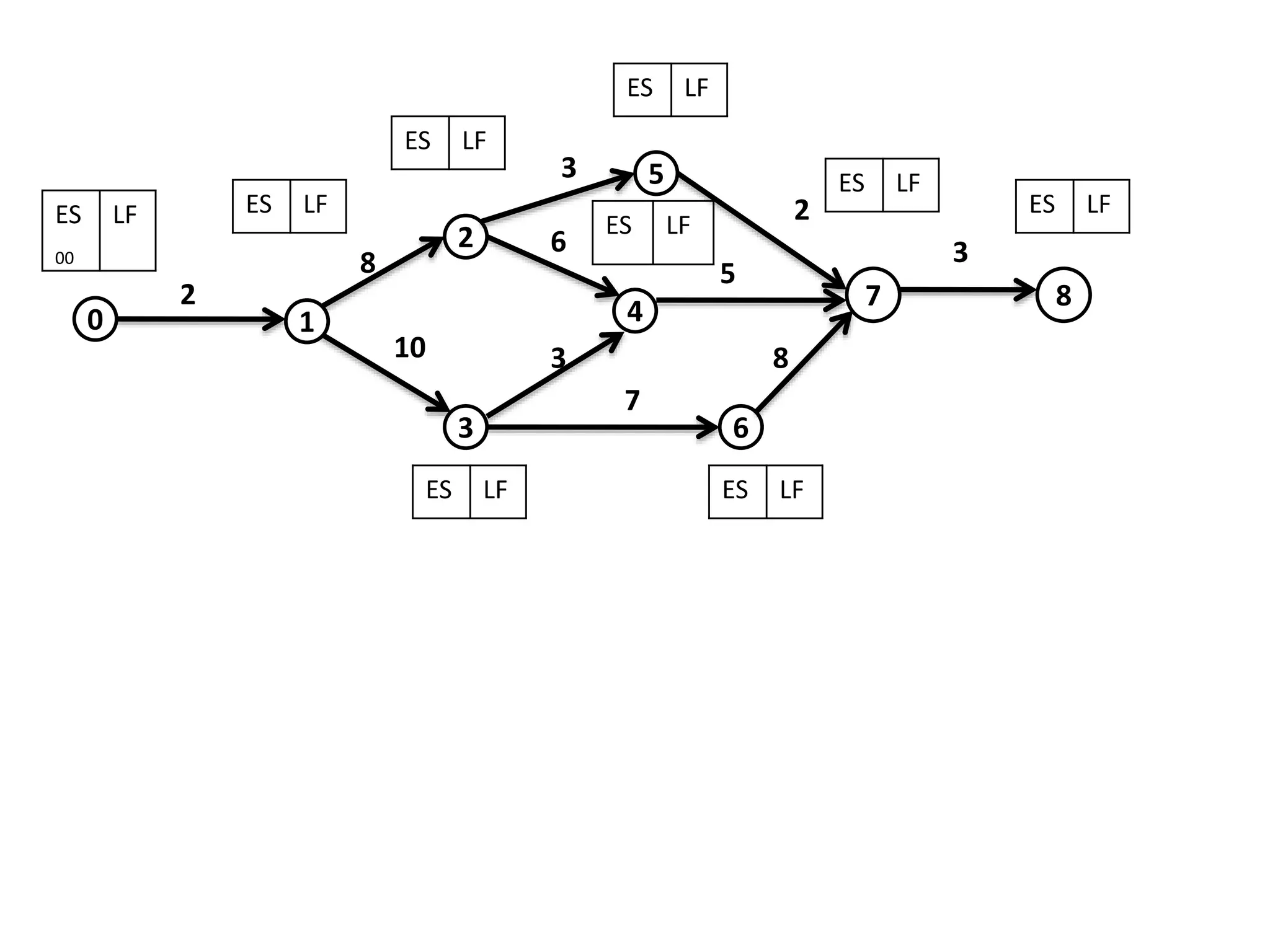
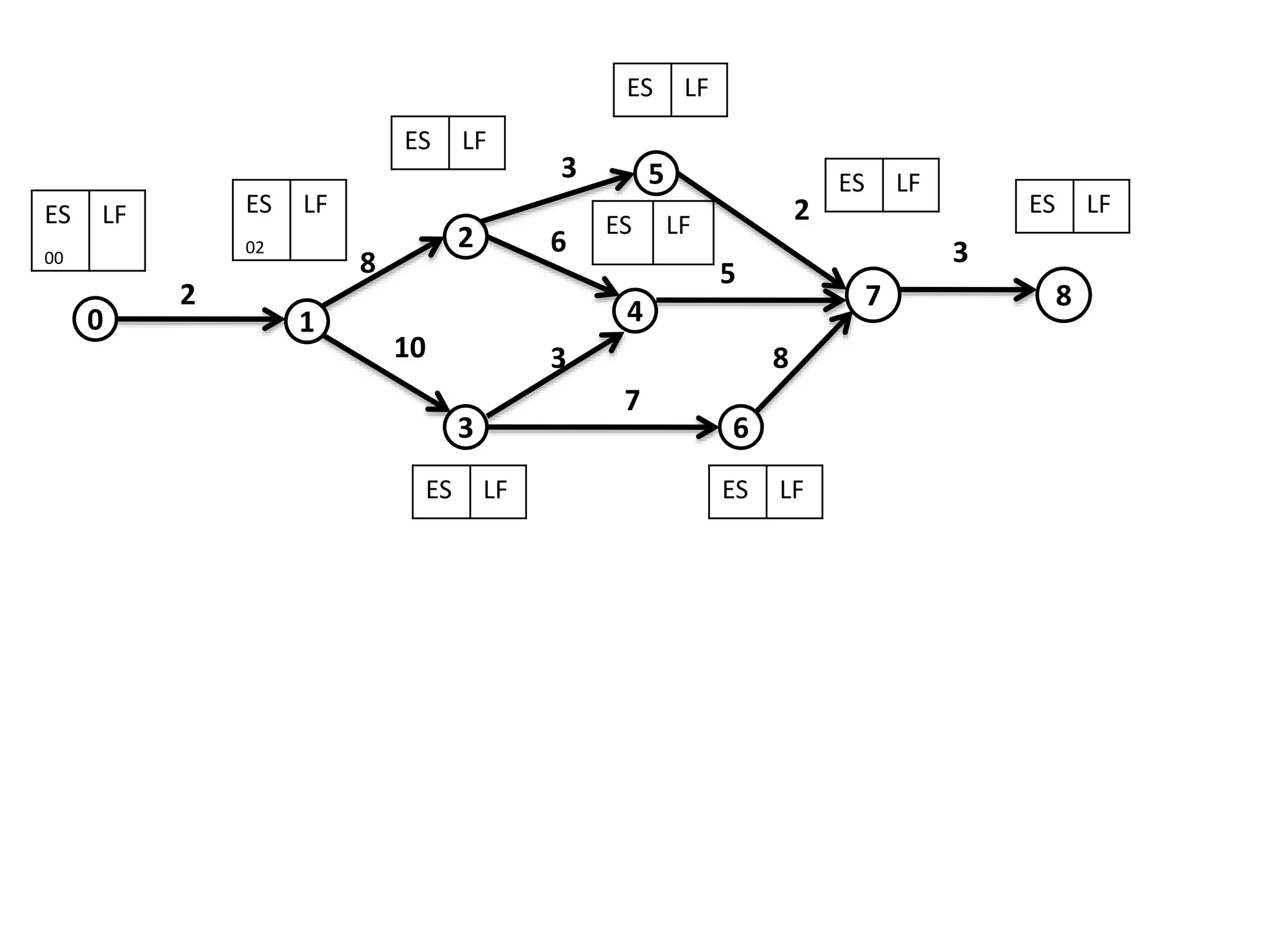
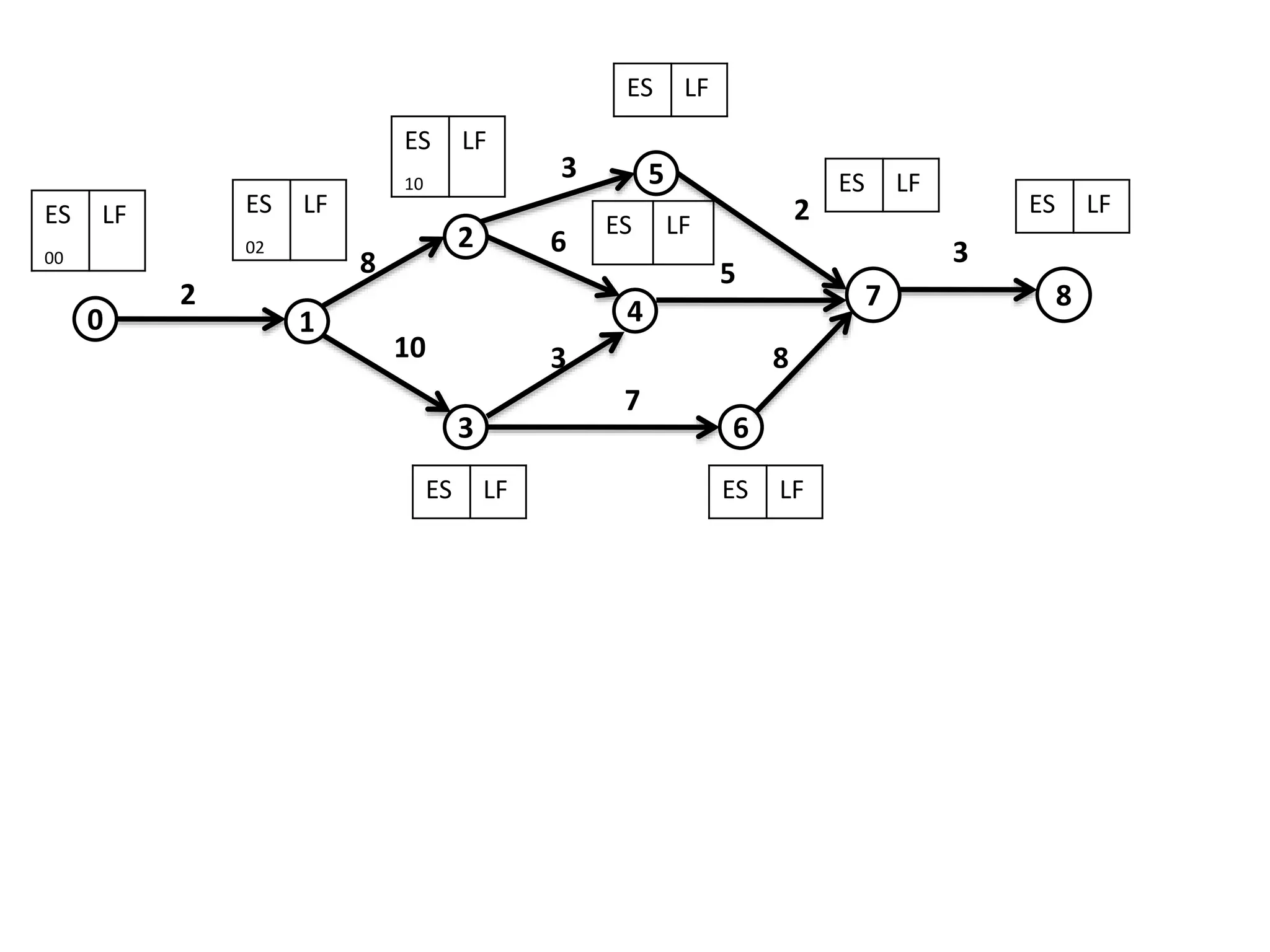
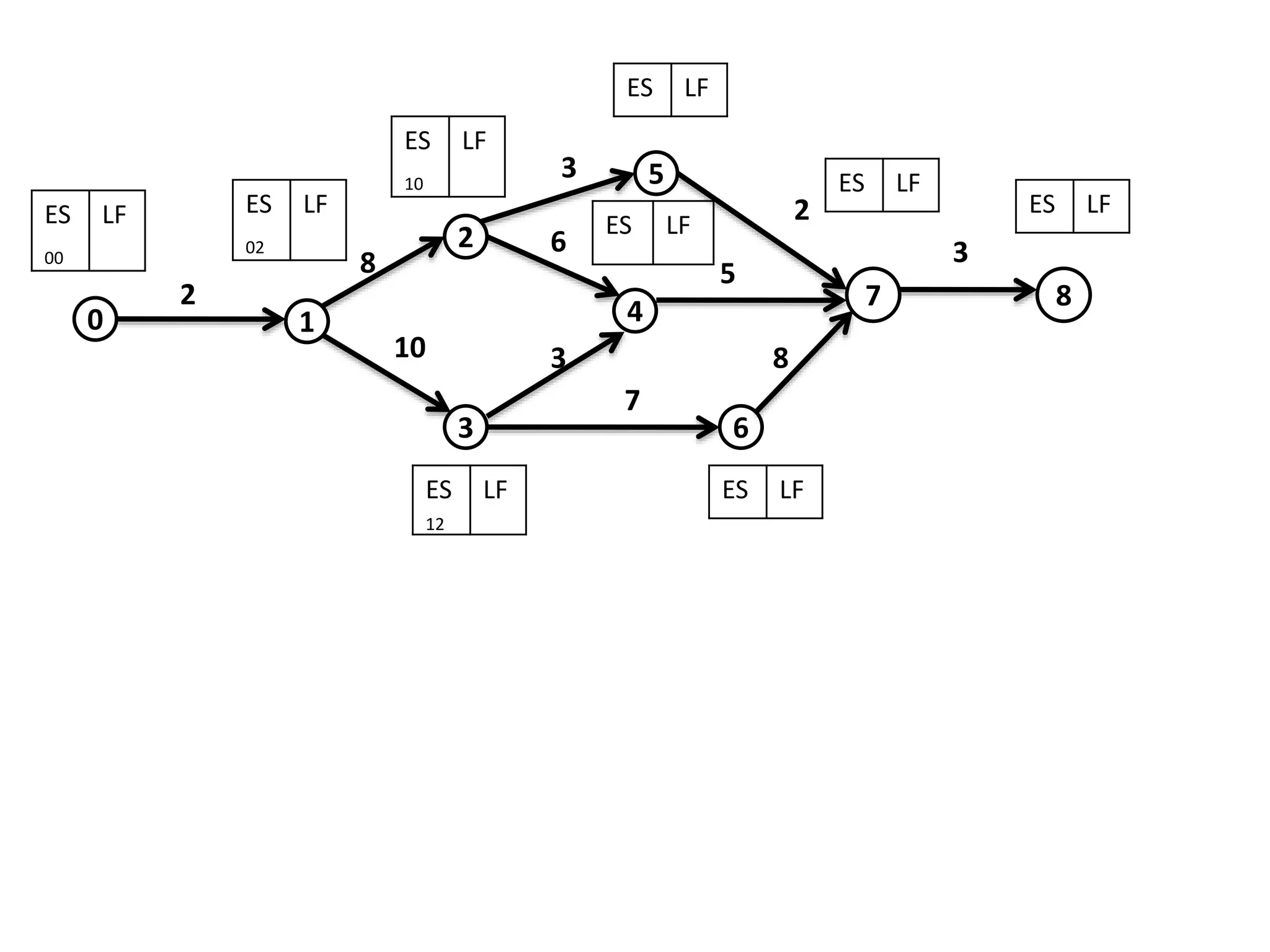
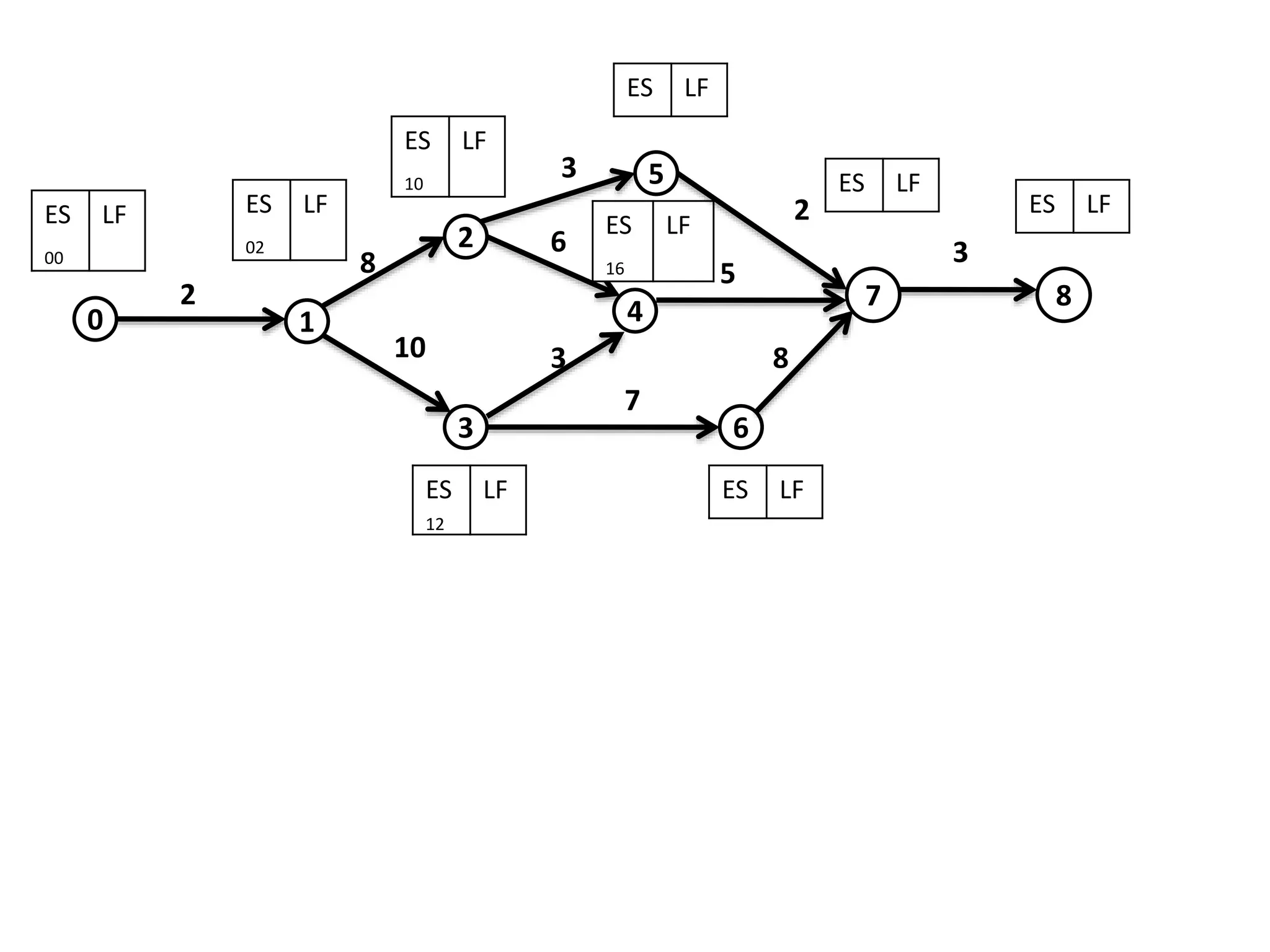
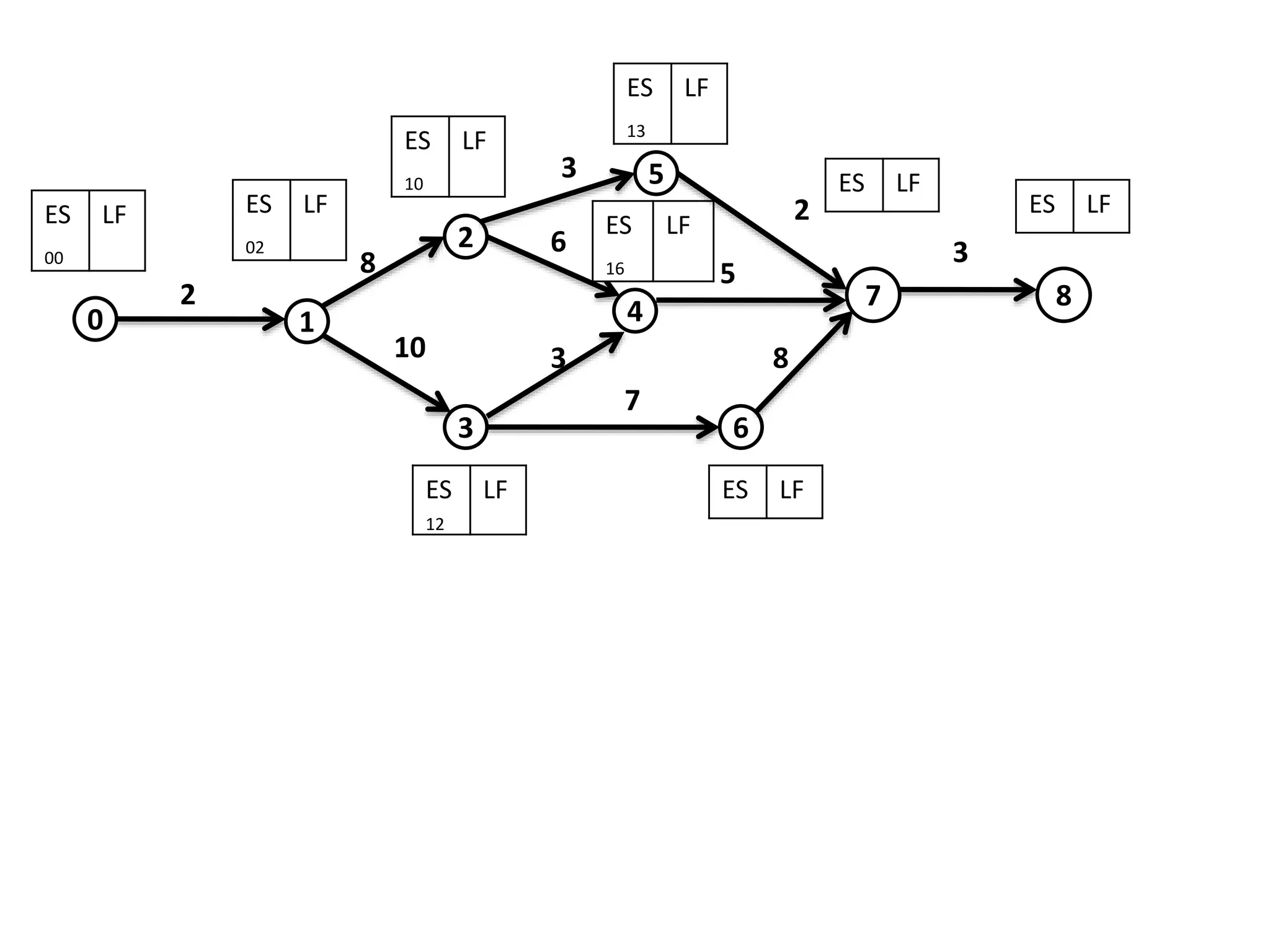
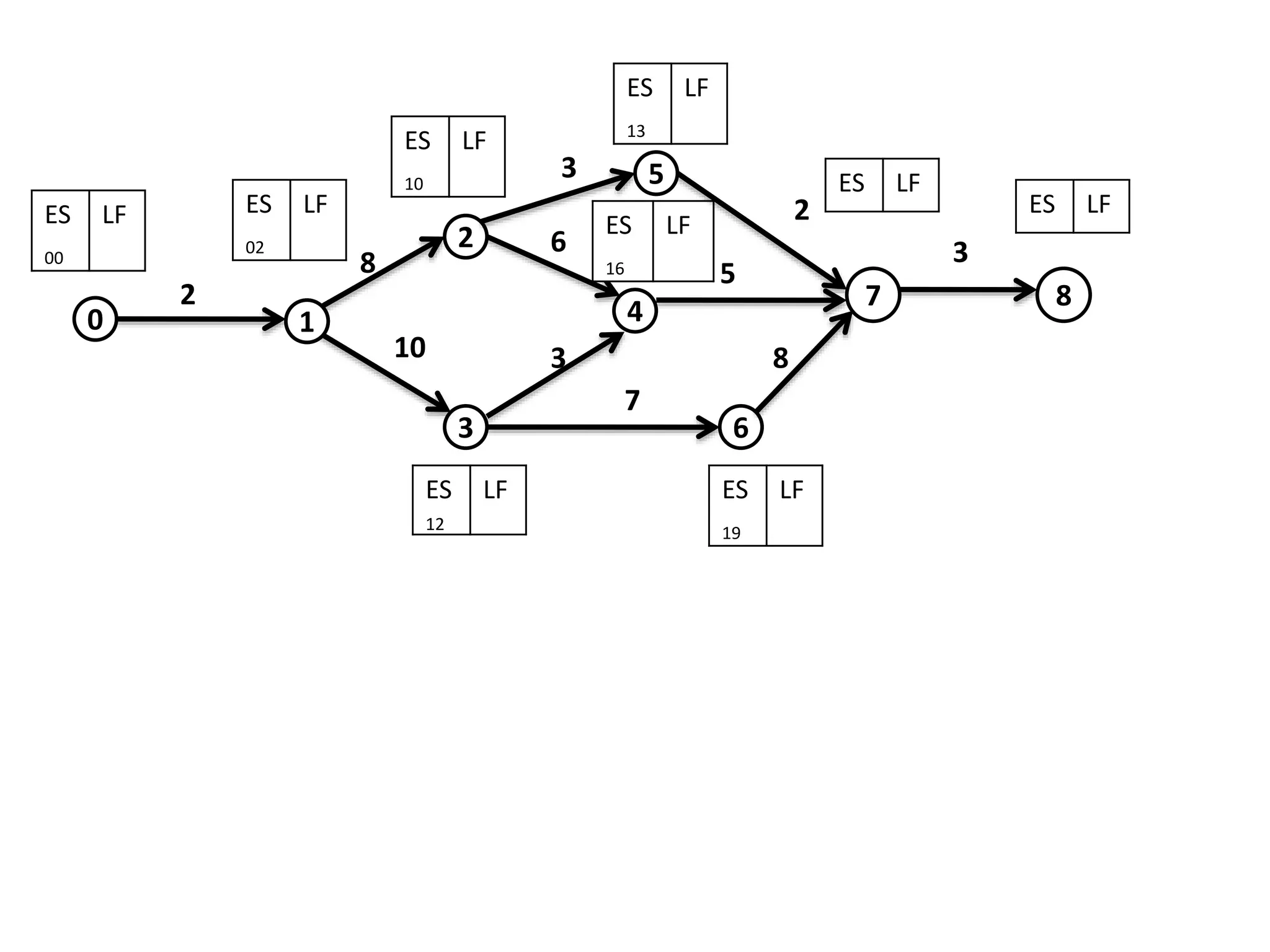
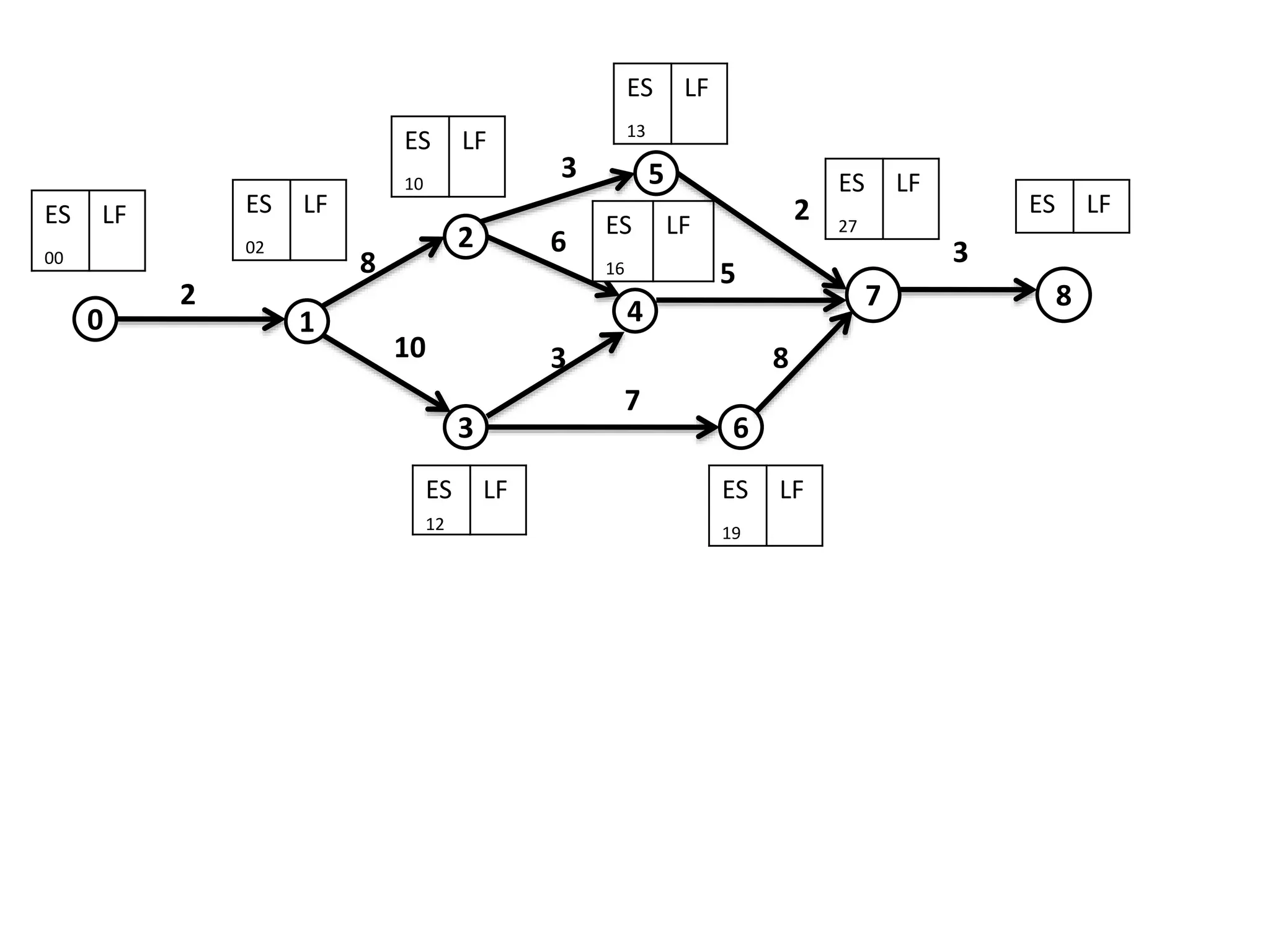
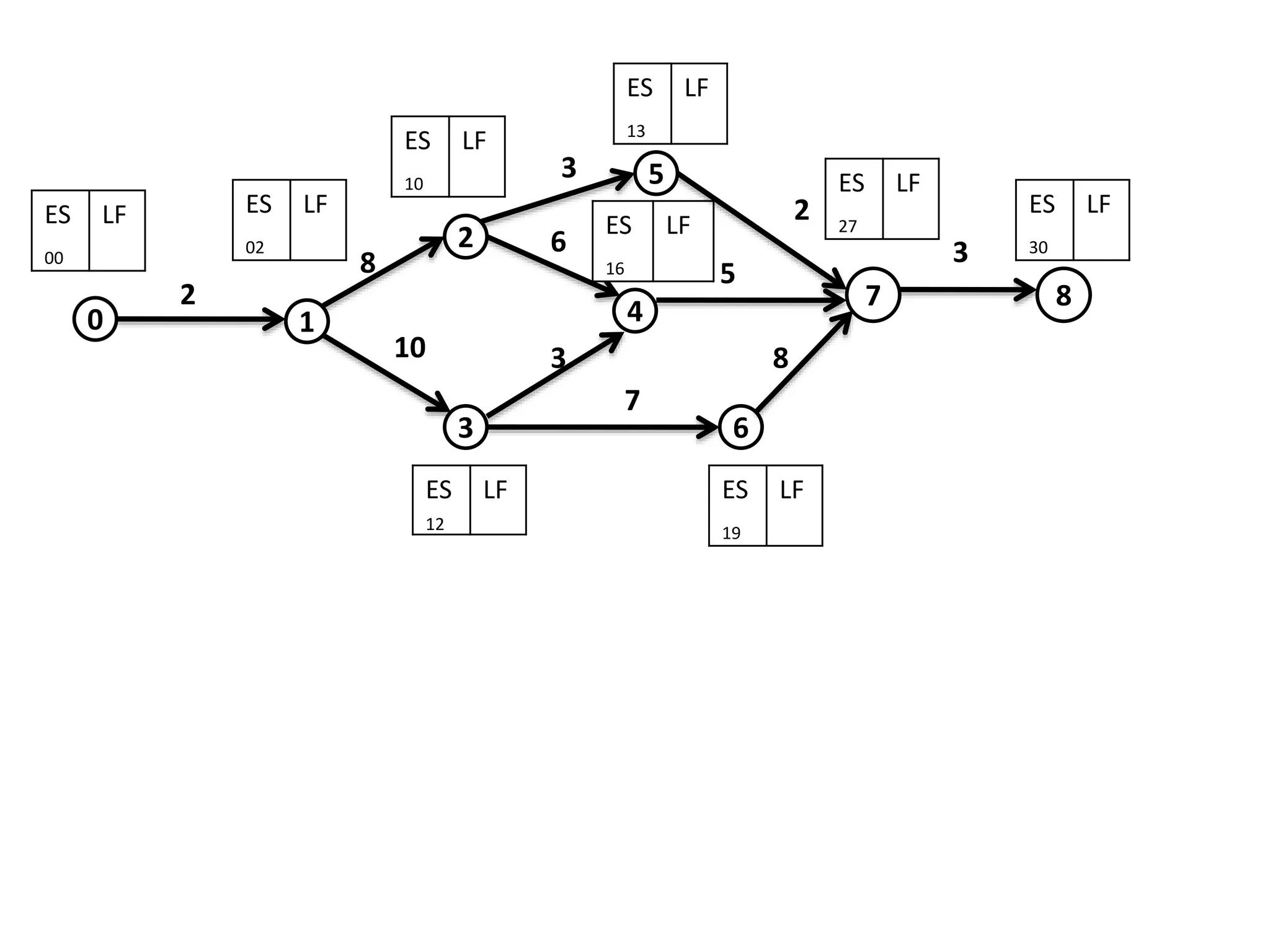
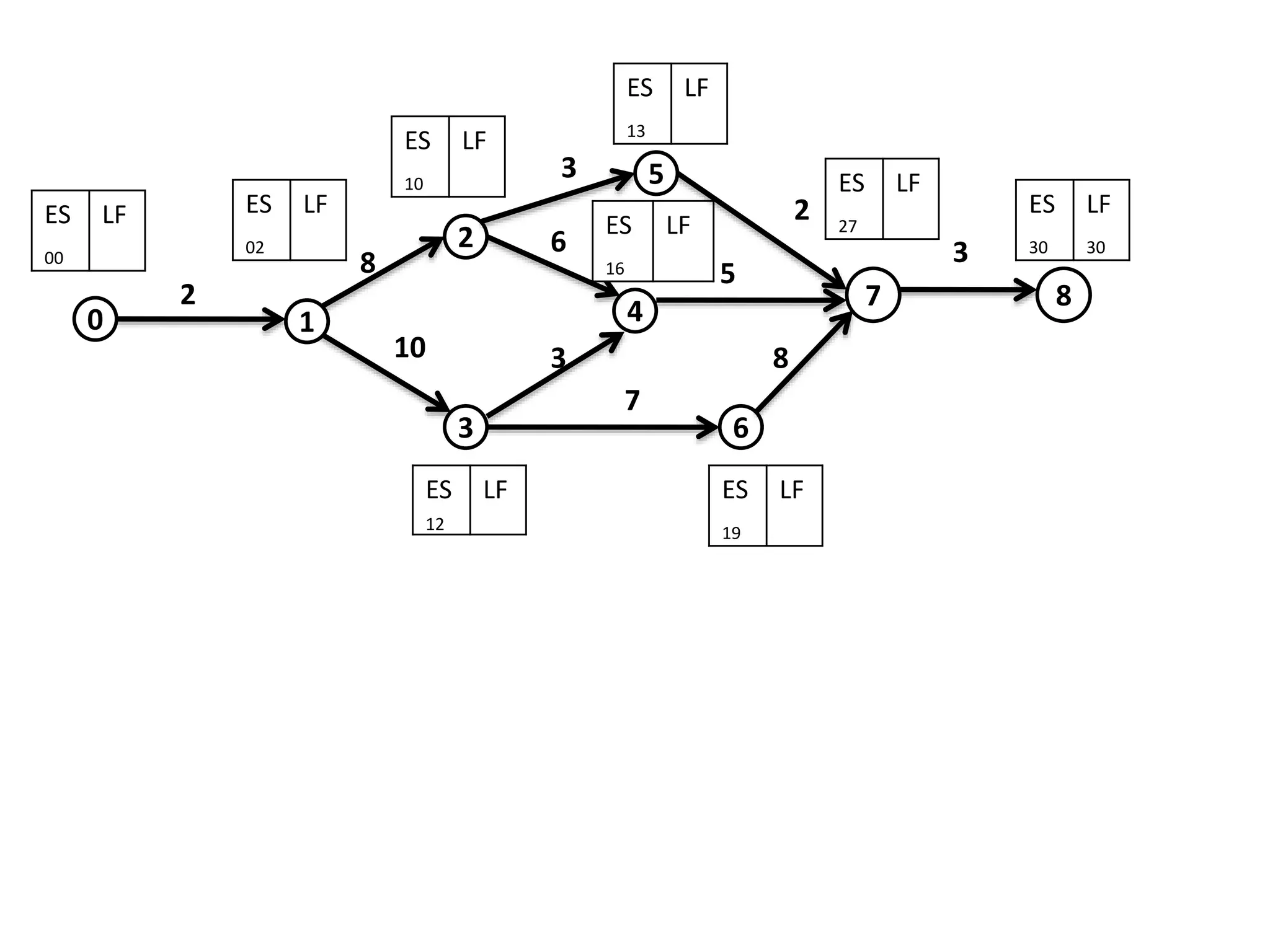
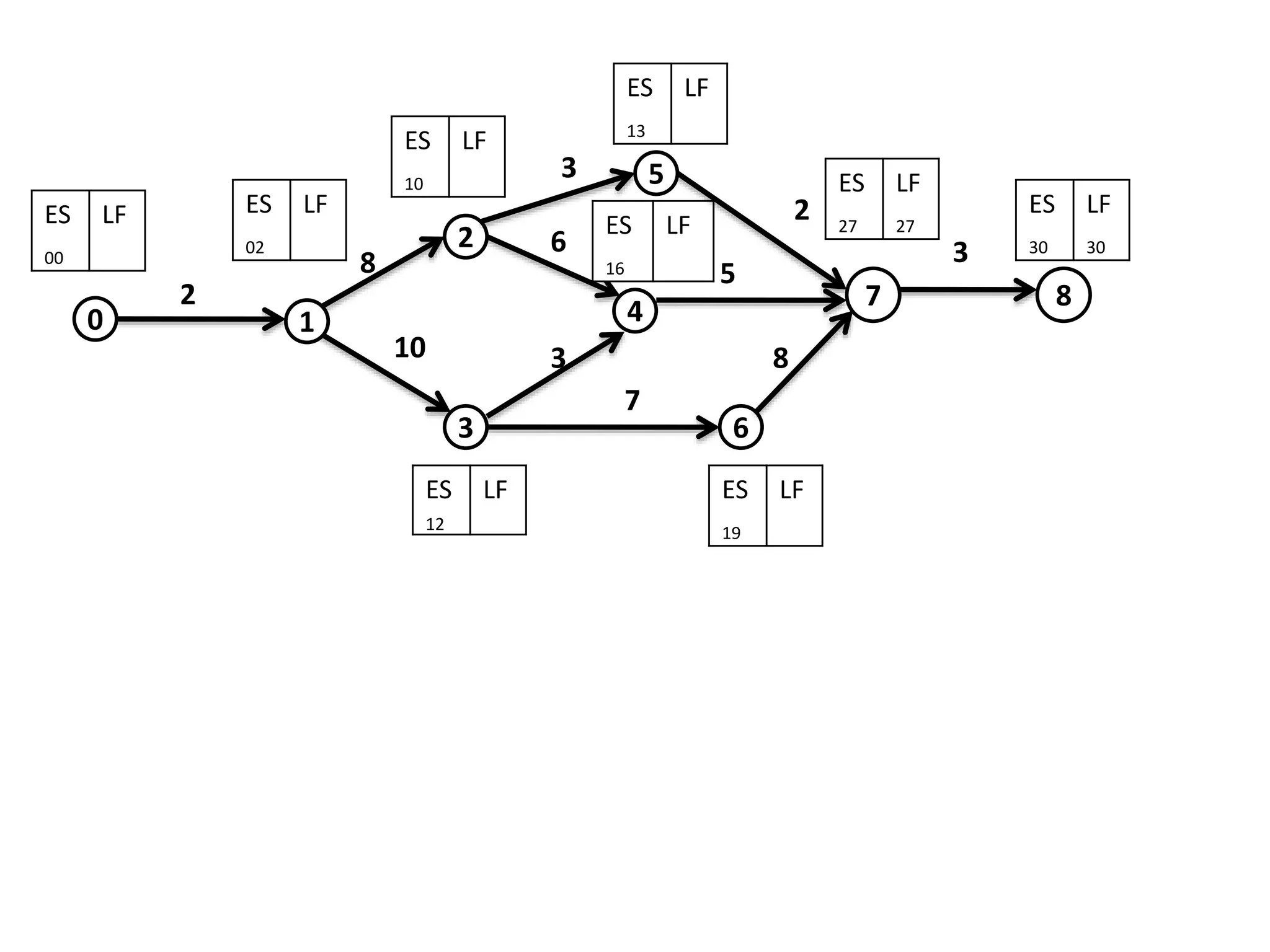
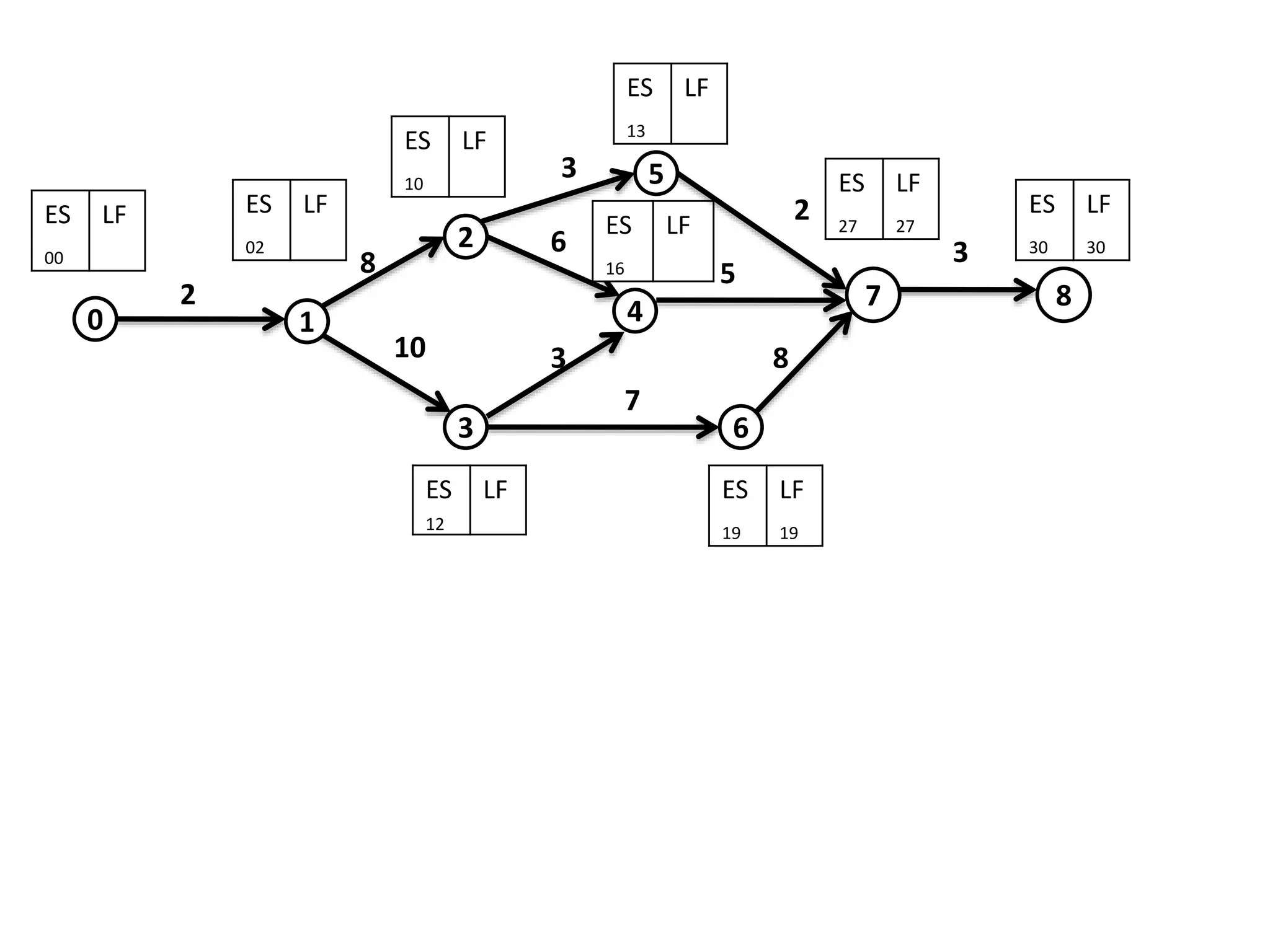
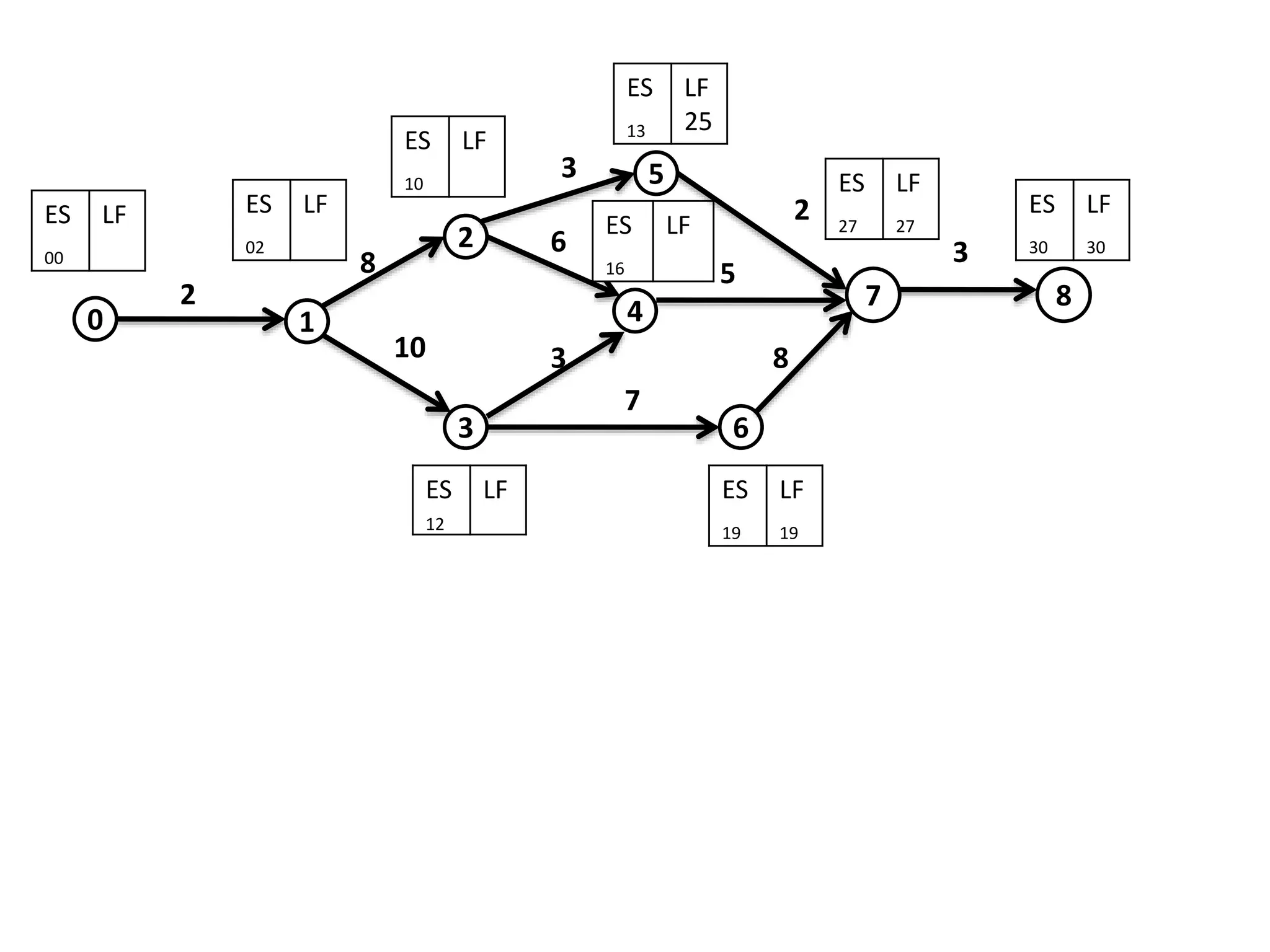
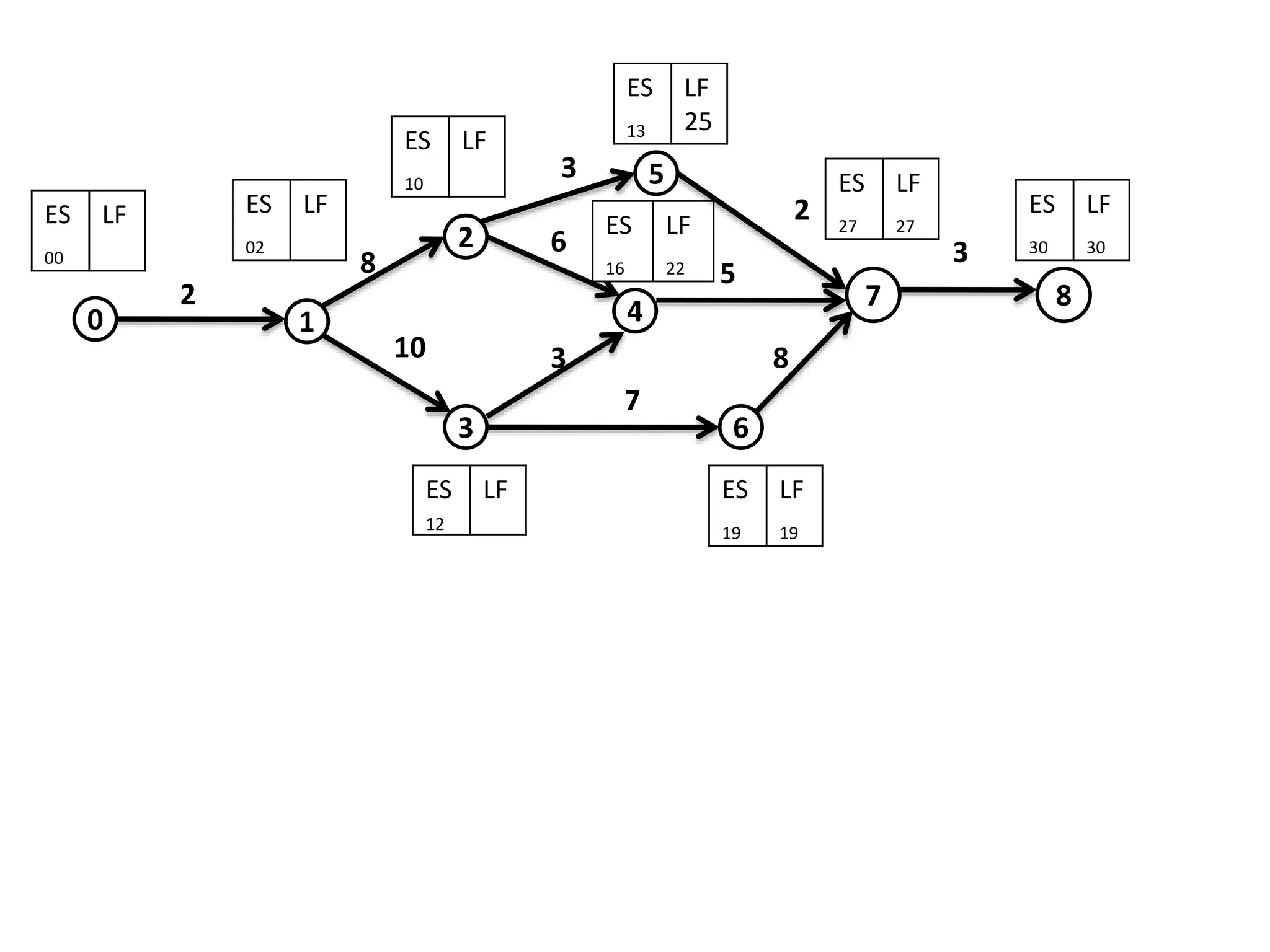
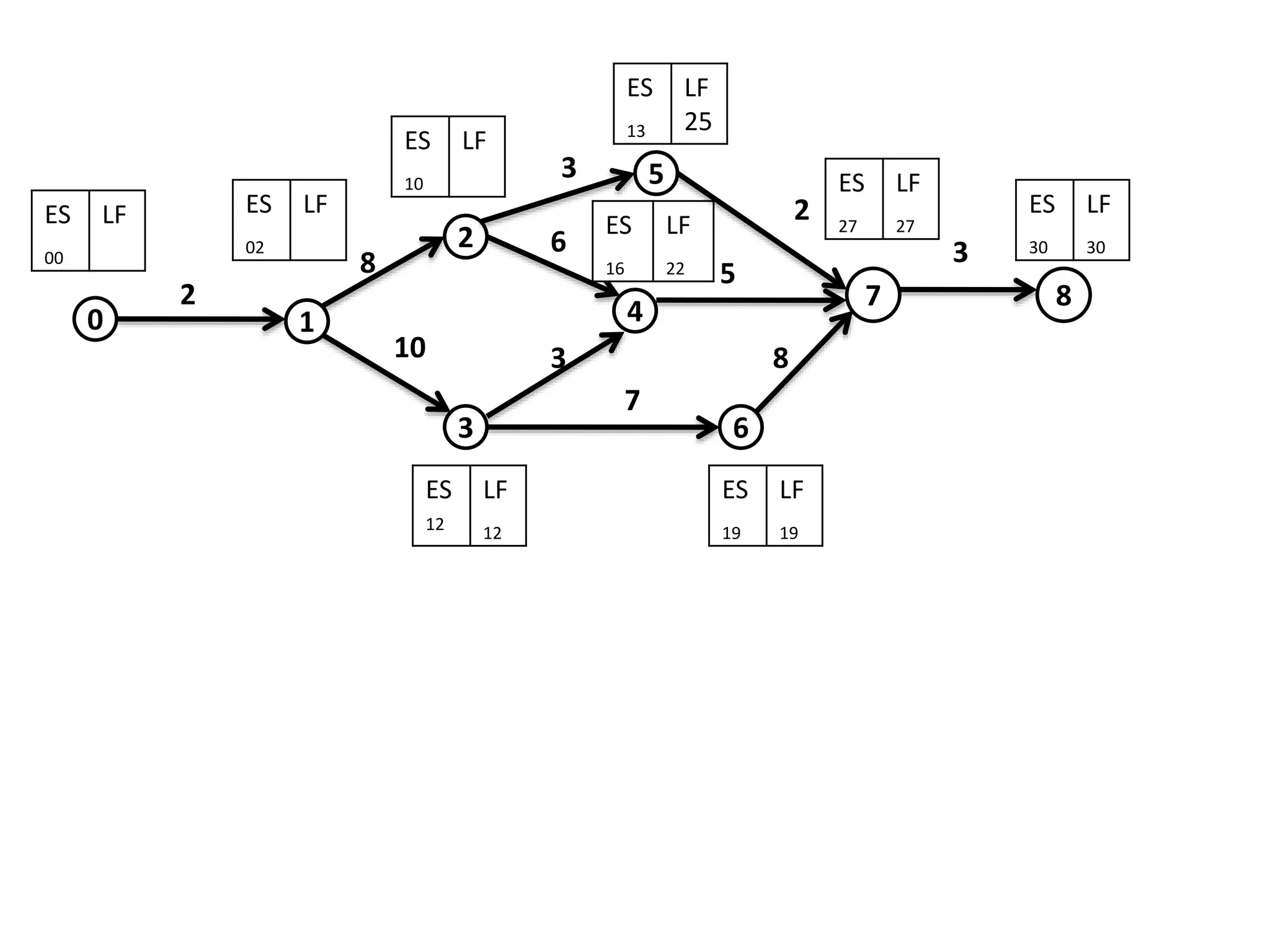
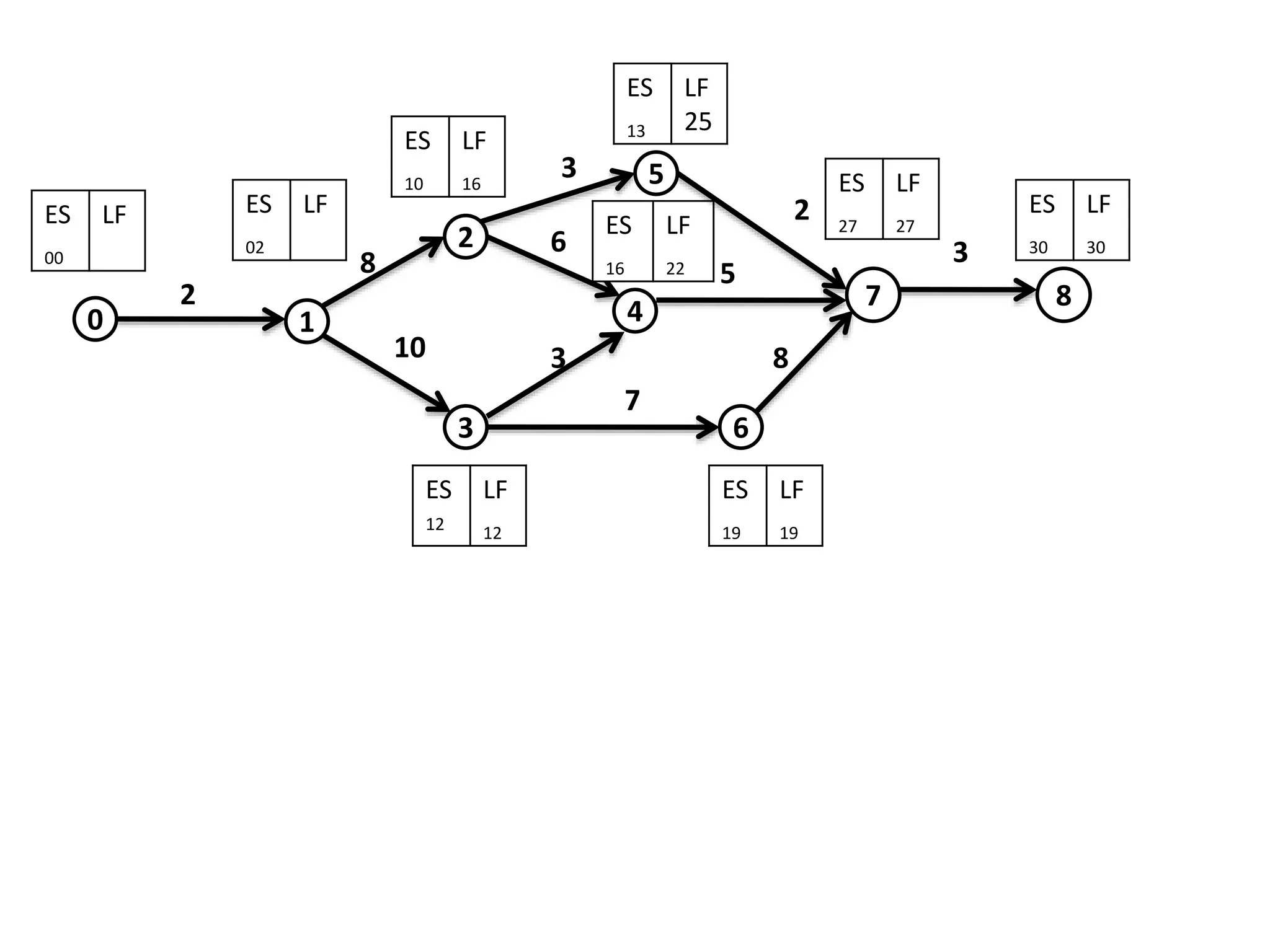
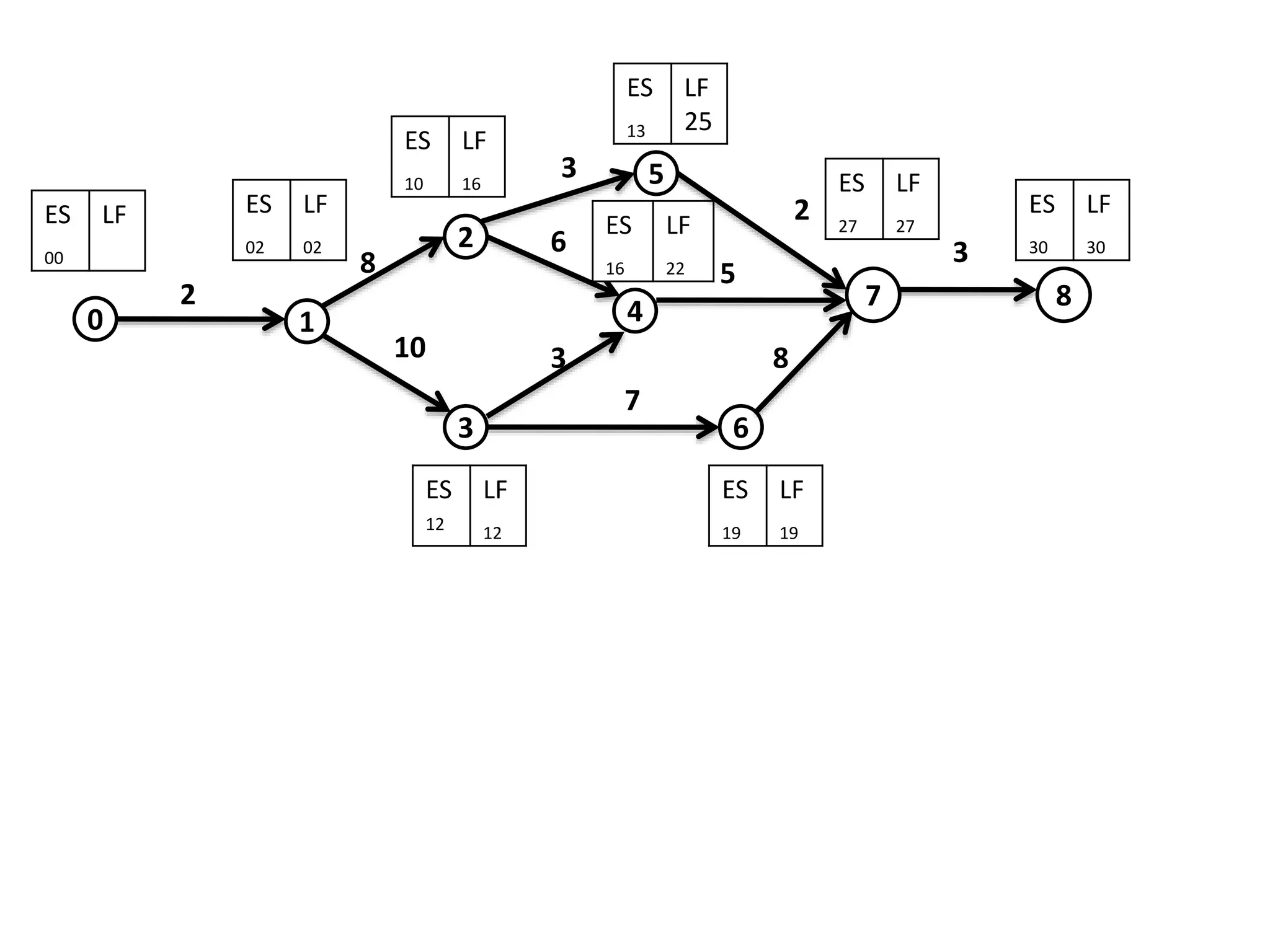
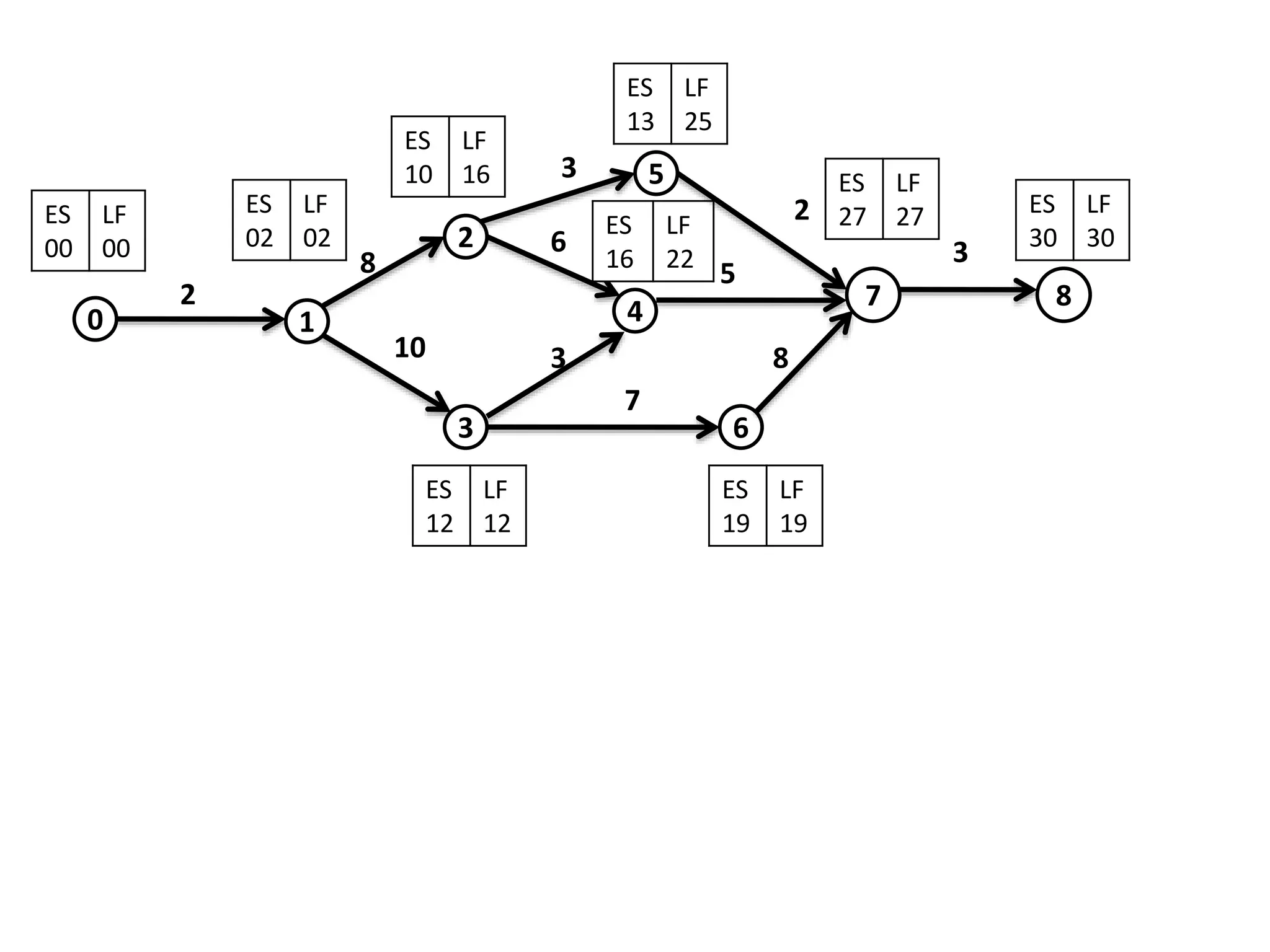
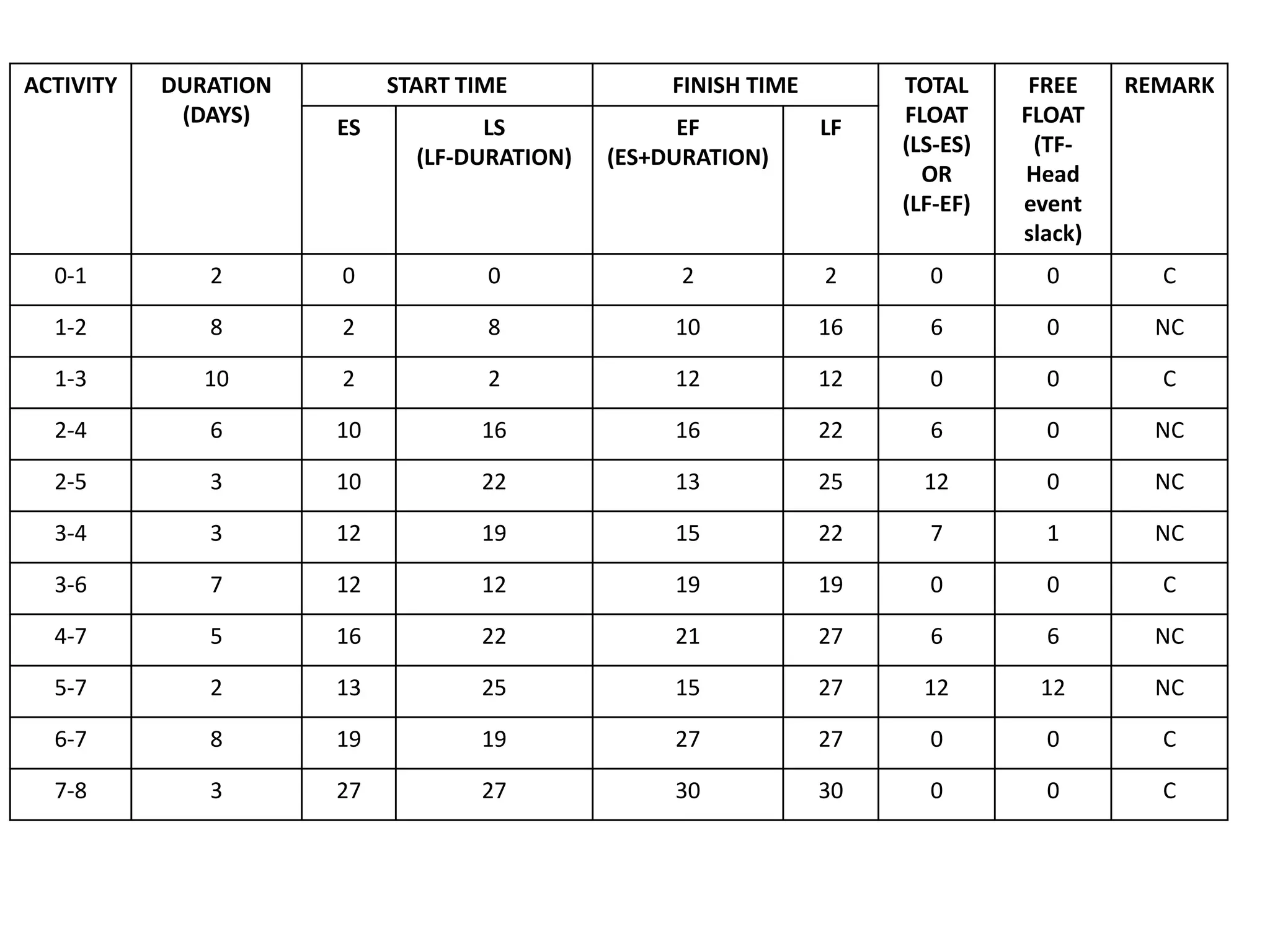
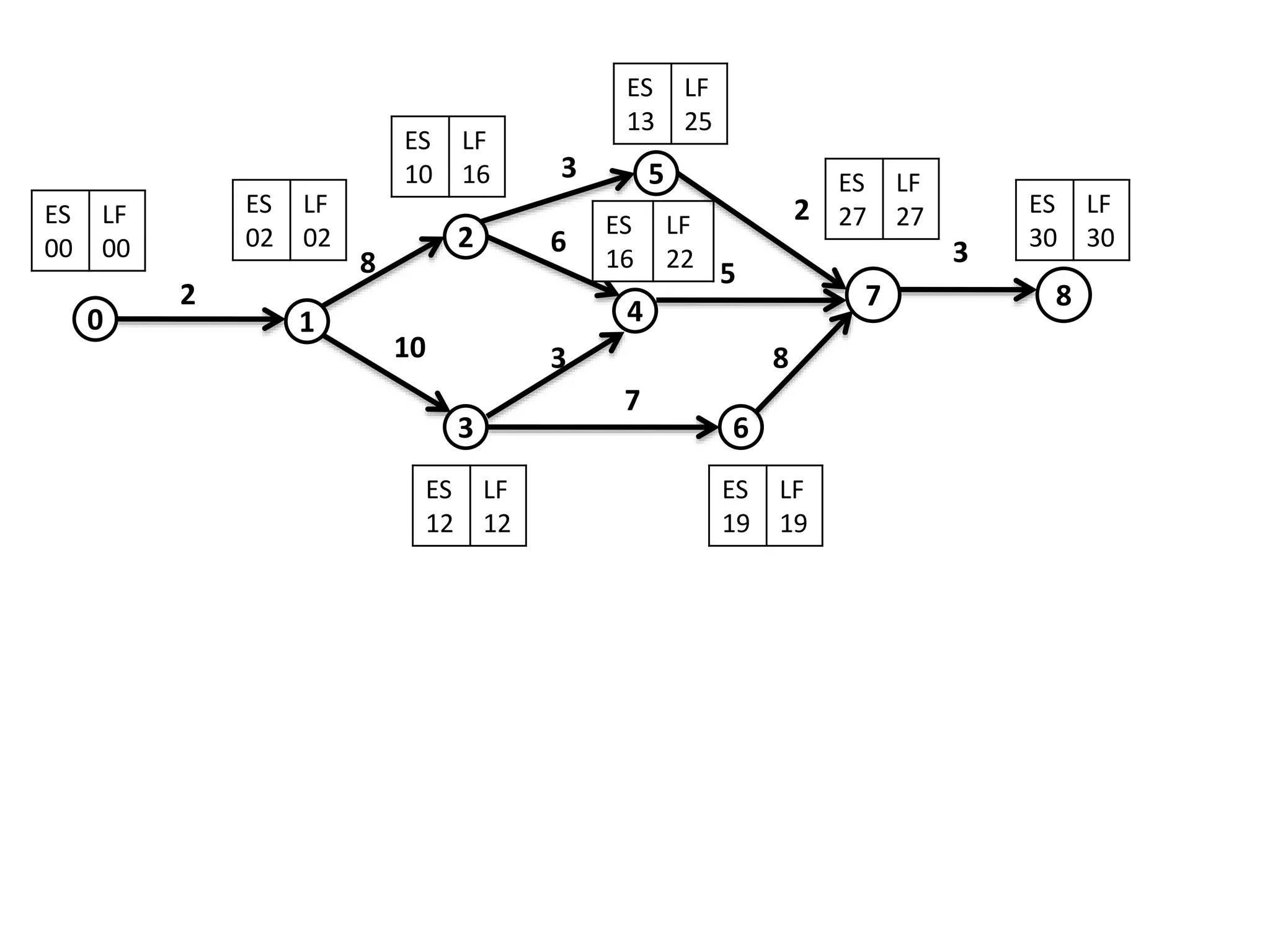
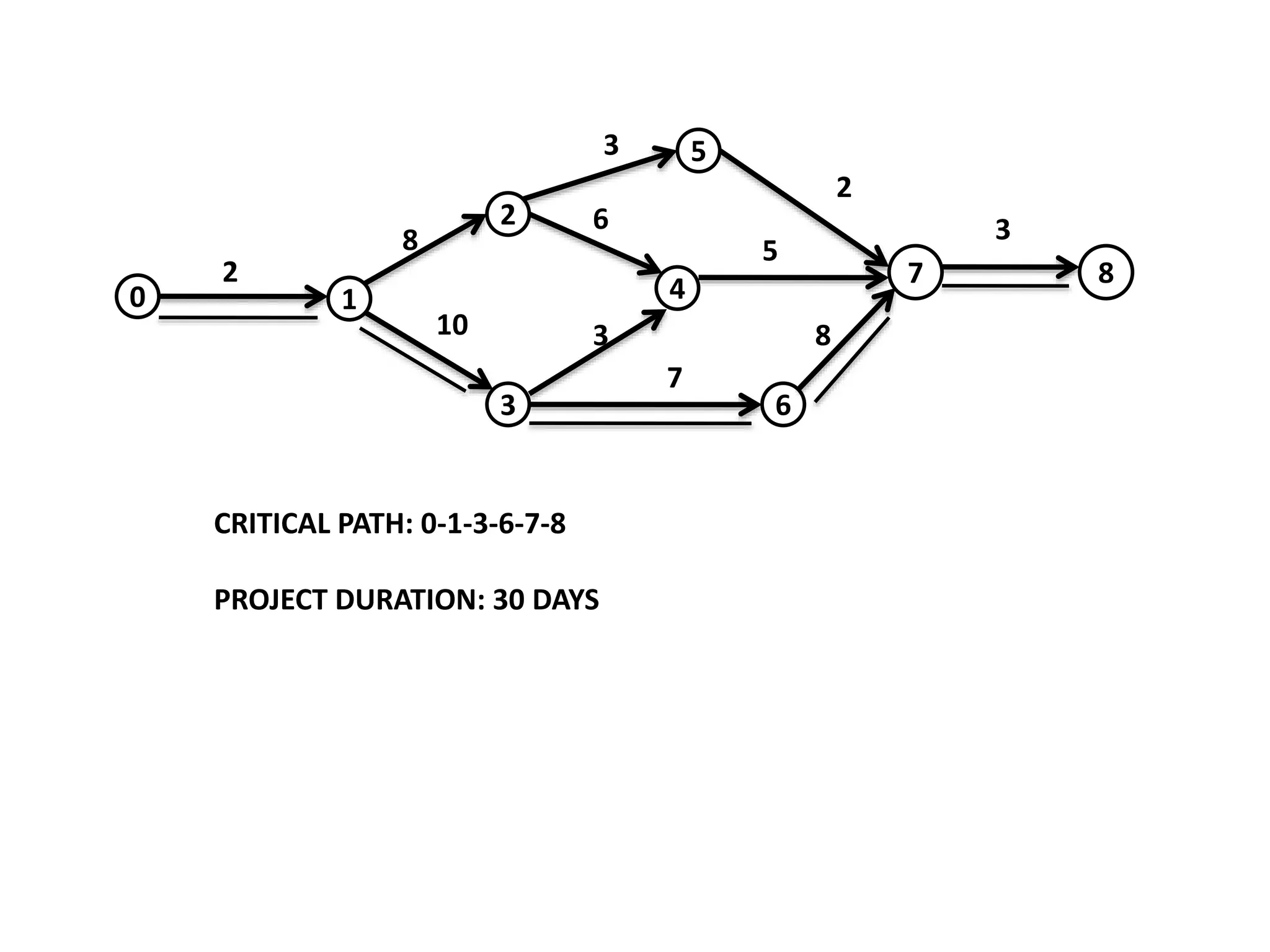
The document discusses the construction of network diagrams in operations research, explaining key terms such as activities, events, paths, and networks. It presents two methods for constructing network diagrams: Activity-on-Arrow (AOA) and Activity-on-Node (AON), along with their respective benefits and limitations. Additionally, it highlights Fulkerson's rule for event numbering and compares the applications of PERT and CPM in project management.