The document discusses Sir Isaac Newton's contributions to the understanding of force and gravitational law, detailing his three laws of motion and the formulation of the law of universal gravitation. It explains how Newton connected the force of gravity to both terrestrial and celestial bodies, supported by experiments including those conducted by Henry Cavendish to measure the gravitational constant. The text highlights the implications of gravitational force on various phenomena, such as tides and satellite orbits.









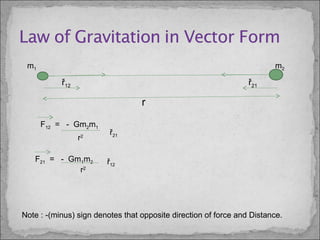
![F = GMm
r2
where,
– F = Force of attraction between the two particles.
– M = mass of first particle.
– m = mass of second particle.
– r = distance between the centers of the first and second particle.
– G = Universal gravitational constant. = 6.67 × 10-11
N·m2
/kg
Dimensional formula of F is [MLT-2
]
S.I. Unit = N (Newton)
C.G.S. Unit = dyne](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/akshatsaxenaphysics-160226171940/85/Newton-s-Law-of-Universal-Gravitation-11-320.jpg)