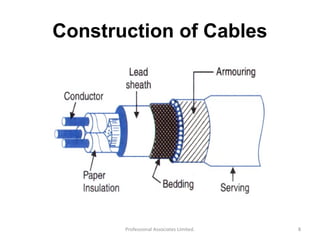
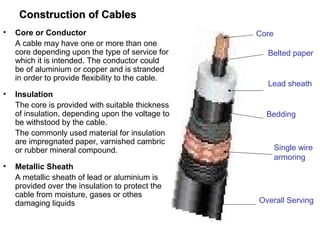
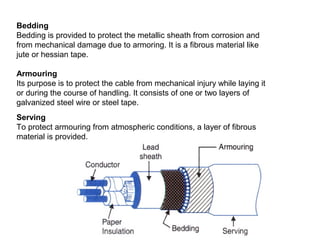
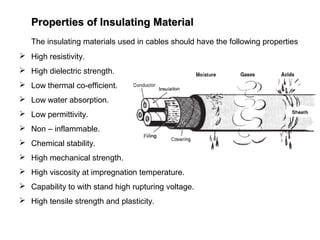
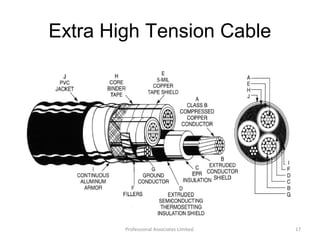
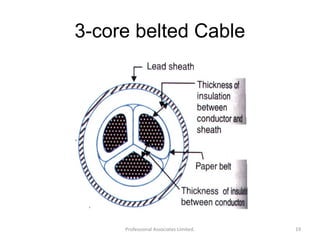
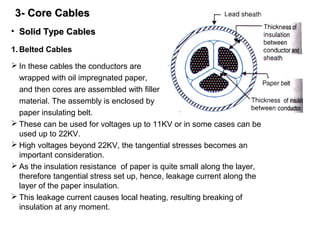
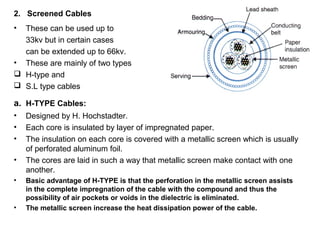
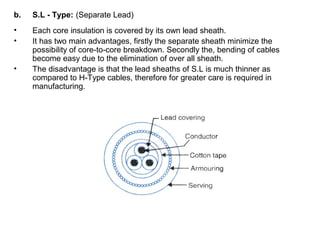
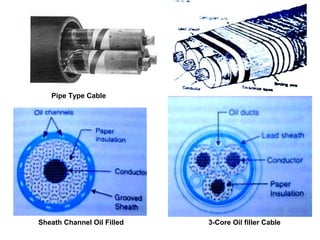
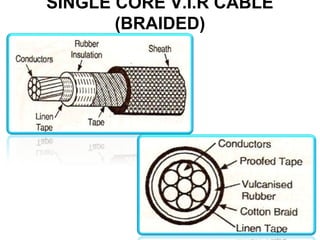
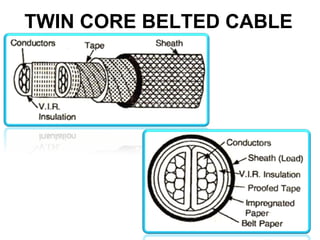
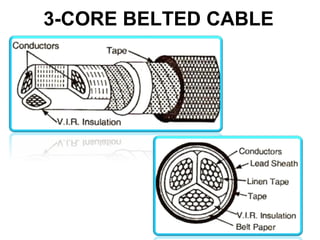
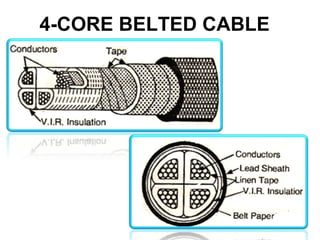
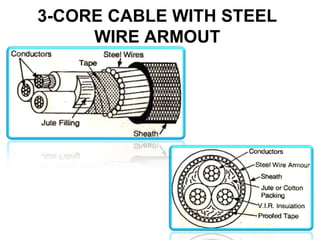
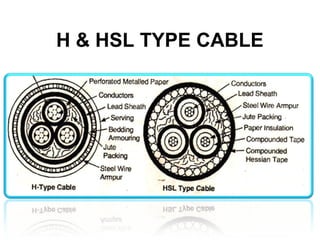
Underground cables have several advantages over overhead cables including better appearance, reduced damage from external factors like storms and lighting, lower maintenance costs, and fewer faults. Underground cables consist of one or more insulated conductors surrounded by protective layers. Key components include the conductor, insulation like paper or rubber, a metallic sheath, bedding, armor for protection, and an outer serving. Different types are used for various voltage applications up to extra high voltage cables over 33kV. Selection depends on factors like the number of cores needed, insulation material, and whether solid or pressure cables are required.