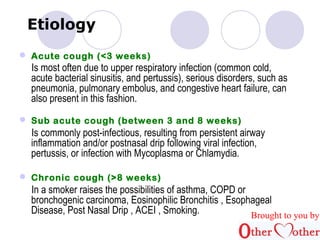
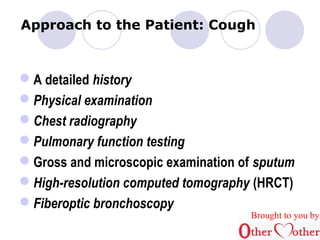
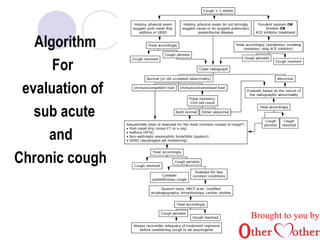
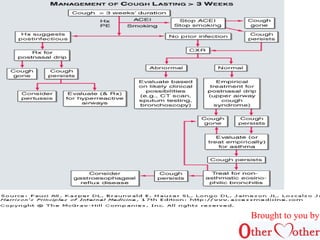
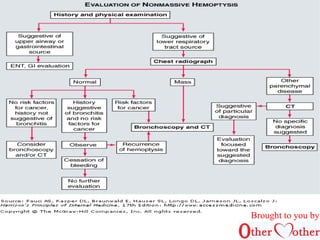
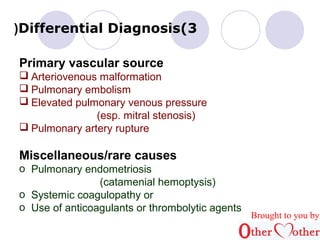
This document discusses cough and hemoptysis (coughing up blood). It defines cough as a protective mechanism to clear the airways and hemoptysis as blood coming from the respiratory tract. It covers the mechanisms, common causes, approaches to evaluation, and treatment options for cough and hemoptysis. The document is brought to you by an organization called Other Mother that aims to improve healthcare access in India.