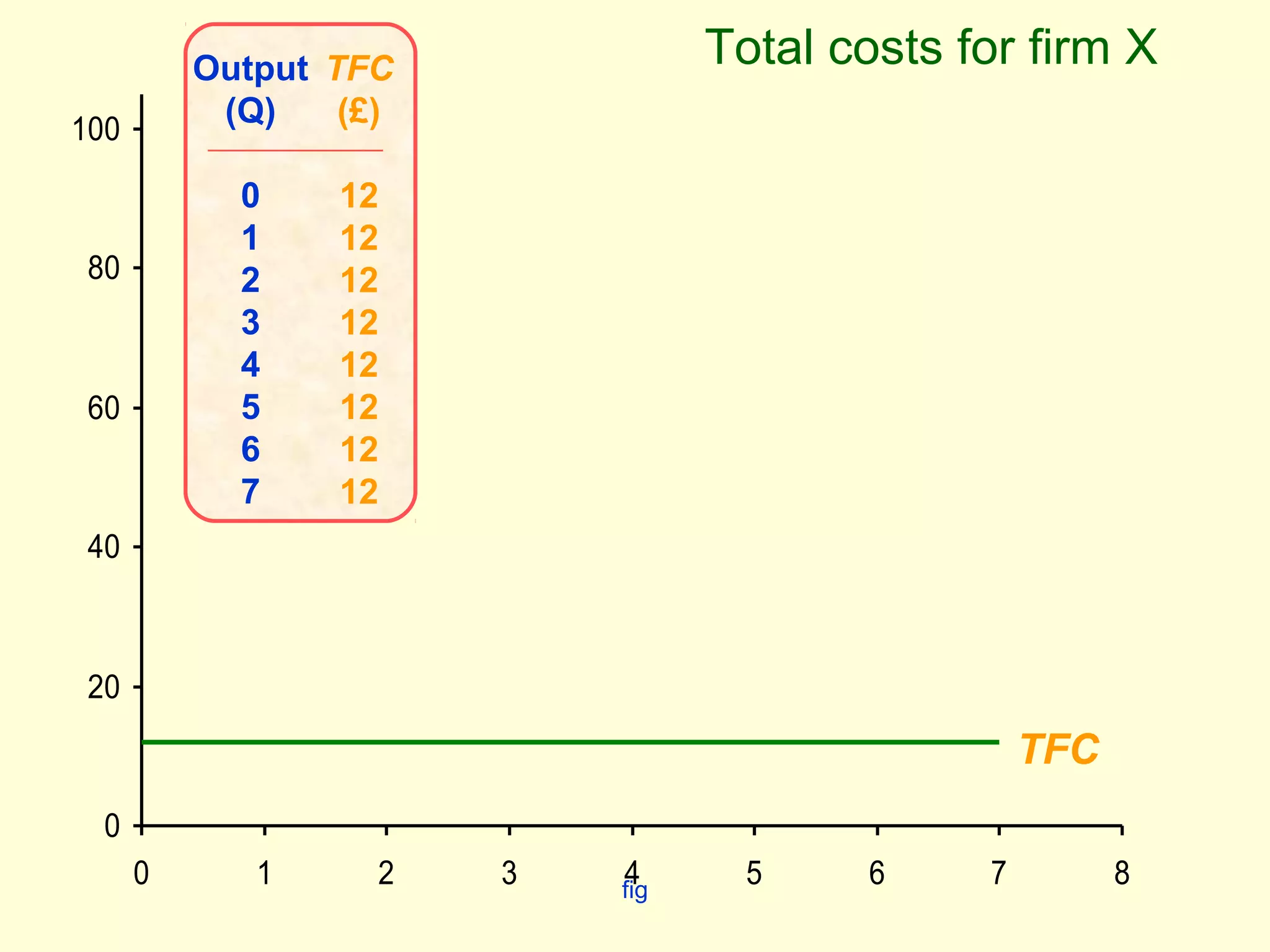
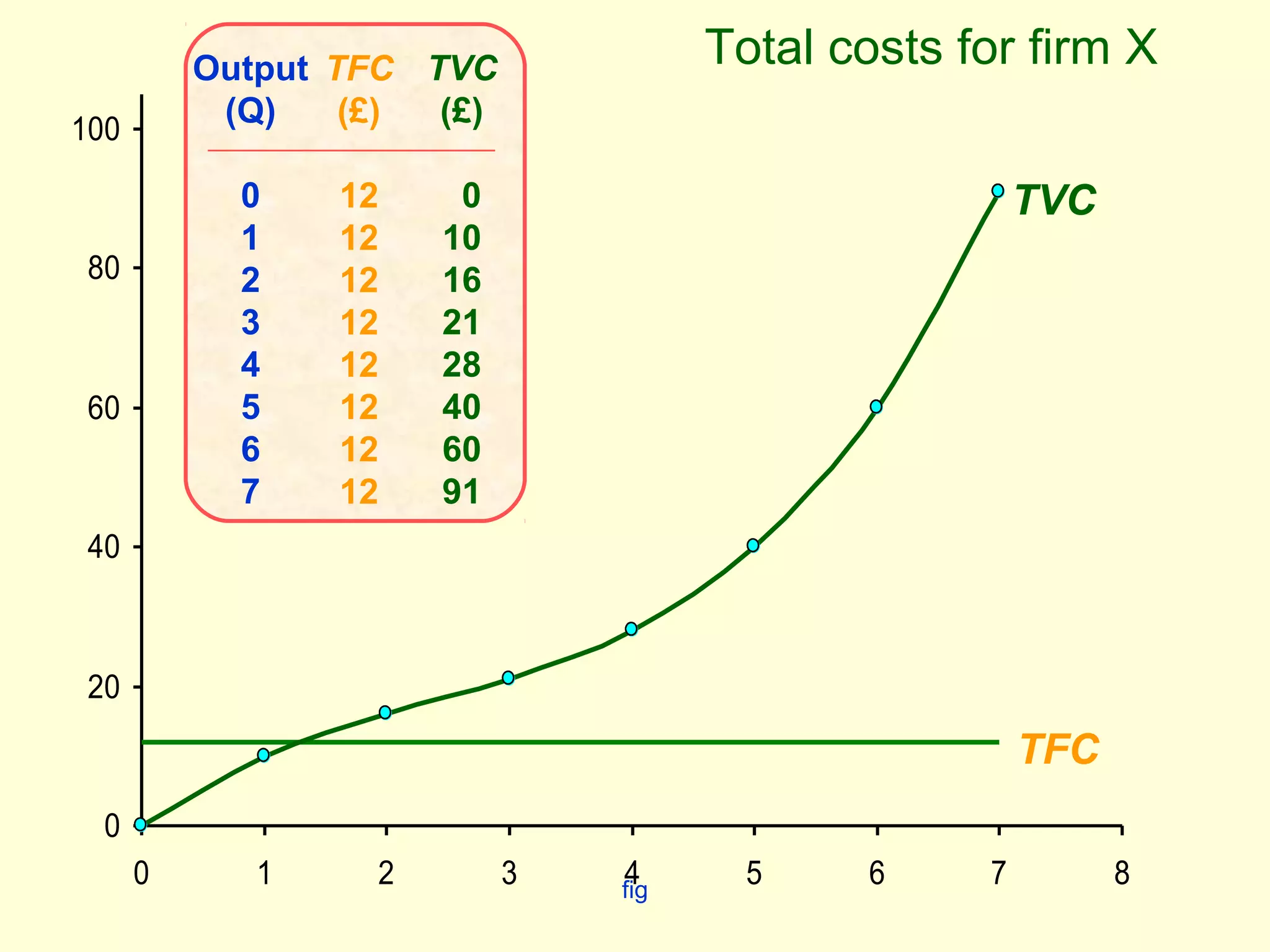
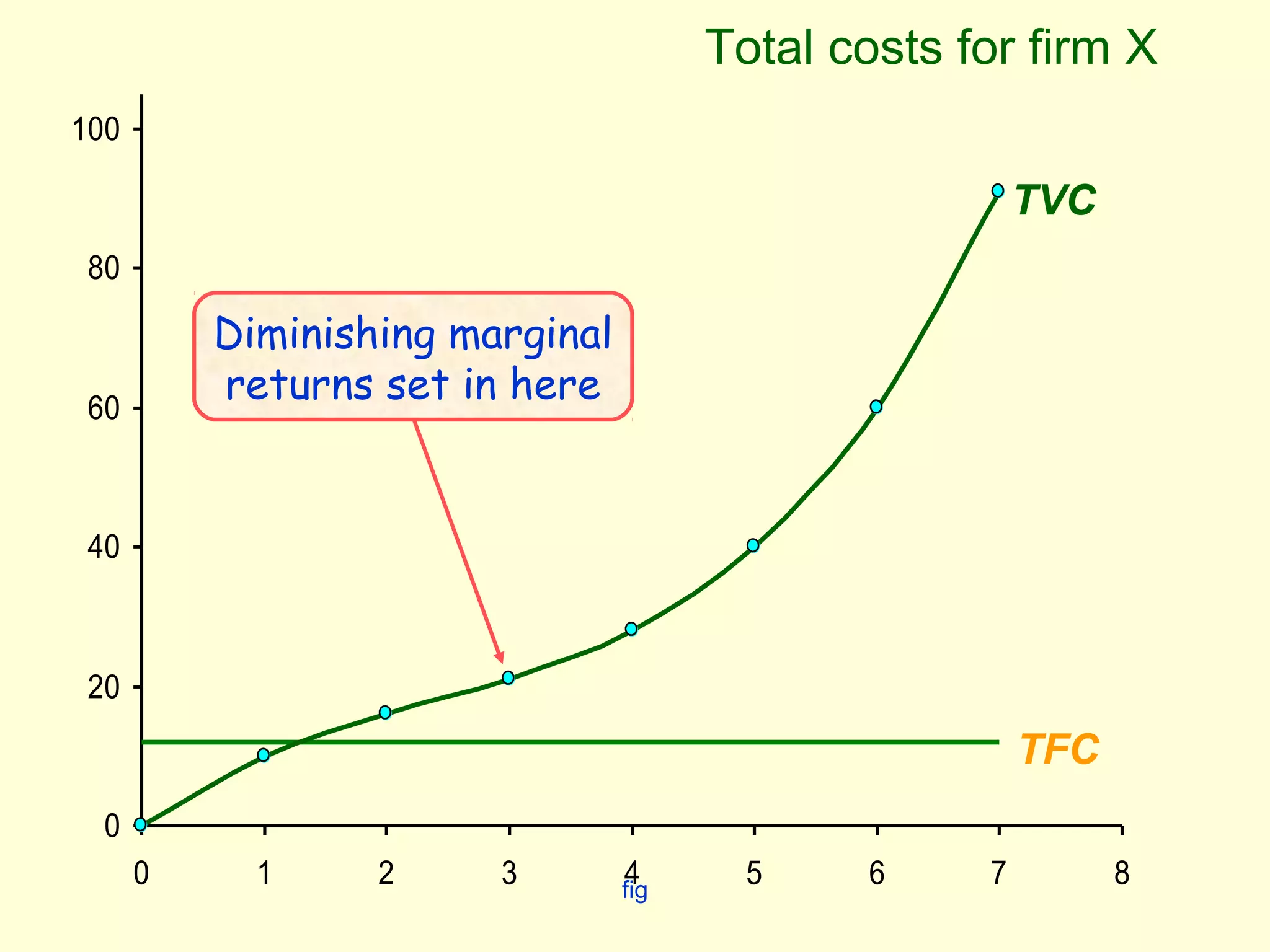
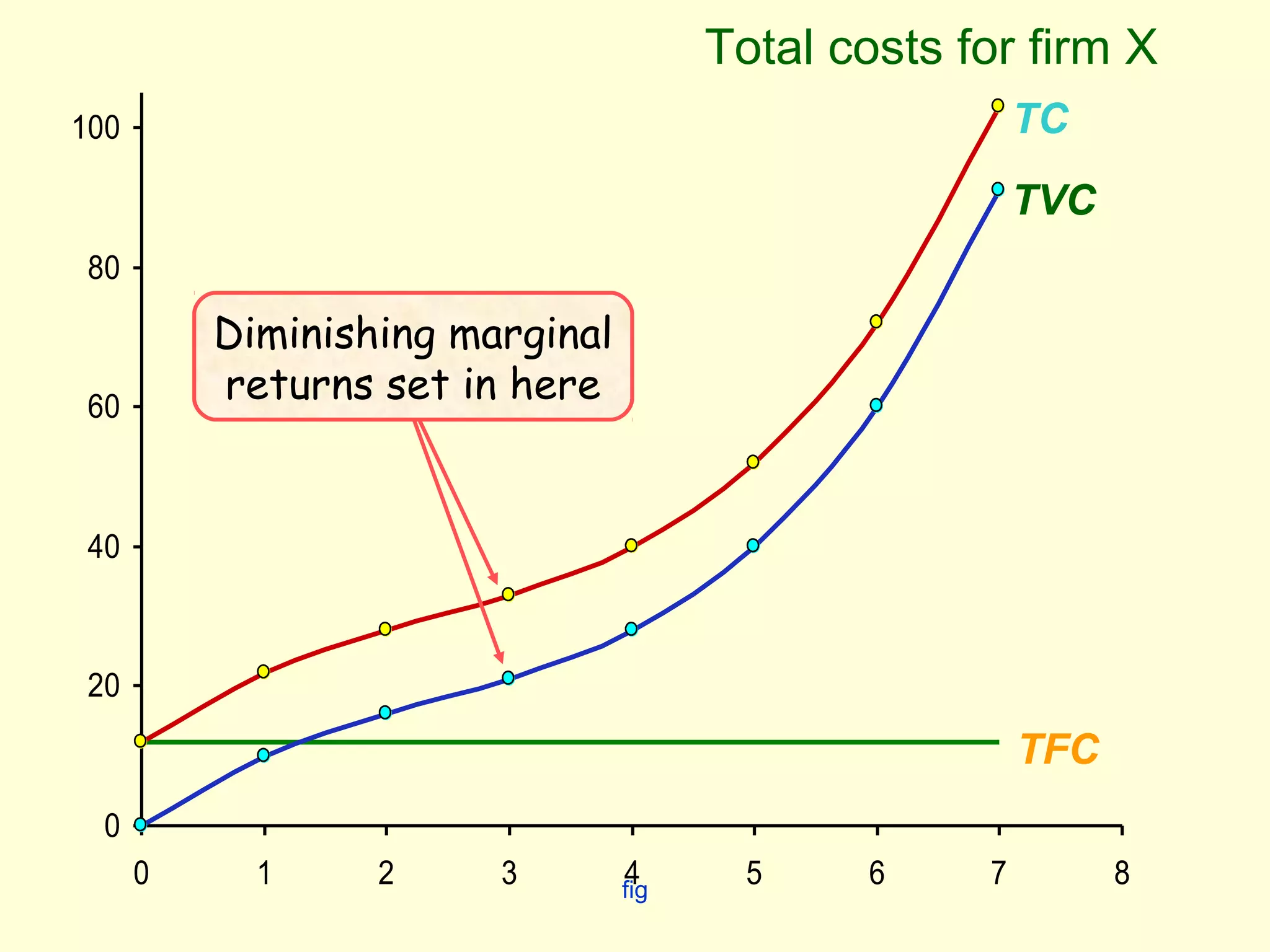
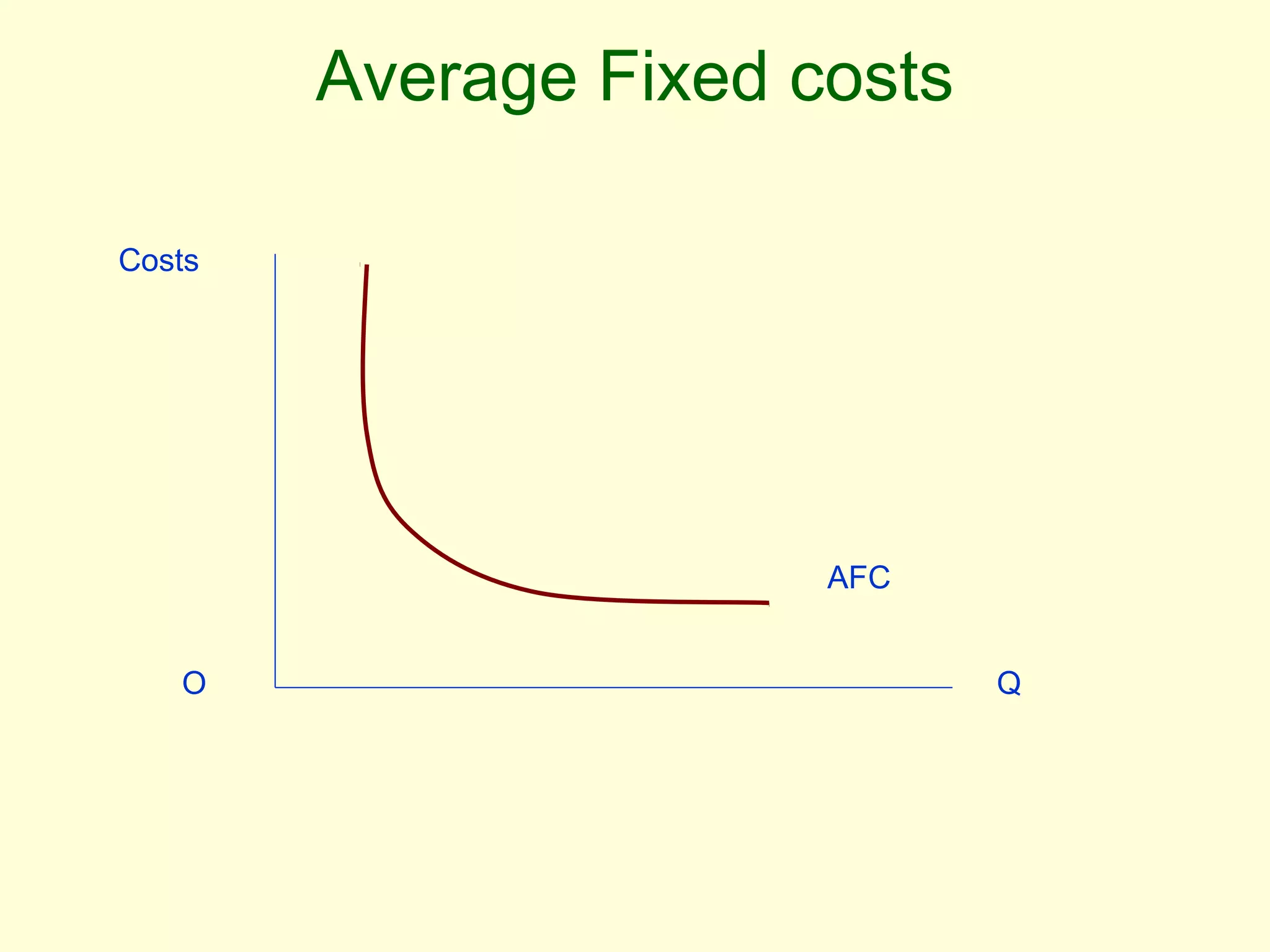
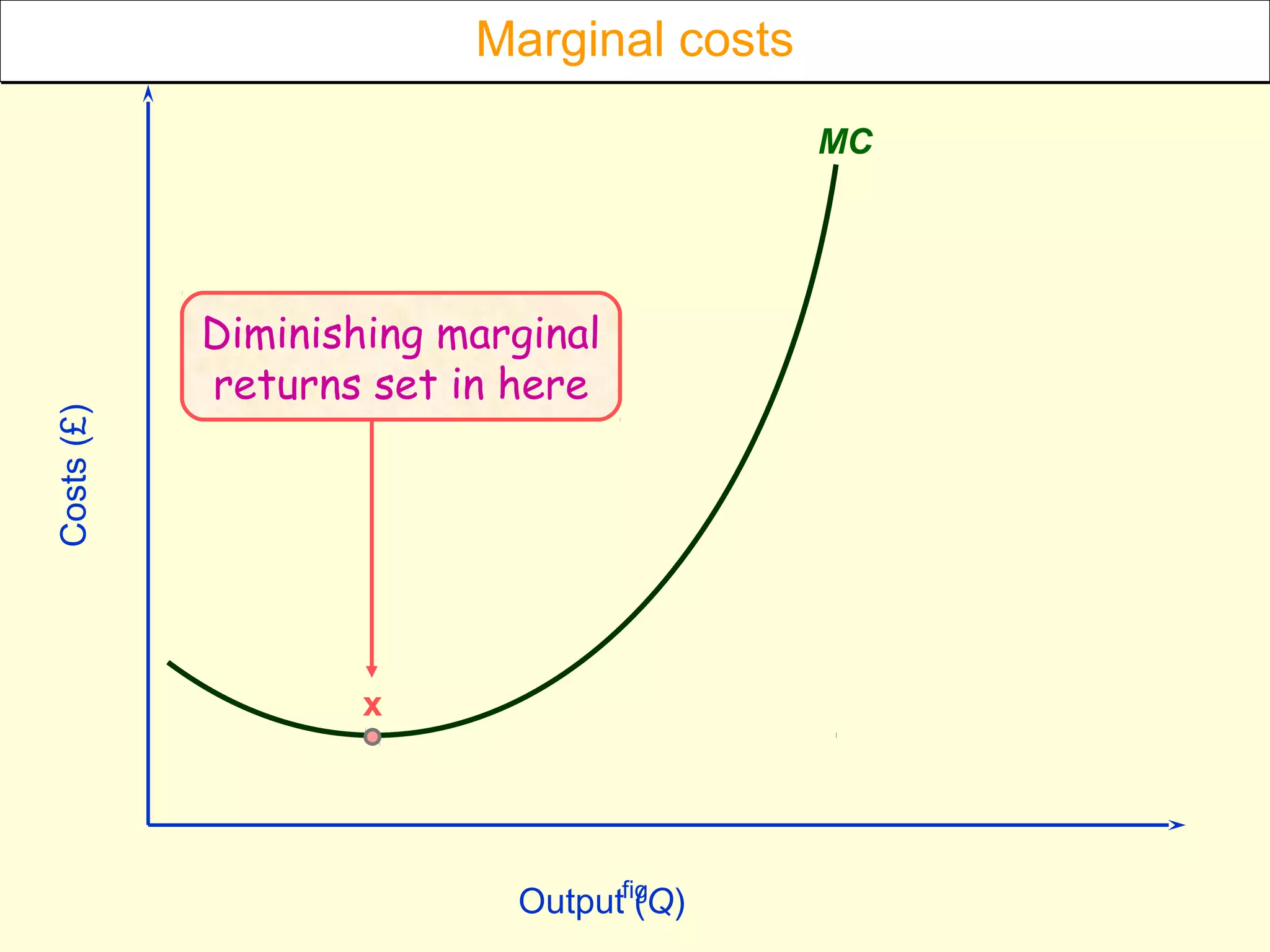
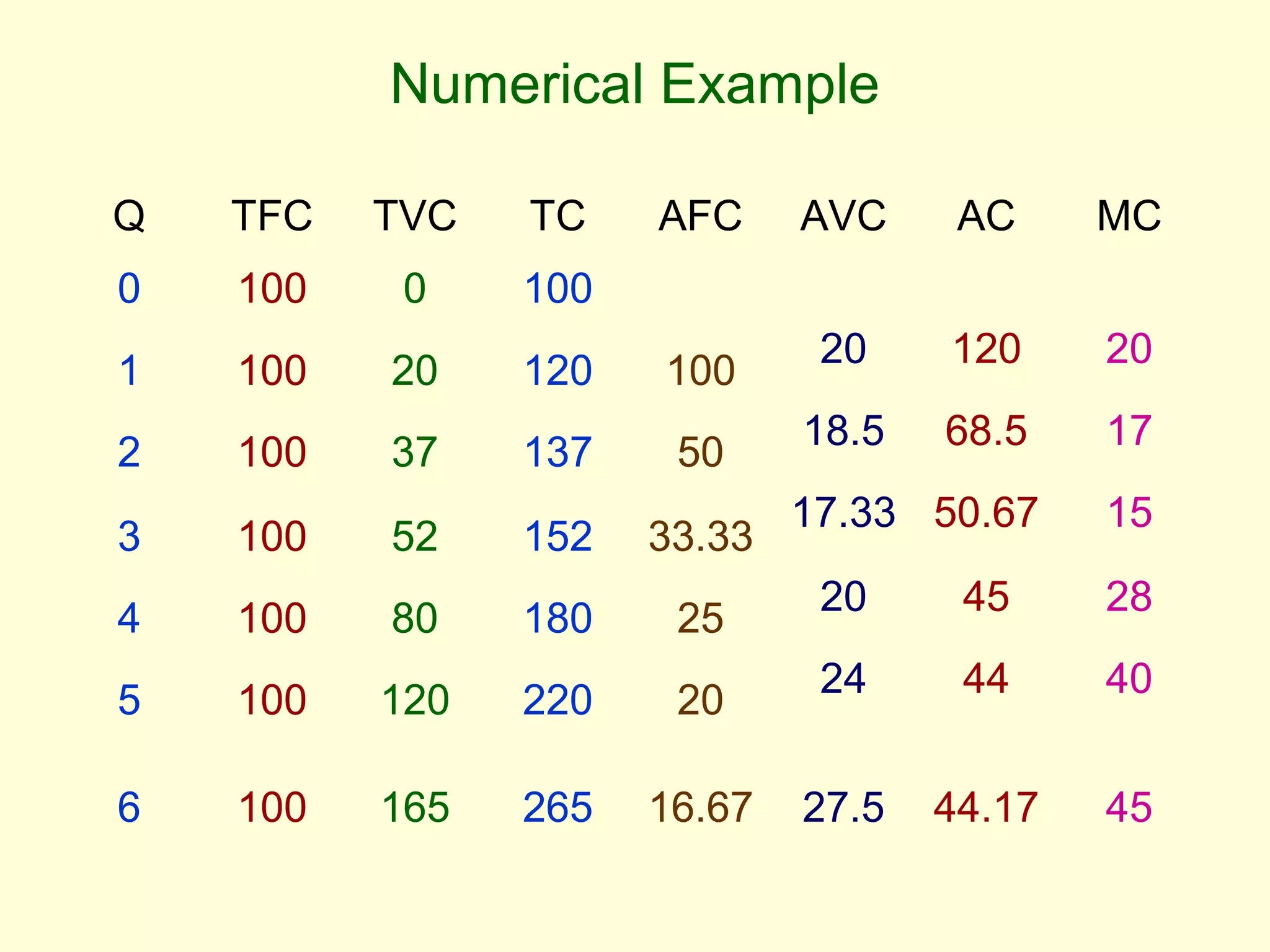
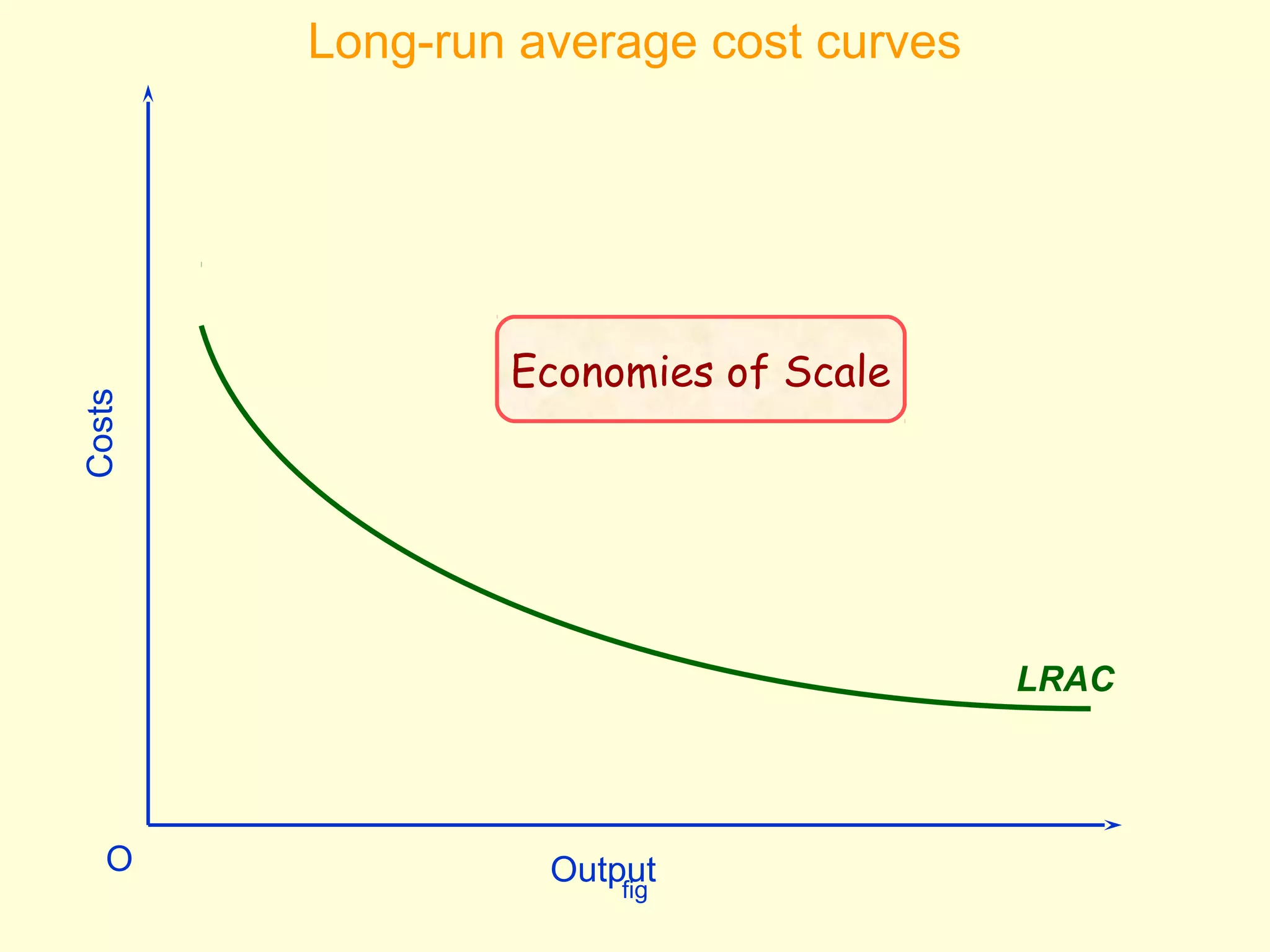
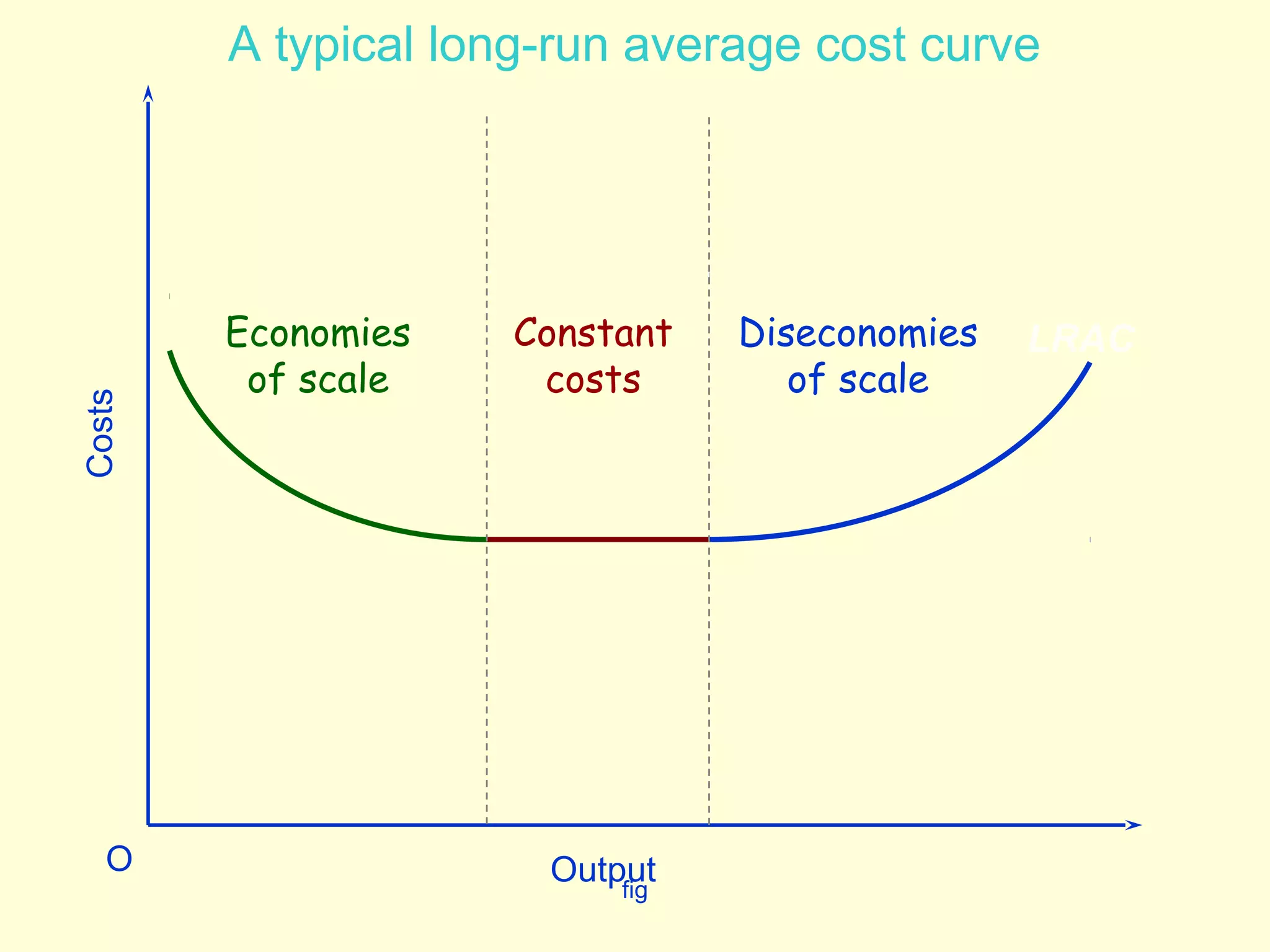
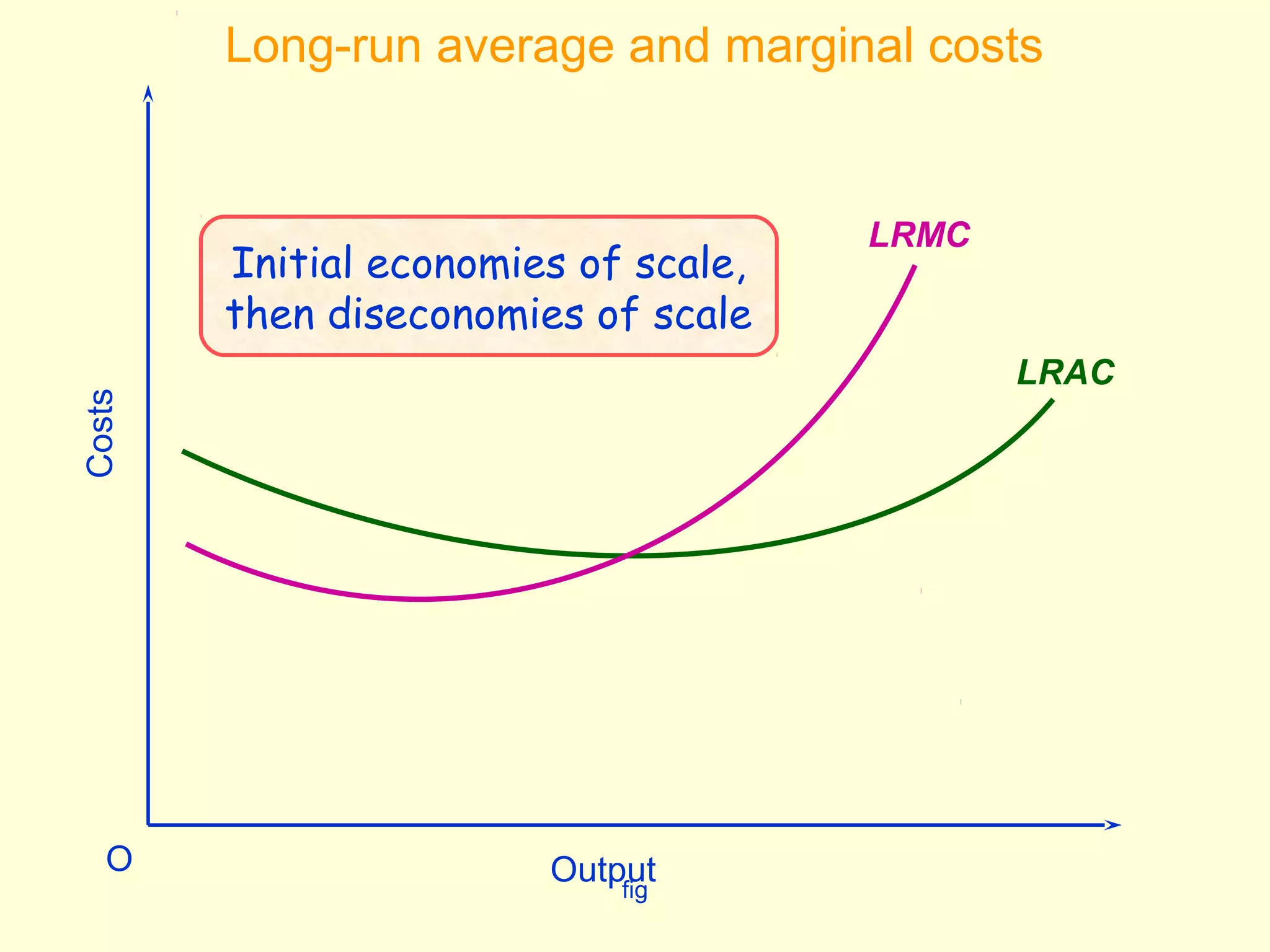
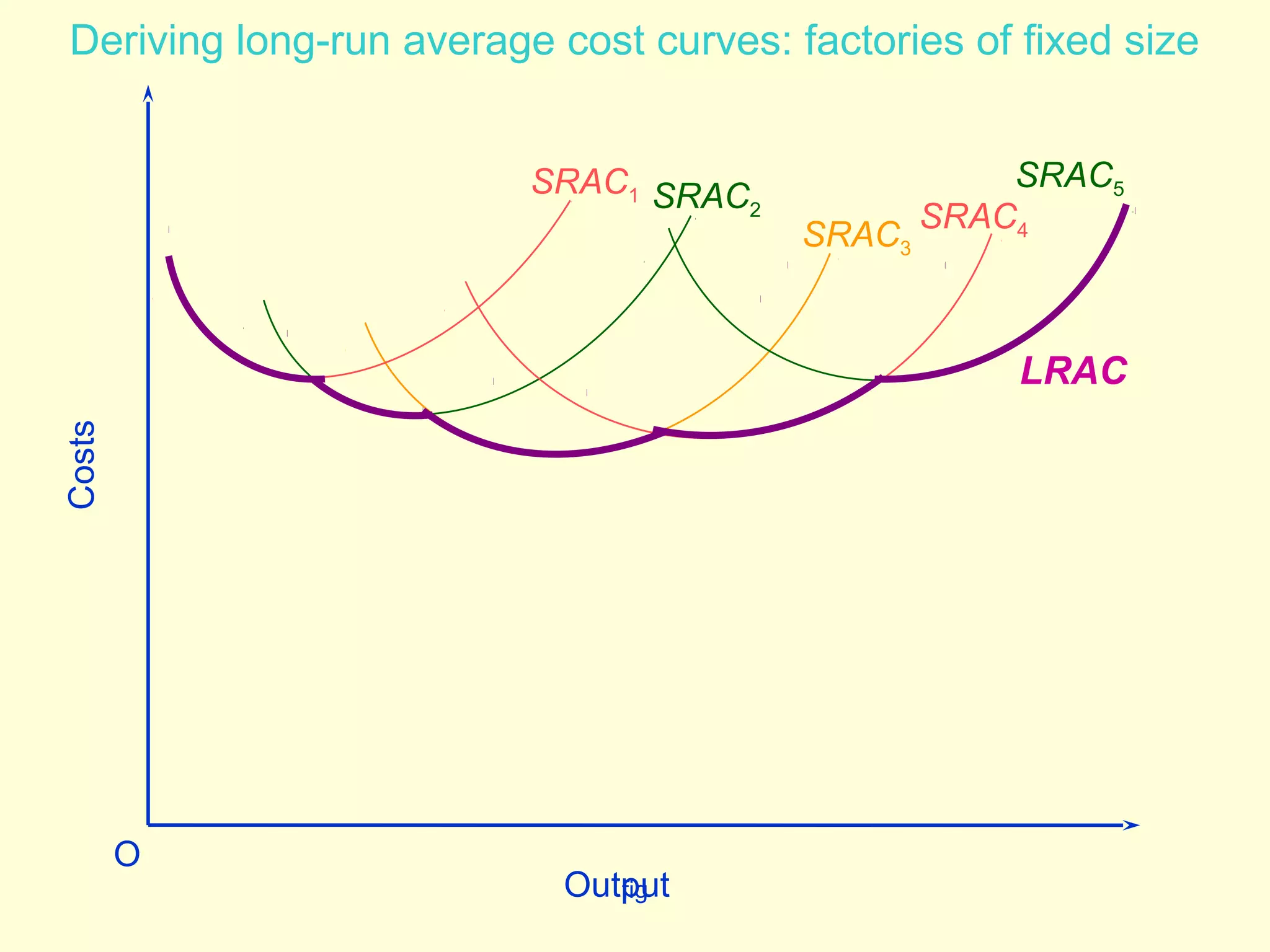
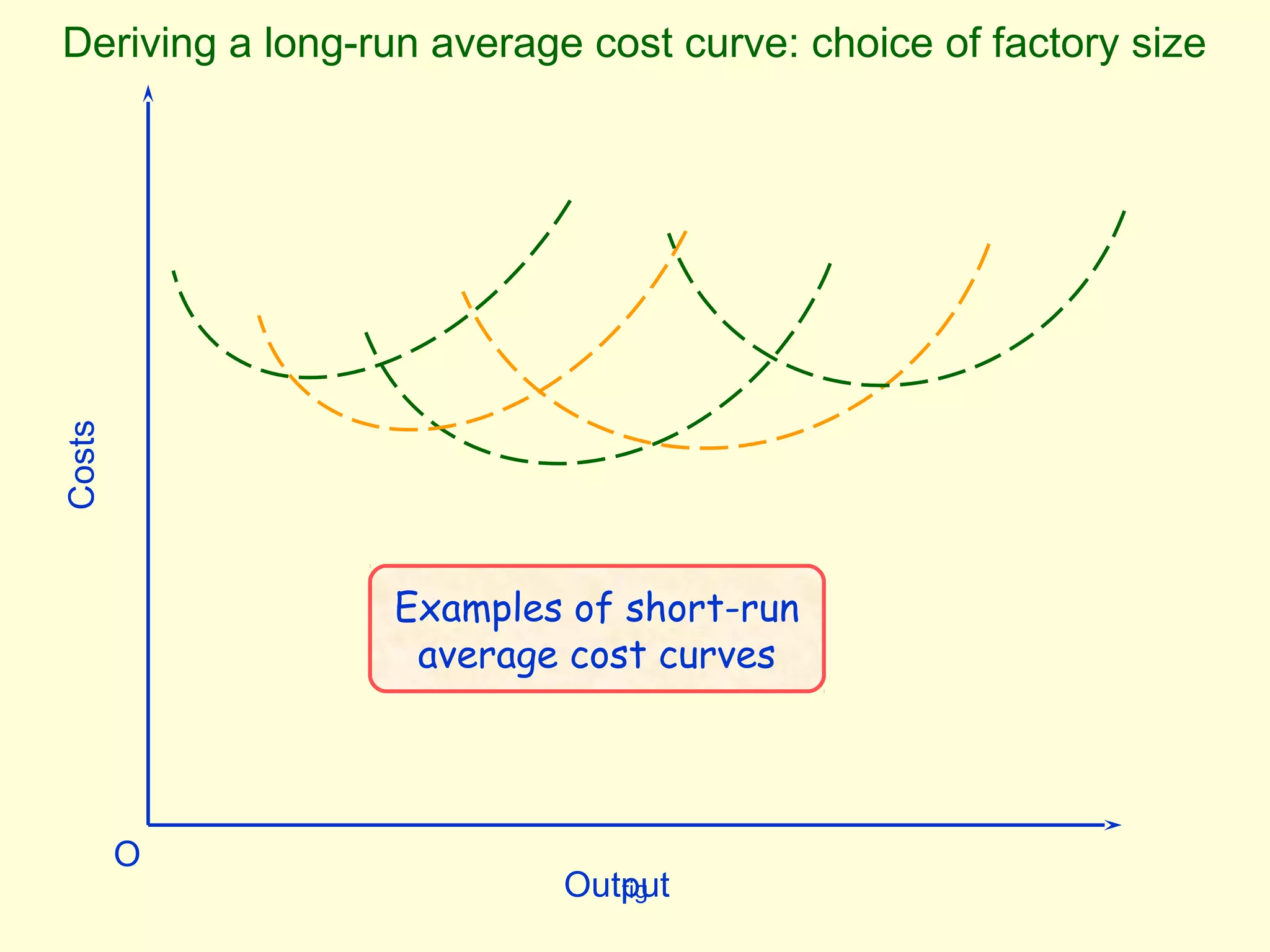
This document discusses theories of costs in the short run and long run for firms. It defines fixed costs as expenses that do not change with output, and variable costs as expenses that change proportionally with output. In the short run, total costs are the sum of fixed and variable costs. In the long run, when all costs are variable, the long run average cost curve is derived from the minimum points of multiple short run average cost curves and can exhibit economies or diseconomies of scale.