Embed presentation
Download to read offline

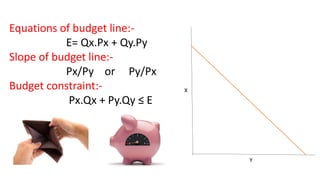
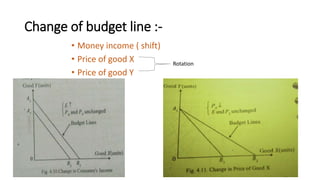

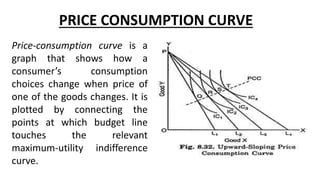
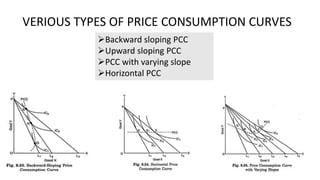


This document discusses budget lines, consumer equilibrium, and price consumption curves. It defines a budget line as representing alternative combinations of two goods given money and prices. Consumer equilibrium occurs where the indifference curve is tangent to the budget line, maximizing utility subject to the budget constraint. A price consumption curve graphs how consumption choices change when the price of one good changes, by connecting points where the budget line touches the highest indifference curve. Various types of price consumption curves are defined such as backward sloping, upward sloping, varying slope, and horizontal.







